-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 11
2. Electronics (Feather)
The second part of building the remote is to assemble and test the electronics. This is the hardest part, as it involves a lot of soldering and wiring, however, if you follow the schematics and take your time, it's quite an entertaining task.
The first thing to do is to make sure you got everything you need. Here is a list of all needed electronics:
- Two Adafruit Feather M0 RFM69HCW
- One Hall Effect sensor (DRV5053OAQLPG)
- One OLED 128x64px display
- One LiPo battery (3,7V 500-1000mAh)
- One tactile push button
- A small switch with a lever
- Some electrolytic capacitors (47-220 uF)
- Some resistors (1 kOhm)
- Some good wire (silicone wire 28-30 AWG)
Full list: docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/13rUPX8...
Important: Make sure to follow the schematics, otherwise your remote might not work as excepted or you might fry some components.
In the bottom half of the remote, there is room for a 51x34x6mm battery. Simply connect a 4.2/3.7V Lithium Polymer (Lipo/Lipoly) or Lithium Ion (LiIon) battery to the JST jack. This will let the Feather run on a rechargable battery. When the USB power is powered, it will automatically switch over to USB for power, as well as start charging the battery at 100mA.
The above shows the Lipoly JST jack (top left), as well as the 3.3V regulator and changeover diode (just to the right of the JST jack) and the Lipoly charging circuitry (to the right of the Reset button). There's also a CHG LED, which will light up while the battery is charging.
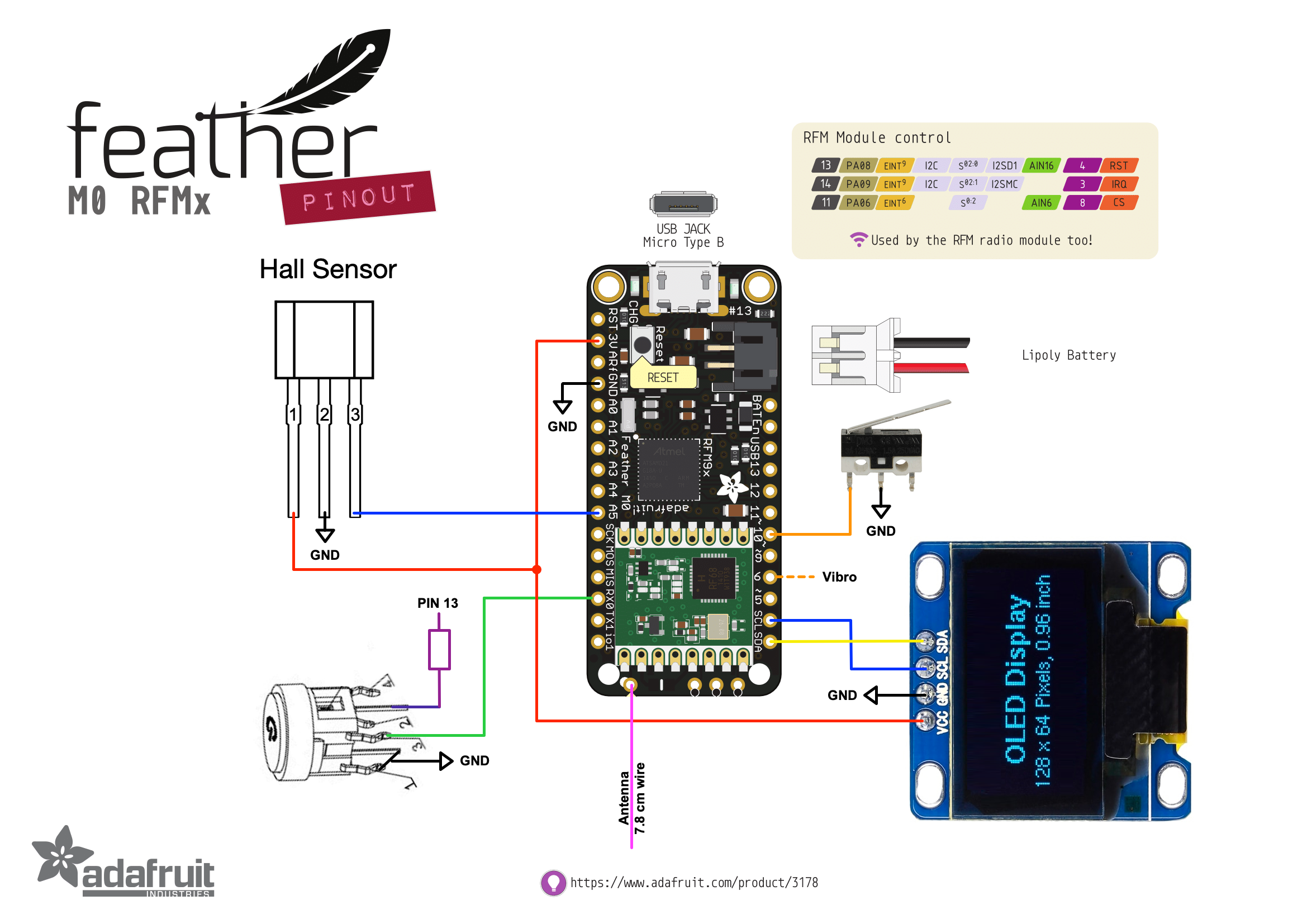
After this, you can begin assembling circuit according to the schematics below. I recommend assembling this outside the remote, as a hot soldering iron easily can melt your remote housing!
Before continuing to the next step make sure to test everything.
Due to small remote size, please use 28-30 AWG wire. I recommend soldering all the necessary wires (with enough length) to all the individual components before soldering anything to the Feather. You will need wires for all these modules:
- 3 wires for the Hall Effect sensor
- 4 wires for the OLED display
- 2 wires for the trigger switch
- 3 wires for the button with LED
- 3 wires for vibration motor (optional)
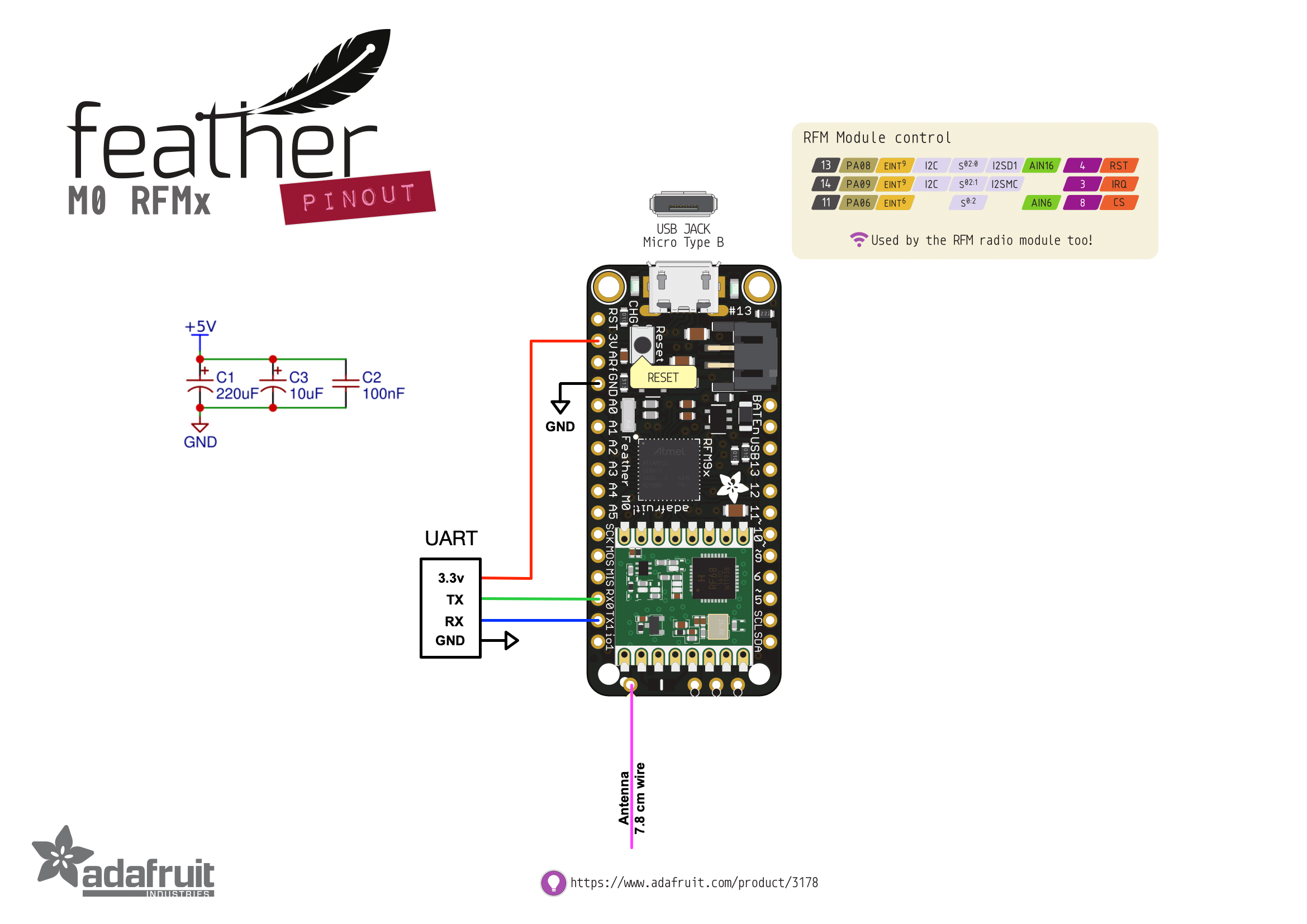
The schematic for the receiver is rather simple, and some parts are optional depending on your use. A power filter is recommended to stabilize the voltage from VESC. Connect it between 3.3v and the ground wires.