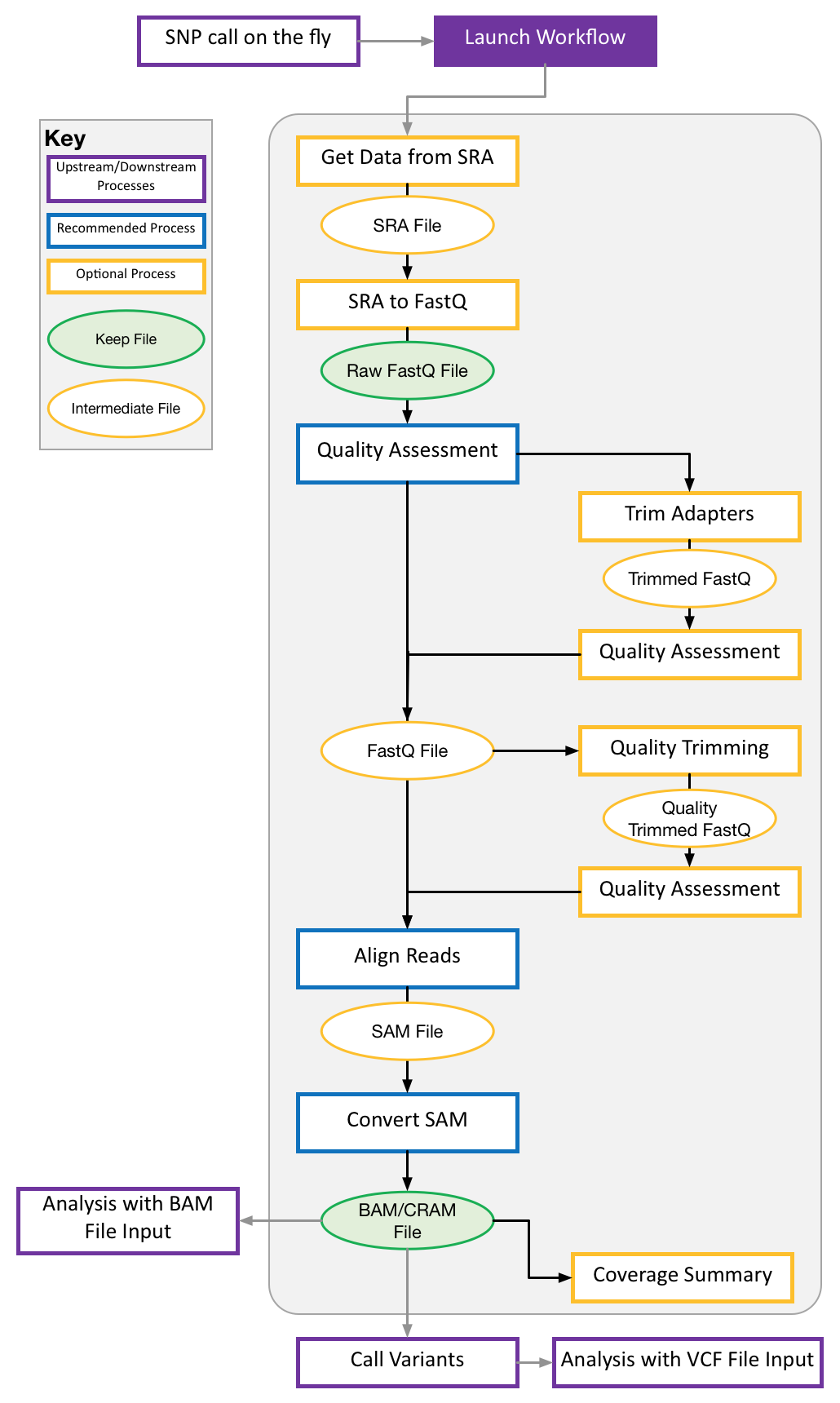
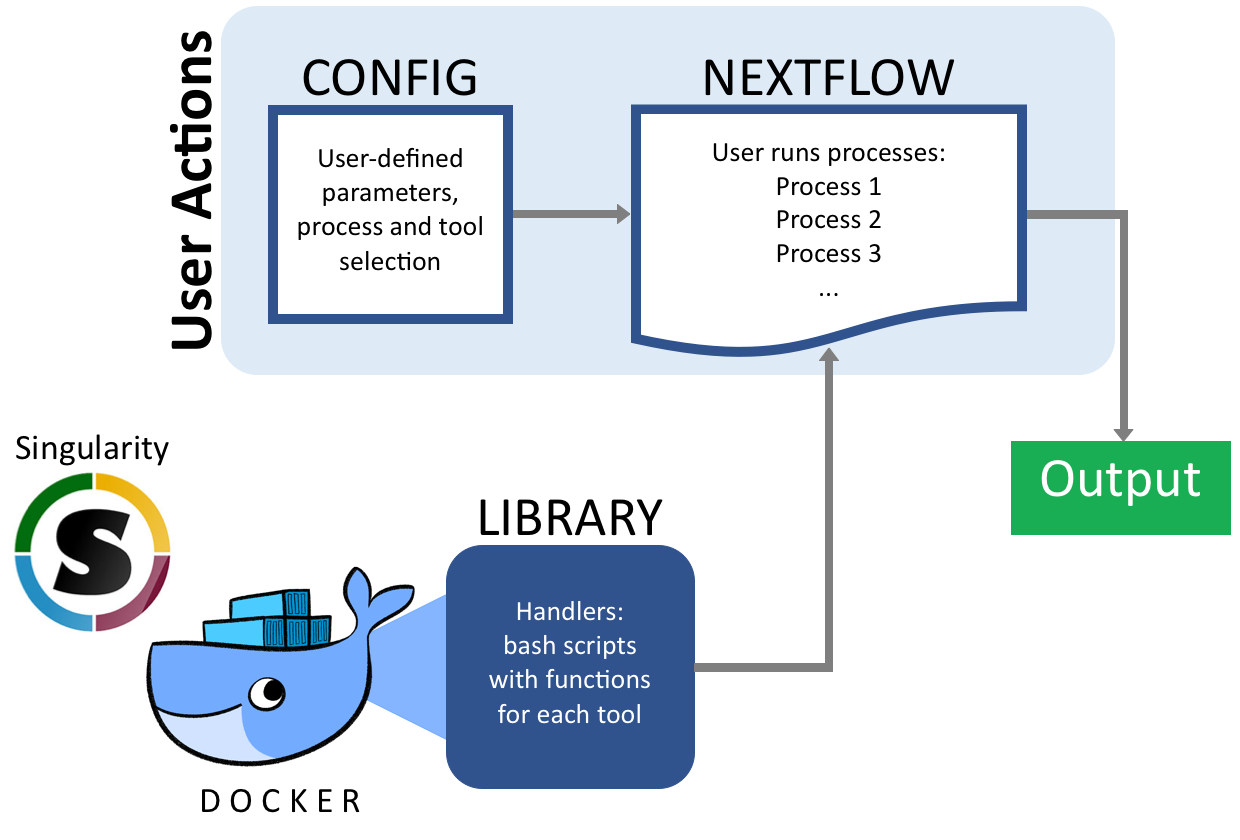
A fast, easy way to present complex bioinformatics pipelines to biologists, built on top of ATACFlow and sequence_handling. This pipeline allows users with basic Linux command line knowledge to quickly customize sequence processing pipelines for their study. This pipeline provides support for using multiple popular tools at each stage of the pipeline.
There is currently a plethora of tools that process genetic data at various stages of the workflow. With new tools and scripts popping up everyday, navigating different options for file cleaning, processing, and conversion can be difficult. Amalgamating easy-to-use tools in a centralized, dockerized application can help facilitate reproducibility by alleviating some of the burden on bioinformatists. Our application helps researchers move away from producing countless scripts for data load and processing, automating the entire workflow process by allowing users to choose from a suite of pre-defined functions and tools. FlowBio lets users choose their own adventure after an initial on the fly variant lookup.
There are too many pipelines to ingest and run data. New pipelines appear every time a lab wants to use a particular set of tools. This prevents pipeline standardization and takes too much time to customize. Often times it is faster for experienced bioinformaticians to write new pipelines because previous pipelines may be difficult to undersand and apply.
Our pipeline allows users to “build” their own pipelines by selecting the pieces and tools they want to include. Our pipeline goes from Fastq files to variant calls. At each stage in the process our pipeline supports multiple tools so users can pick the most appropriate tool for their organism of study. The pipeline uses NextFlow and Singularity as back-end so it follows a standard syntax and can be modified and re-used easily. This allows biologists with limited computational training to build and customize their own sequencng processing pipelines for their own studies.
To run pipeline, there are two steps.
Step 1: Fill out the config file with filepaths and parameters for processes and tools you select.
Here is a snippet from the config file:
// Fill out the following to specify custom filepaths and parameters
params{
/*
* Name of the process and tool we want to run
* Syntax is Process:Tool
* Users can specify "Run_All" to run entire predefined pipeline
* or provide a comma separated list of selected processes to run
* Example: PIPELINE="Quality_Assessment:FastQC,Adapter_Trimming:Scythe,Read_Mapping:BWA"
*
* Valid Process and Tool options are (See docs for more info):
* Run_All
* Data_Fetching
* Quality_Assessment
* FastQC
* Adapter_Trimming
* Scythe
* Trimmomatic
* Quality_Trimming
* Read_Mapping
* BWA
* Minimap2
* SAM_Processing
* Samtools
* Variant_Calling
* Freebayes
* GATK (..in development, available soon!)
* Platypus
* SAMTools (bcftools)
*/
PIPELINES=""General syntax to select process and tools: Process:Tool
For example:
If users want to only run Quality_Assessment and Adapter_Trimming processes using FastQC and Scythe, respectively, fill out the PIPELINES="" line like so with commas delimiting the processes:
PIPELINES="Quality_Assessment:FastQC,Adapter_Trimming:Scythe"If users want to run our entire predefined pipeline with our default tool set, they can do it like this:
PIPELINES="Run_All"Step 2: Run the pipeline with Nextflow
Option 1:
We can specify our pipelines in the config file and provide a path to the config. This will run only user selected pipelines.
nextflow run -c /path/to/configOption 2:
We can run/re-run specific parts of our pipeline.
nextflow run --PIPELINE="Quality_Assessment" -c /path/to/configStep 1: Install Nextflow
Nextflow runs on any POSIX compatible system (i.e. Linux, OS X, Solaris, etc.). Once you have Java 8 or later installed, please use the following steps to install Nextflow:
# Check version of Java
java -version
# Download and set up Nextflow
curl -s https://get.nextflow.io | bash
# Add Nextflow to PATH
mv nextflow /usr/local/binThis pipeline requires Nextflow version >= 0.30.
For more info on using Nextflow, please see Nextflow documentation and NGI-NextflowDocs.
Nextflow automatically fetches pipeline from NCBI-Hackathons/Flowbio.
Install docker on your system: Docker Installation Instructions
Then, simply run the analysis pipeline:
nextflow run NCBI-Hackathons/Flowbio -profile docker --reads '<path to your reads>'Nextflow will recognise NCBI-Hackathons/FlowBio and download the pipeline from GitHub. The -profile docker configuration lists the ncbihackathons/atacflow image that we have created and is hosted at dockerhub, and this is downloaded.
The public docker images are tagged with the same version numbers as the code, which you can use to ensure reproducibility. When running the pipeline, specify the pipeline version with -r, for example -r v1.3. This uses pipeline code and docker image from this tagged version.
Many HPC environments are not able to run Docker due to security issues. Singularity is a tool designed to run on such HPC systems which is very similar to Docker.
To use the singularity image for a single run, use -with-singularity 'docker://ncbihackathons/FlowBio'. This will download the docker container from dockerhub and create a singularity image for you dynamically.
If you intend to run the pipeline offline, nextflow will not be able to automatically download the singularity image for you. Instead, you'll have to do this yourself manually first, transfer the image file and then point to that.
First, pull the image file where you have an internet connection:
singularity pull --name ncbihackathons-flowbio.img docker://ncbihackathons/FlowBioThen transfer this file and run the pipeline with this path:
nextflow run /path/to/NCBI-Hackathons/FlowBio -with-singularity /path/to/ncbihackathons-flowbio.img