Create and deploy a DeFi App to Ethereum
In this repo we will build a DeFi Application with Solidity where users can deposit an ERC20 token to the smart contract and it will mint and transfer Farm Tokens to them. The users can later withdraw their ERC20 tokens by burning their Farm Token on smart contract and the ERC20 tokens will be transferred back to them.
brew install truffle
or
npm install truffle
If this is the first time you are writing a smart contract, you will need to set up your environment. We are going to use two tools: Truffle and Ganache.
Truffle is a development environment and testing framework for developing smart contracts for Ethereum. With Truffle it is easy to build and deploy smart contracts to the blockchain. Ganache allow us to create a local Ethereum blockchain in order to test smart contracts. It simulates the features of the real network and the first 10 accounts are funded with 100 test Ether, thus making the smart contract deployment and testing free and easy. Ganache is available as a desktop application and a command-line tool. For this article we will be using the UI desktop application.
To create the project, run the following commands
mkdir YourProjectName
cd YourProjectName
truffle initThis will create a blank project for the development and deployment of our smart contracts. The created project structure is the following:
-
contracts: Folder for the solidity smart contracts -
migrations: Folder for the deployment scripts -
test: Folder for testing our smart contracts -
truffle-config.js: Truffle configuration file
To compile our smart contract, we must first check our solidity compiler version. You can check that by running the command:
truffle version
The default version is the Solidity v0.5.16. Since our token is written using the solidity version 0.8.10, if we run the command to compile our contracts we will get a compiler error. In order to specify which solidity compiler version to use, go to the file truffle-config.js and set to the desired compiler version as seen below:
// Configure your compilers
compilers: {
solc: {
version: "0.8.10", // Fetch exact version from solc-bin (default: truffle's version)
// docker: true, // Use "0.5.1" you've installed locally with docker (default: false)
// settings: { // See the solidity docs for advice about optimization and evmVersion
// optimizer: {
// enabled: false,
// runs: 200
// },
// evmVersion: "byzantium"
// }
}
}First we need to create our ERC20 token that we will use to stake on the smart contract. To create our fungible token, we will first need to install the OpenZeppelin library. This library contains the implementations of standards such as the ERC20 and the ERC721. To install it, run the command:
npm install @openzeppelin/contracts
Using the openzeppelin library we can create our ERC20 token called MyToken with the following solidity code:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.2;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
contract MyToken is ERC20 {
constructor() ERC20("MyToken", "MTKN"){
_mint(msg.sender, 1000000000000000000000000);
}
}In the code above on:
-
Line 3: We import the contract ERC20.sol from openzeppelin that contains the implementation for this token standard.
-
Line 5: We inherit from the ERC20.sol contract.
-
Line 6: We are calling the ERC20.sol constructor and passing for the name and symbol parameters as
"MyToken"and"MTKN"respectively. -
Line 7: We are minting and transferring 1 million tokens for the account that is deploying the smart contract (we are using the default 18 decimals for the ERC20 token, that means that if we want to mint 1 token, you will represent it as 1000000000000000000, 1 with 18 zeros).
We can see below the ERC20.sol constructor implementation where the _decimals field is set to 18:
string private _name;
string private _symbol;
uint8 private _decimals;
constructor (string memory name_, string memory symbol_) public {
_name = name_;
_symbol = symbol_;
_decimals = 18;
}On the migrations folder, create a file called 2_deploy_Tokens.js. This file is where we will deploy both our ERC20 Token and our FarmToken smart contract. The code below is used to deploy our MyToken.sol contract:
const MyToken = artifacts.require('MyToken')
module.exports = async function(deployer, network, accounts) {
// Deploy MyToken
await deployer.deploy(MyToken)
const myToken = await MyToken.deployed()
}Now we can compile our smart contract by running the following command:
truffle compile
After compiling, we can now deploy our token. For this open Ganache and select the option "Quickstart" to start a local Ethereum blockchain. To deploy our contract, run:
truffle migrate
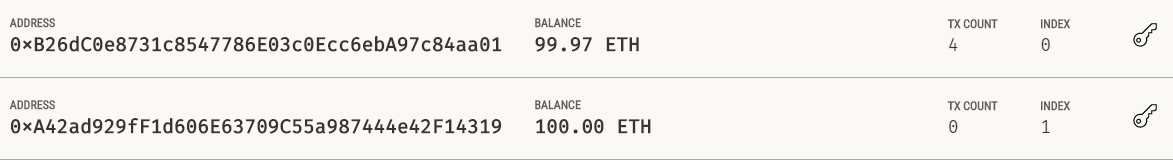
The address used to deploy our contracts is the first one from the list of addresses that Ganache shows us. To verify that, we can open the Ganache desktop application and we can verify that the balance of Ether for the first account has been reduced due to the cost of Ether to deploy our smart contracts:
To verify that 1 million MyToken tokens have been sent to the deployer address, we can use the Truffle Console to interact with our deployed smart contract.
Truffle Console is a a basic interactive console connecting to any Ethereum client.
In order to interact with our smart contract, run the following command:
truffle console
Now we can write the following commands in the terminal:
-
Get the smart contract:
myToken = await MyToken.deployed() -
Get the array of accounts from Ganache:
accounts = await web3.eth.getAccounts() -
Get the balance for the first account:
balance = await myToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]) -
Format the balance from 18 decimals:
web3.utils.fromWei(balance.toString())
By running the commands above, we will see that the first address has in fact 1 million MyTokens:

The FarmToken smart contract will have 3 functions:
-
balance(): Get the MyToken balance on the FarmToken smart contract. -
deposit(uint256 _amount): Transfer MyToken on behalf of the user to the FarmToken smart contract then mint and transfer FarmToken to the user. -
withdraw(uint256 _amount): Burn user's FarmTokens and transfer MyTokens to the user's address.
Let's look at the FarmToken constructor:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity 0.8.10;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/IERC20.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Address.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/utils/SafeERC20.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/math/SafeMath.sol";
contract FarmToken is ERC20 {
using Address for address;
using SafeMath for uint256;
using SafeERC20 for IERC20;
IERC20 public token;
constructor(address _token) ERC20("FarmToken", "FRM") {
token = IERC20(_token);
}
}-
Lines 3-6: We are importing the following contracts from openzeppelin: IERC20.sol, Address.sol, SafeERC20.sol and ERC20.sol.
-
Line 8: The FarmToken will inherit from the ERC20 contract.
-
Lines 14-19: The FarmToken constructor will receive as parameter the address of MyToken contract and we will assign its contract to our public variable called
token.
Let's implement the balance() function. It will receive no parameters and it will return the balance of MyToken on this smart contract. It is implemented as shown below:
function balance() public view returns (uint256) {
return token.balanceOf(address(this));
}For the deposit(uint256 _amount) function, it will receive as parameter the amount the user wants to deposit and it will mint and transfer FarmTokens to the user:
function deposit(uint256 _amount) public {
// Amount must be greater than zero
require(_amount > 0, "amount cannot be 0");
// Transfer MyToken to smart contract
token.safeTransferFrom(msg.sender, address(this), _amount);
// Mint FarmToken to msg sender
_mint(msg.sender, _amount);
}For the withdraw(uint256 _amount) function, we will receive as parameter the amount of FarmTokens the user wants to burn and then transfer the same amount of MyTokens back to the user:
function withdraw(uint256 _amount) public {
// Burn FarmTokens from msg sender
_burn(msg.sender, _amount);
// Transfer MyTokens from this smart contract to msg sender
token.safeTransfer(msg.sender, _amount);
}Now we will deploy our smart contract. To do so, we will go back to the file 2_deploy_Tokens.js and add the new contract to be deployed:
const MyToken = artifacts.require('MyToken')
const FarmToken = artifacts.require('FarmToken')
module.exports = async function(deployer, network, accounts) {
// Deploy MyToken
await deployer.deploy(MyToken)
const myToken = await MyToken.deployed()
// Deploy Farm Token
await deployer.deploy(FarmToken, myToken.address)
const farmToken = await FarmToken.deployed()
}Note that when deploying the FarmToken, we pass as parameter the address of the deployed MyToken contract.
Now, run truffle compile and truffle migrate to deploy our contracts.
Let's test our smart contract. Instead of using the truffle console to interact with our smart contract, we will create a script to automate this process. Create a folder called scripts and add the following file getMyTokenBalance.js. It will check the balance of MyTokens on the FarmToken smart contract:
const MyToken = artifacts.require('MyToken');
const FarmToken = artifacts.require("FarmToken");
module.exports = async function(callback) {
myToken = await MyToken.deployed()
farmToken = await FarmToken.deployed()
balance = await myToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address)
console.log(web3.utils.fromWei(balance.toString()))
callback();
}To execute this script, run the following cli command:
truffle exec .\scripts\getMyTokenBalance.jsWe will get the expected result that is 0.
Now, let's stake the MyToken to the smart contract. Since the function deposit(uint256 _amount) calls the function safeTransferFrom from the ERC20, the user must first approve the smart contract to transfer MyToken on the user's behalf. So on the script below, we will first approve this step then we will call the function:
const MyToken = artifacts.require("MyToken");
const FarmToken = artifacts.require("FarmToken");
module.exports = async function(callback) {
const accounts = await new web3.eth.getAccounts();
const myToken = await MyToken.deployed();
const farmToken = await FarmToken.deployed();
// Returns the remaining number of tokens that spender will be allowed to spend on behalf of owner through transferFrom.
// This is zero by default.
const allowanceBefore = await myToken.allowance(accounts[0], farmToken.address);
console.log('Amount of MyToken FarmToken is allowed to transfer on our behalf Before: ' + allowanceBefore.toString());
// In order to allow the Smart Contract to transfer to MyToken (ERC-20) on the accounts[0] behalf,
// we must explicitly allow it.
// We allow farmToken to transfer x amount of MyToken on our behalf
await myToken.approve(farmToken.address, web3.utils.toWei('100', 'ether'));
// Validate that the farmToken can now move x amount of MyToken on our behalf
const allowanceAfter = await myToken.allowance(accounts[0], farmToken.address);
console.log('Amount of MyToken FarmToken is allowed to transfer on our behalf After: ' + allowanceAfter.toString());
// Verify accounts[0] and farmToken balance of MyToken before and after the transfer
balanceMyTokenBeforeAccounts0 = await myToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
balanceMyTokenBeforeFarmToken = await myToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address);
console.log('*** My Token ***')
console.log('Balance MyToken Before accounts[0] ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceMyTokenBeforeAccounts0.toString()))
console.log('Balance MyToken Before TokenFarm ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceMyTokenBeforeFarmToken.toString()))
console.log('*** Farm Token ***')
balanceFarmTokenBeforeAccounts0 = await farmToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
balanceFarmTokenBeforeFarmToken = await farmToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address);
console.log('Balance FarmToken Before accounts[0] ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceFarmTokenBeforeAccounts0.toString()))
console.log('Balance FarmToken Before TokenFarm ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceFarmTokenBeforeFarmToken.toString()))
// Call Deposit function from FarmToken
console.log('Call Deposit Function')
await farmToken.deposit(web3.utils.toWei('100', 'ether'));
console.log('*** My Token ***')
balanceMyTokenAfterAccounts0 = await myToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
balanceMyTokenAfterFarmToken = await myToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address);
console.log('Balance MyToken After accounts[0] ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceMyTokenAfterAccounts0.toString()))
console.log('Balance MyToken After TokenFarm ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceMyTokenAfterFarmToken.toString()))
console.log('*** Farm Token ***')
balanceFarmTokenAfterAccounts0 = await farmToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
balanceFarmTokenAfterFarmToken = await farmToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address);
console.log('Balance FarmToken After accounts[0] ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceFarmTokenAfterAccounts0.toString()))
console.log('Balance FarmToken After TokenFarm ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceFarmTokenAfterFarmToken.toString()))
// End function
callback();
}To run this script: truffle exec .\scripts\transferMyTokenToFarmToken.js. You should see on your console:
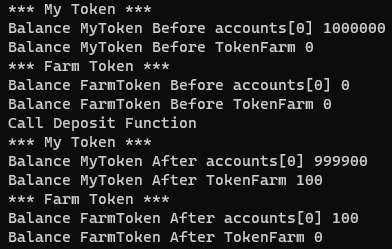
As we can see, we have successfully deposited MyTokens to the smart contract as the first account has now FarmTokens.
In order to withdraw:
const MyToken = artifacts.require("MyToken");
const FarmToken = artifacts.require("FarmToken");
module.exports = async function(callback) {
const accounts = await new web3.eth.getAccounts();
const myToken = await MyToken.deployed();
const farmToken = await FarmToken.deployed();
// Verify accounts[0] and farmToken balance of MyToken before and after the transfer
balanceMyTokenBeforeAccounts0 = await myToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
balanceMyTokenBeforeFarmToken = await myToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address);
console.log('*** My Token ***')
console.log('Balance MyToken Before accounts[0] ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceMyTokenBeforeAccounts0.toString()))
console.log('Balance MyToken Before TokenFarm ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceMyTokenBeforeFarmToken.toString()))
console.log('*** Farm Token ***')
balanceFarmTokenBeforeAccounts0 = await farmToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
balanceFarmTokenBeforeFarmToken = await farmToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address);
console.log('Balance FarmToken Before accounts[0] ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceFarmTokenBeforeAccounts0.toString()))
console.log('Balance FarmToken Before TokenFarm ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceFarmTokenBeforeFarmToken.toString()))
// Call Deposit function from FarmToken
console.log('Call Withdraw Function')
await farmToken.withdraw(web3.utils.toWei('100', 'ether'));
console.log('*** My Token ***')
balanceMyTokenAfterAccounts0 = await myToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
balanceMyTokenAfterFarmToken = await myToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address);
console.log('Balance MyToken After accounts[0] ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceMyTokenAfterAccounts0.toString()))
console.log('Balance MyToken After TokenFarm ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceMyTokenAfterFarmToken.toString()))
console.log('*** Farm Token ***')
balanceFarmTokenAfterAccounts0 = await farmToken.balanceOf(accounts[0]);
balanceFarmTokenAfterFarmToken = await farmToken.balanceOf(farmToken.address);
console.log('Balance FarmToken After accounts[0] ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceFarmTokenAfterAccounts0.toString()))
console.log('Balance FarmToken After TokenFarm ' + web3.utils.fromWei(balanceFarmTokenAfterFarmToken.toString()))
// End function
callback();
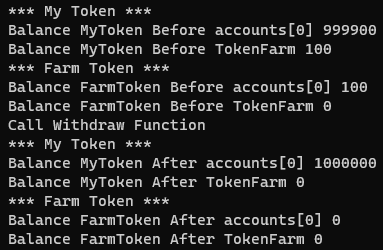
}To run this script: truffle exec .\scripts\withdrawMyTokenFromTokenFarm.js. As we can see on the output below, we have successfully got the MyTokens back and we have burned the FarmTokens:
Sweet Tools for Smart Contracts | Truffle Suite
What is DeFi? A Begginer's Guide (2021 Updated) (99bitcoins.com)