This repository contains some problems and their solutions.
- You need to create a ROS package to localize the robot using only the GPS, Odometer and INS sensor information. You can use the EKF- package for developing your project.
- To stand out, instead of using ROS EKF or UKF package, you can code your own EKF, UKF or any other sensor fusion algorithm from scratch. You will be evaluated based upon your mathematical problem formulation and coding skills.
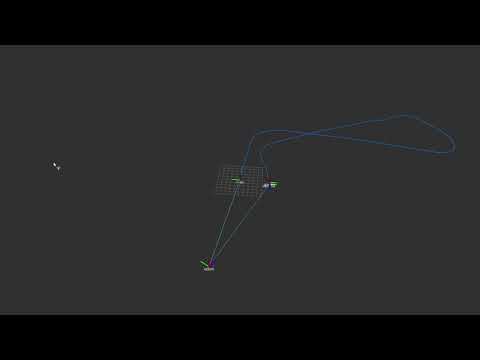
The goal is to build a ROS package to localize Clearpath Robotics' Warthog robot using the provided data.
The robot localization is done using the provided sensor data of Warthog robot in the form of ROS bag. To achieve this task, two ROS packages are used. One is the robot_localization which fuses sensors (GPS, IMU and Odometry) using Extended Kalman Filter. Second package is hector_slam. Hector slam is not fully used but a module of this package is utilized to plot robot's trajectory. The visualization is done in rviz.
This project is built and tested on Ubuntu18 using ROS Melodic. Compatibility with other Ubuntu or ROS distributions is not gauranteed.
Run the following commands to install the required packages.
cd to the workspace
sudo apt-get install ros-melodic-geographic-msgs
sudo apt-get install libgeographic-dev
sudo apt-get install geographiclib-tools
catkin_make
After the installation,
- launch the following command to run localization, trajectory plotting and visualization.
- play tha bag file
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch robot_localization dual_ekf_navsat_example.launch
rosbag play [bag filename]
You need to create a ROS navigation package for clearpath warthog for waypoint navigation. You can follow the links below for basic installation and launch files.
https://www.clearpathrobotics.com/assets/guides/kinetic/warthog/index.html
Your final result should look like this: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hP6NiGzOLmI&t=8s
The goal is to built a package for waypoint navigation of Clearpath Robotics' Warthog robot in Gazebo simulation environment using Robot Operating System (ROS).
This project is built and tested on Ubuntu16 using ROS Kinetic. Compatibility with other Ubuntu or ROS distributions is not gauranteed.
Run the following commands to install and setup Gazebo environment
cd dewa_evaluation_zeeshan/p2_waypoint_nav/warthog_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/warthog-cpr/warthog.git
git clone https://github.com/warthog-cpr/warthog_simulator.git
git clone https://github.com/warthog-cpr/warthog_desktop.git
git clone https://github.com/clearpathrobotics/cpr_gazebo.git
cd dewa_evaluation_zeeshan/p2_waypoint_nav/warthog_ws
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro=kinetic -y
sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-uuv-gazebo-worlds
catkin_make
After the installation, launch the gazebo simulation and run the waypoint navigation node.
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch warthog_gazebo warthog_world.launch
# Open a new terminal
source devel/setup.bash
rosrun warthog_nav waypoint_nav.py
Try to implement a swarm of 6 robots to map an area of 100 meters squared collectively. All Unmanned ground vehicles are equipped with an Odometer, IMU, GPS, LIDAR, telemetry to communicate with other robots and a temperature sensor.
- You need to create a random temperature gradient as shown in the figure. The grid lines represent Latitude and Longitude values. Each cell of 1 meter squared represents only 1 temperature reading.
- Initialize robots from random latitude and longitude points within the range of the scan area.
- The trajectory of each robot should not overlap so that the swarm robots scan the area collectively with minimum cost.
- Display the robot trajectories and the recovered heat map using information from all robots. Note: You can use MATLAB, ROS, Python, C++ or any programming language of your choice to implement this problem. You can use any two-wheeled or four-wheeled robot in this case.
The goal is to implement a multi-agent system to explore the hidden underlaying field.
This task is under development. This is being done in Python3 using jupyter notebook.
You are provided with two excel files as input and output. You need to find a way to map the
inputs to the respective outputs with minimum possible error. We need to see your code with
results and your problem-solving journey. You may explain which techniques you applied and
the reasons for using the selected technique.
Note: Use the below link to download the data to work with. This data is for the problem 1 and 4.
The goal is to build a model capable of mapping the input to the output with the minimum error.
There are 21920 samples (rows) of the data. Input has 23 features (columns) and there are four outputs. By looking at the data, it's clear that the model to map them has to be continuous in nature so a regression could be a better choice for fitting the model into it.
For this purpose, a Neural Network twrok is trained using Pytorch framework. This network has three hidden layers, one input and one output layer. The data is divided into 80% training and 20% test datasets and network is trained for 200 epochs resulting in 113 mean squared error (MSE).
This task in done in Python using Jupter Notebbok. Install the following dependencies before using it.
pip install torch torchvision
pip install pandas
pip install matplotlib
pip install sklearn
pip install imageio
pip install numpy