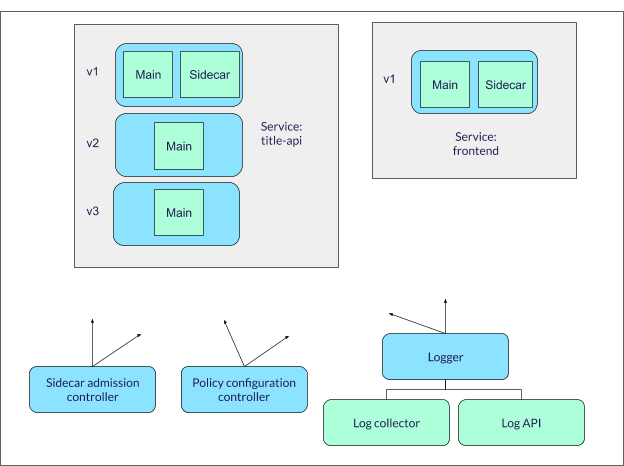
The framework provides an easy-to-use solution to implement policies to target a group of containers. An independent analytics tool capable of identifying incoming threats to the cluster is part of the framework. The framework can quarantine the pods to prevent the spread of the vulnerability that can compromise the entire service. User ease has been a top priority for the framework, which provides easy installation and a familiar approach to apply policies to the Kubernetes cluster.
- Easy cluster-wide setup
- Intuitive policy configuration
- Independent analytics tool
- Preventive actions to avoid failures
- The framework deploys a sidecar to monitor the health of the main application container in the pod. The data collected by the sidecar can be used by various analytical engines. The analysis would be beneficial in manging the cluster health and to avoid failures.
- In case a pod on a worker node fails, it can be quarantined and possibly pushed to another node. A service disruption can be prevented by taking appropriate action on similar pods.
-
- Access to a running Kubernetes cluster and kubectl
- On a local system, it can be run by using minikube
- Docker (using version 19.03.8), Go (using Version 1.14)
- Ensure that a docker image has been created for all components (steps mentioned below)
-
- Run
./install.sh: This will install all the required components - Add label
sidecar-injection: enabledto the namespace where you want to add sidecar - Run
kubectl create -f sidecar/clusterrole.yamlto apply necessary RBAC permissions to access the namespace where you want to add the sidecar. Currentlysidecar/clusterrole.yamladds necessary permissions fornamespace: default. This can be edited to apply to any other namespace. - Create a policy. A sample policy can be observed in
CustomResource/deployment/sample-resource.yaml. Apply the policy to the cluster usingkubectl create -f CustomResource/deployment/sample-resource.yaml. - The setup is now complete. A sidecar will be injected to all the matching pods.
- Run
-
Before setting up framework, create docker images for each individual component: 1. Custom Resource: Run
CustomResource/build.sh2. Wehook: Runcd webhook; make3. Log Aggregator: Runcd logger; make build-collector4. Log API: Runcd logger; make build-endpoint5. Log Sender: Runmake build-sender6. Sidecar: Runcd sidecar; make -
Setting up the Mutating Admission Controller for sidecar injection:
- Switch context to
namespace: sidecar-injector - Run
kubectl create -f webhook/deployment/inject_sidecar.yamlto create sidecar configuration - Run
./webhook/deployment/webhook-create-signed-cert.sh \ --service sidecar-injector-webhook-svc \ --secret sidecar-injector-webhook-certs \ --namespace sidecar-injectorto create necessary certificates for enabling TLS communication with kube-apiserver - Run
kubectl create -f webhook/deployment/clusterrole.yamlfor necessary RBAC permissions - Run
kubectl create -f webhook/deployment/deployment.yaml && kubectl create -f webhook/deployment/service.yaml - Run
kubectl create -f webhook/deployment/mutatingwebhook-ca-bundle.yaml && cat webhook/deployment/mutating-webhook.yaml | ./webhook/deployment/webhook-patch-ca-bundle.sh > webhook/deployment/mutatingwebhook-ca-bundle.yaml
- Switch context to
-
Setting up the Custom Resource:
- Switch context to
namespace: sidecar-injector - Run
kubectl create -f CustomResource/deployment/sample-operator.yamlto setup the custom controller.
- Switch context to
-
Setting up the Custom Resource:
- Switch context to
namespace: sidecar-injector - Run
kubectl create -f logger/deployment/deployment.yamlto setup the logger application.
- Switch context to