A terraform build that creates a fully functional environment to demonstrate how the VM-Series can secure Azure Virtual WAN traffic. Approximate time to complete 30 minutes.
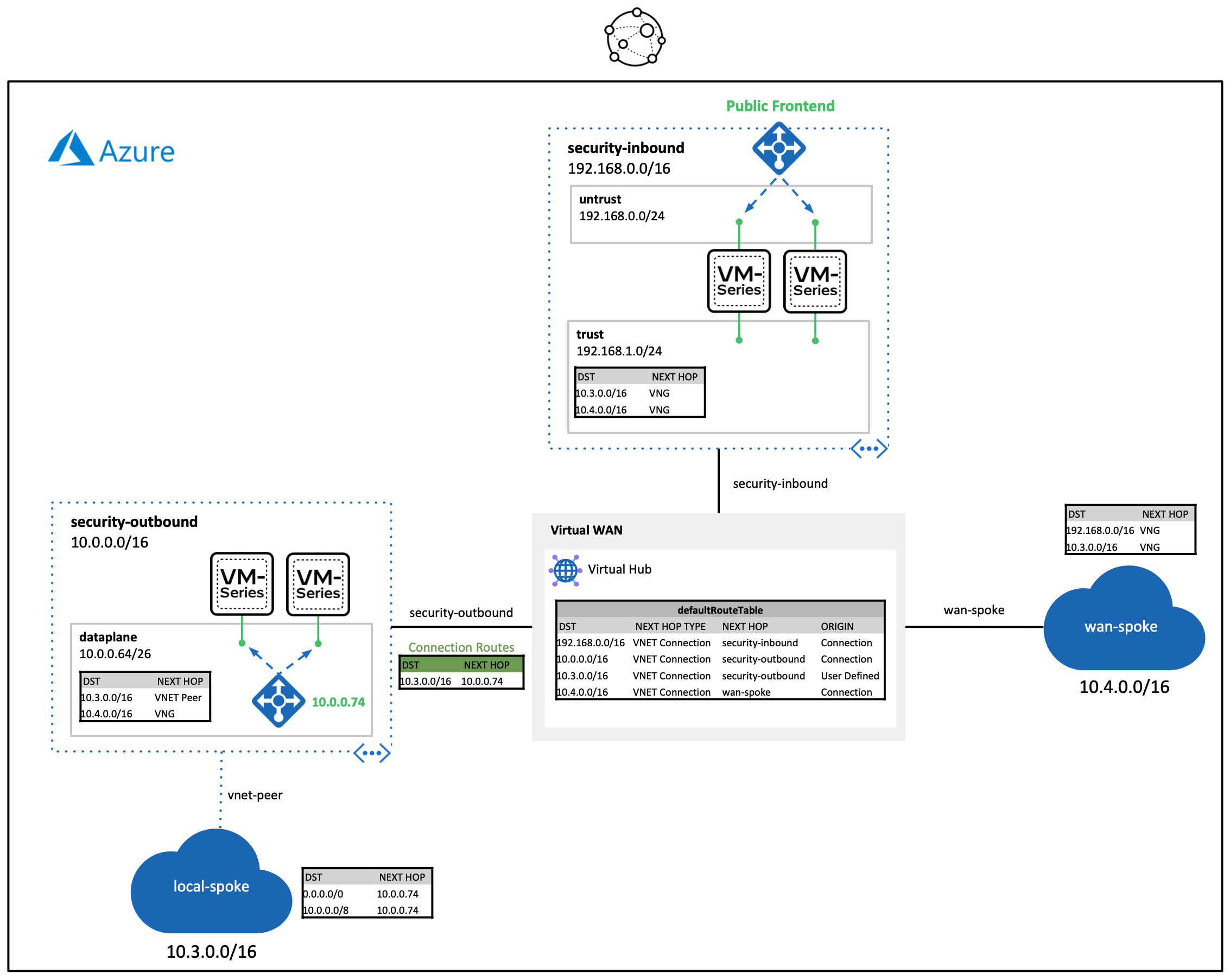
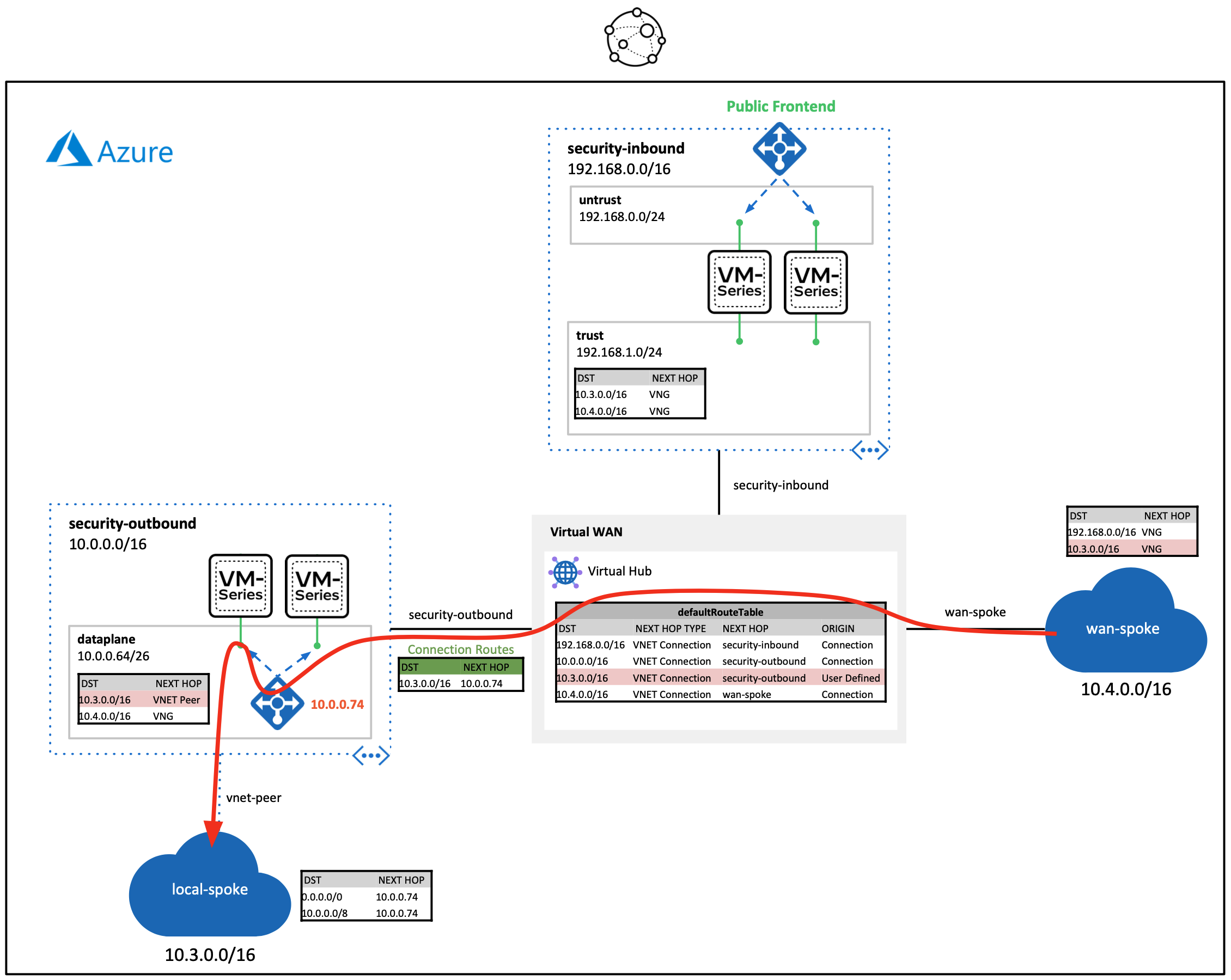
The build demonstrates the following VM-Series traffic flows through a virtual WAN hub.
- Inbound traffic: Dedicated set of VM-Series firewalls that secure internet inbound requests destined to networks connected to a virtual WAN hub.
- Additional firewall sets can be added throughout different Azure regions to achieve a globally scalable inbound security edge.
- Outbound traffic: Dedicated set of VM-Series firewalls that secure lateral traffic traversing through a virtual WAN hub.
- This design can be integrated into larger infrastructures that include regional hub and spoke architectures.
- An active Azure subscription with appropriate permissions and resource allocation quota.
- Access to Azure cloud shell.
In the Azure Portal, open cloud shell in Bash mode.
Run the following commands. Replace licensing_option with your preferred licensing type: byol, bundle1, or bundle2.
# Accept VM-Series EULA for desired license type (BYOL, Bundle1, or Bundle2)
$ az vm image terms accept --urn paloaltonetworks:vmseries-flex:<licensing_option>:10.0.3
# Download repository and change directories
$ git clone https://github.com/wwce/azure-tf-virtual-wan; cd azure-tf-virtual-wan
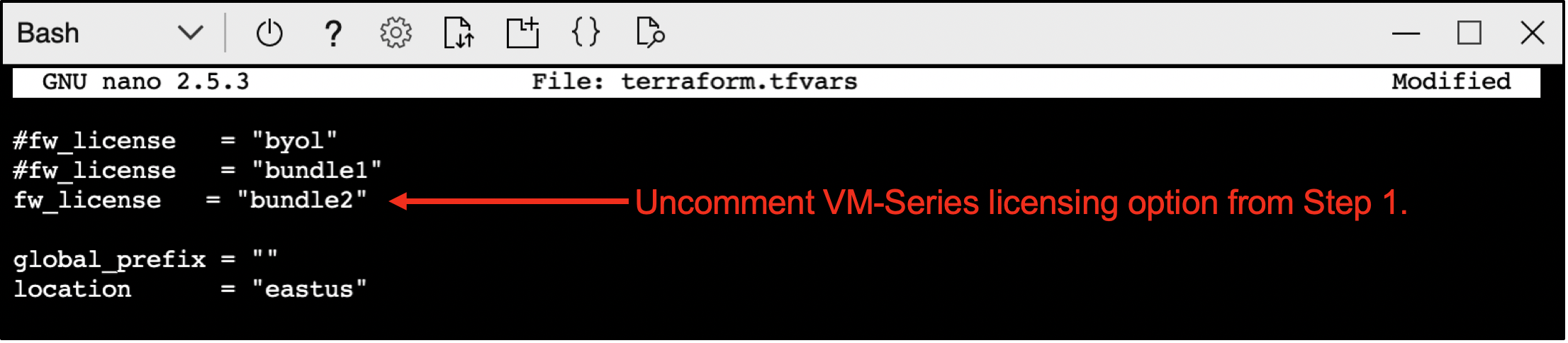
Open terraform.tfvars and uncomment the fw_license variable that matches your licensing option from step 1.
$ vi terraform.tfvars
Your terraform.tfvars should look like this before proceeding
Run the following commands to initalize and build the environment. A total of 104 resources will be created. Deployment time is approximately 25 minutes.
$ terraform init
$ terraform apply
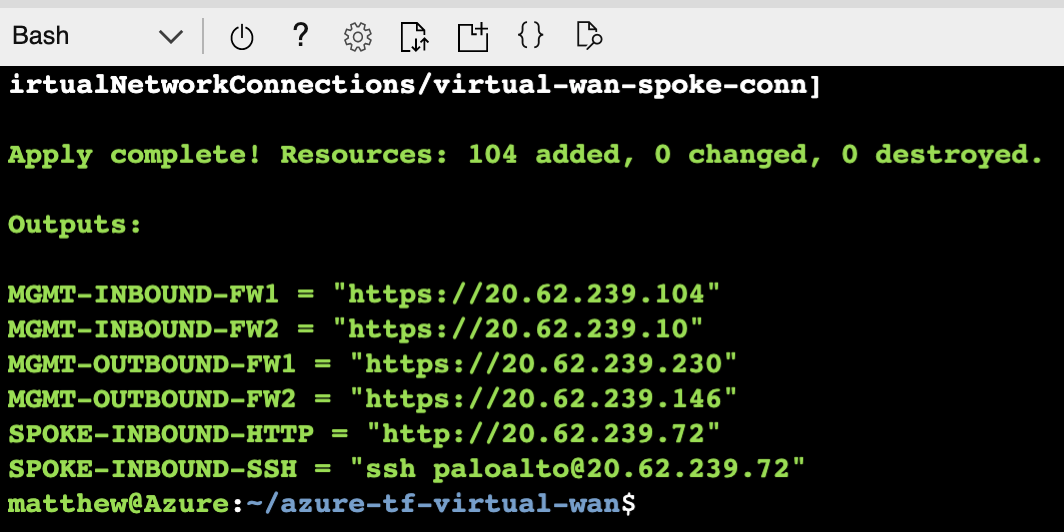
When the deployment finishes, the following output will be displayed.
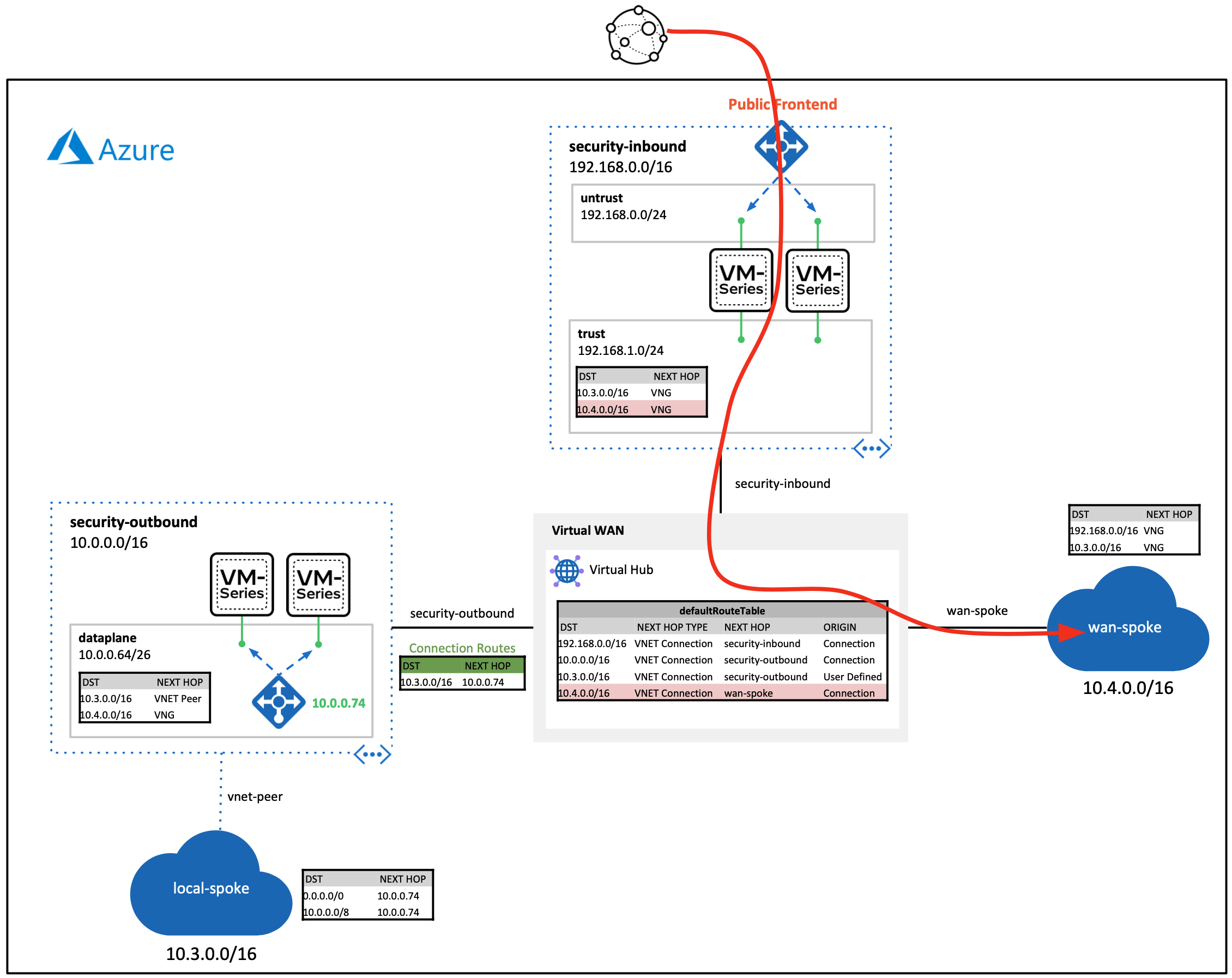
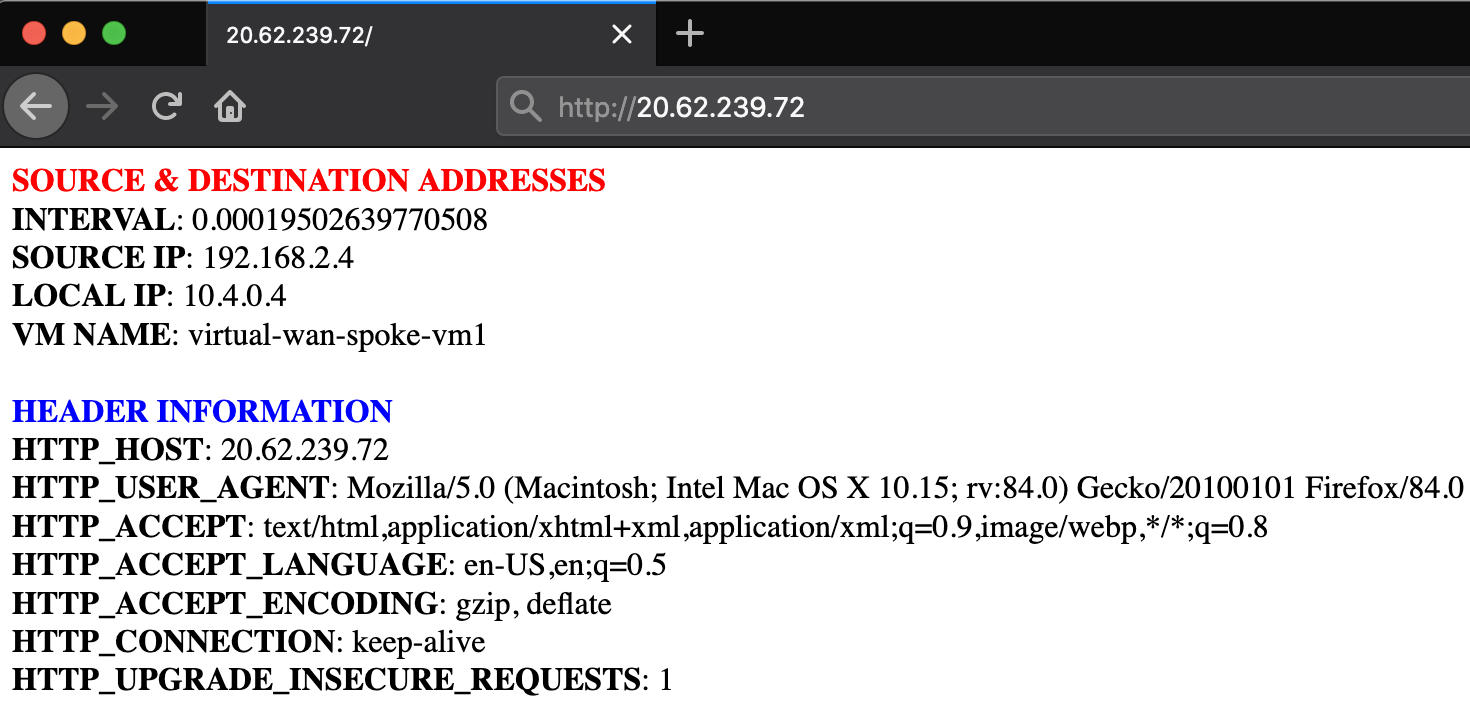
Once the deployment finishes, paste the SPOKE-INBOUND-HTTP output value into a web-browser. The URL is the public load balancer's frontend of the inbound VM-Series firewalls. Once the VM-Series inspects the traffic, a NAT is applied to send inbound request through the virtual WAN hub.
Next, SSH to the web-server by pasting the SPOKE-INBOUND-SSH output into your existing cloud shell (UN/PW: paloalto/Pal0Alt0@123). This SSH session takes the same path as the previous HTTP path.
After you have logged into the web-server, try to ping/SSH the Ubuntu VM running in the local-spoke VNET (10.3.0.4). This request will flow through the virtual WAN hub. The virtual hub routes the traffic to the outbound VM-Series firewalls. After inspection, the traffic is routed to the locally peered spoke VNET.
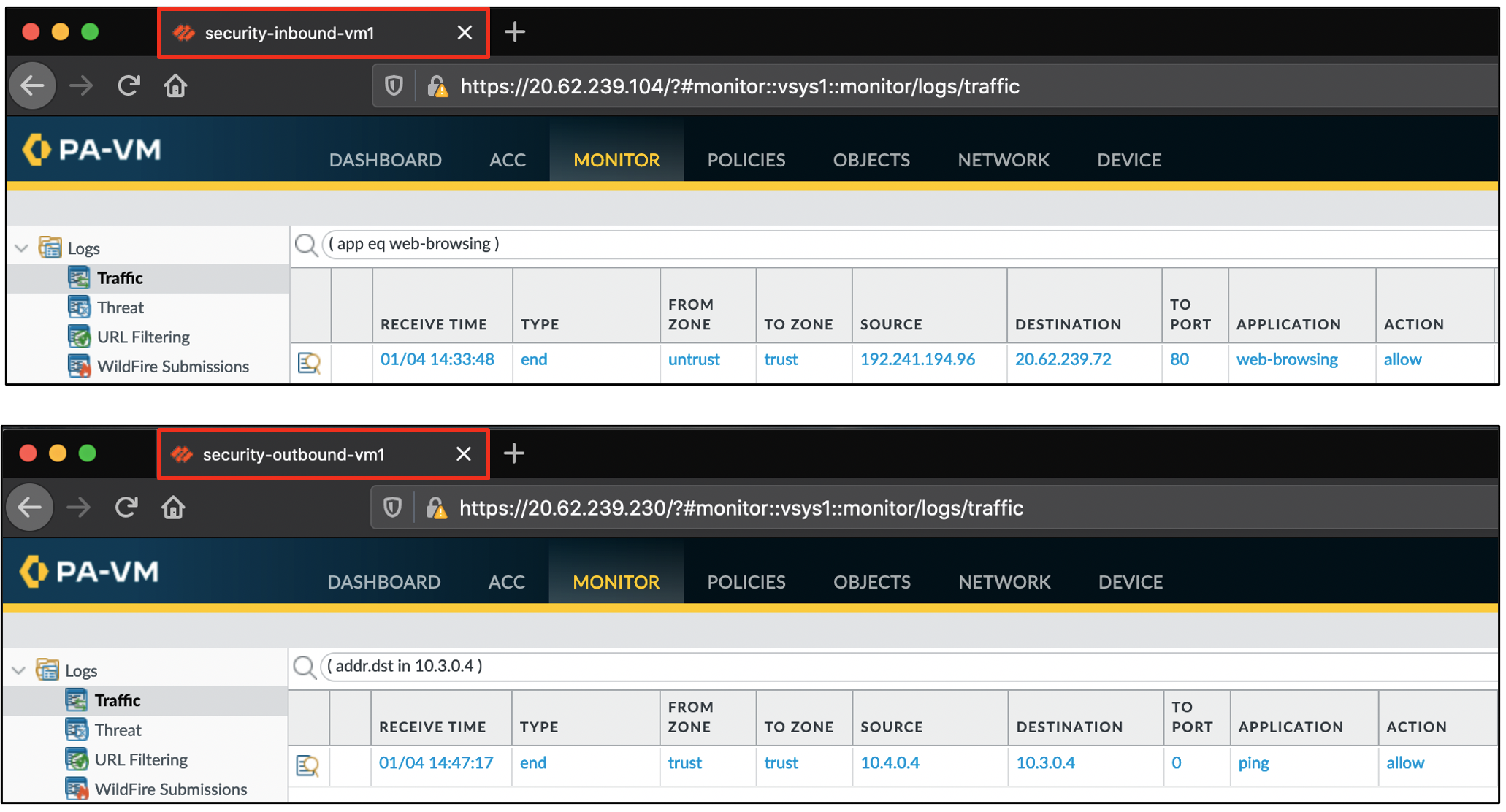
Log into the VM-Series firewalls using the MGMT- output values (UN/PW: paloalto/Pal0Alt0@123). Go to the monitor tab to view the traffic logs.
Once you ahve tested the enivronment, you can delete the Azure resources by running the follow command from your Azure cloud shell.
$ terraform destroy