-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 43
Spark SQL
Spark SQL is a component on top of Spark Core that introduces a new data abstraction called SchemaRDD, which provides support for structured and semi-structured data.Spark SQL is to execute SQL queries written using either a basic SQL syntax or HiveQL. Spark SQL can also be used to read data from an existing Hive installation.It provides a programming abstraction called DataFrame and can act as distributed SQL query engine. Spark’s interface for working with structured and semi structured data. Structured data is any data that has a schema—that is, a known set of fields for each record. When you have this type of data, Spark SQL makes it both easier and more efficient to load and query.There are several ways to interact with Spark SQL including SQL, the DataFrames API and the Datasets API. When computing a result the same execution engine is used, independent of which API/language you are using to express the computation.
To create a basic SQLContext, all you need is a SparkContext.
val sc = SparkCommon.sparkContext
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
Spark SQL can load JSON files and infer the schema based on that data. Here is the code to load the json files, register the data in the temp table called "Cars1" and print out the schema based on that. To make a query against a table, we call the sql() method on the SQLContext. The first thing we need to do is tell Spark SQL about some data to query. In this case we will load some Cars data from JSON, and give it a name by registering it as a “Cars1” so we can query it with SQL.
Here we are using JSON document named cars.json with the following content and generate a table based on the schema in the JSON document.
[{"itemNo" : 1, "name" : "ferrari", "speed" : 259 , "weight": 800}, {"itemNo" : 2, "name" : "jaguar", "speed" : 274 , "weight":998}, {"itemNo" : 3, "name" : "mercedes", "speed" : 340 , "weight": 1800}, {"itemNo" : 4, "name" : "audi", "speed" : 345 , "weight": 875}, {"itemNo" : 5, "name" : "lamborghini", "speed" : 355 , "weight": 1490},{"itemNo" : 6, "name" : "chevrolet", "speed" : 260 , "weight": 900}, {"itemNo" : 7, "name" : "ford", "speed" : 250 , "weight": 1061}, {"itemNo" : 8, "name" : "porche", "speed" : 320 , "weight": 1490}, {"itemNo" : 9, "name" : "bmw", "speed" : 325 , "weight": 1190}, {"itemNo" : 10, "name" : "mercedes-benz", "speed" : 312 , "weight": 1567}]
object BasicQueryExample {
val sc = SparkCommon.sparkContext
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
import sqlContext.implicits._
val input = sqlContext.read.json("src/main/resources/cars1.json")
input.registerTempTable("Cars1")
val result = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM Cars1")
result.show()
}
}
case class Cars1(name: String)

val cars = sqlContext.sql("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Cars1").collect().foreach(println)

val result1 = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name, COUNT(*) AS cnt FROM Cars1 WHERE name <> '' GROUP BY name ORDER BY cnt DESC LIMIT 10")
.collect().foreach(println)

A DataFrame is a distributed collection of data organized into named columns.DataFrames can be constructed from a wide array of sources such as: structured data files, tables in Hive, external databases, or existing RDDs.
A DataFrame is a distributed collection of data, which is organized into named columns. Conceptually, it is equivalent to relational tables with good optimization techniques. A DataFrame can be constructed from an array of different sources such as Hive tables, Structured Data files, external databases, or existing RDDs. Here we are using JSON document named cars.json with the following content and generate a table based on the schema in the JSON document.
[{"itemNo" : 1, "name" : "Ferrari", "speed" : 259 , "weight": 800}, {"itemNo" : 2, "name" : "Jaguar", "speed" : 274 , "weight":998}, {"itemNo" : 3, "name" : "Mercedes", "speed" : 340 , "weight": 1800}, {"itemNo" : 4, "name" : "Audi", "speed" : 345 , "weight": 875}, {"itemNo" : 5, "name" : "Lamborghini", "speed" : 355 , "weight": 1490}]
package com.tutorial.sparksql
import com.tutorial.utils.SparkCommon
object CreatingDataFarmes {
val sc = SparkCommon.sparkContext
/**
* Create a Scala Spark SQL Context.
*/
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
/**
* Create the DataFrame
*/
val df = sqlContext.read.json("src/main/resources/cars.json")
/**
* Show the Data
*/
df.show()
}
}

Diiferent type of DataFrame operatios are :
Action are operations (such as take, count, first, and so on) that return a value after running a computation on an DataFrame.
Some Action Operation with examples:
If you want to see top 20 rows of DataFrame in a tabular form then use the following command.
carDataFrame.show()

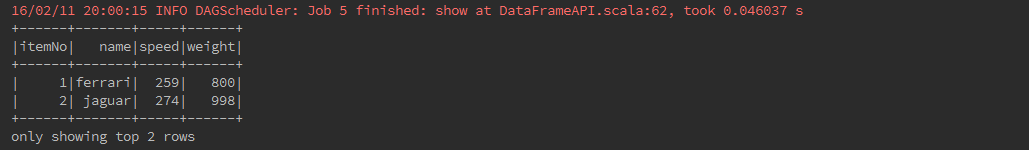
If you want to see n rows of DataFrame in a tabular form then use the following command.
carDataFrame.show(2)
take(n) Returns the first n rows in the DataFrame.
carDataFrame.take(2).foreach(println)

Returns the number of rows.
carDataFrame.groupBy("speed").count().show()

head () is used to returns first row.
val resultHead = carDataFrame.head()
println(resultHead.mkString(","))
head(n) returns first n rows.
val resultHeadNo = carDataFrame.head(3)
println(resultHeadNo.mkString(","))
Returns the first row.
val resultFirst = carDataFrame.first()
println("fist:" + resultFirst.mkString(","))

Returns an array that contains all of Rows in this DataFrame.
val resultCollect = carDataFrame.collect()
println(resultCollect.mkString(","))

If you want to see the Structure (Schema) of the DataFrame, then use the following command.
carDataFrame.printSchema()
toDF() Returns a new DataFrame with columns renamed. It can be quite convenient in conversion from a RDD of tuples into a DataFrame with meaningful names.
val car = sc.textFile("src/main/resources/fruits.txt")
.map(_.split(","))
.map(f => Fruit(f(0).trim.toInt, f(1), f(2).trim.toInt))
.toDF().show()
Returns all column names and their data types as an array.
carDataFrame.dtypes.foreach(println)

Returns all column names as an array.
carDataFrame.columns.foreach(println)

cache() explicitly to store the data into memory. Or data stored in a distributed way in the memory by default.
val resultCache = carDataFrame.filter(carDataFrame("speed") > 300)
resultCache.cache().show()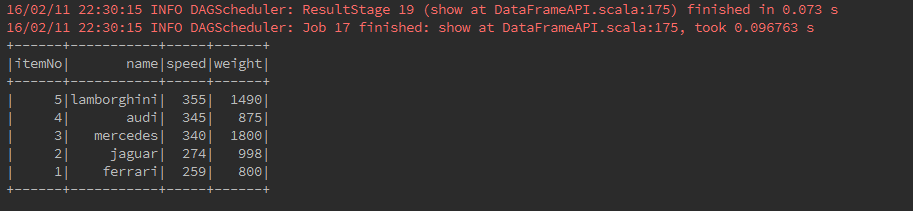
Returns a new DataFrame sorted by the given expressions.
carDataFrame.sort($"itemNo".desc).show()

Returns a new DataFrame sorted by the specified column(s).
carDataFrame.orderBy(desc("speed")).show()

counting the number of cars who are of the same speed .
carDataFrame.groupBy("speed").count().show()

Returns a DataFrameNaFunctions for working with missing data.
carDataFrame.na.drop().show()

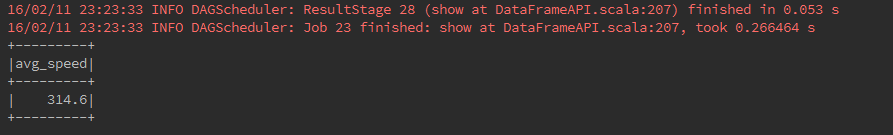
Returns a new DataFrame with an alias set.
carDataFrame.select(avg($"speed").as("avg_speed")).show()
Returns a new DataFrame with an alias set. Same as
as.
carDataFrame.select(avg($"weight").alias("avg_weight")).show()

To fetch speed-column among all columns from the DataFrame.
carDataFrame.select("speed").show()

filter the cars whose speed is greater than 300 (speed > 300).
carDataFrame.filter(carDataFrame("speed") > 300).show()

Filters age using the given SQL expression.
carDataFrame.where($"speed" > 300).show()

Aggregates on the entire DataFrame without groups.
carDataFrame.agg(max($"speed")).show()

Returns a new DataFrame by taking the first n rows.The difference between this function and head is that head returns an array while limit returns a new DataFrame.
carDataFrame1.limit(3).show()

Returns a new DataFrame containing union of rows in this frame and another frame.
carDataFrame.unionAll(empDataFrame2).show()

Returns a new DataFrame containing rows only in both this frame and another frame.
carDataFrame1.intersect(carDataFrame).show()
Returns a new DataFrame containing rows in this frame but not in another frame.
carDataFrame.except(carDataFrame1).show()

Returns a new DataFrame by adding a column or replacing the existing column that has the same name.
val coder: (Int => String) = (arg: Int) => {
if (arg < 300) "slow" else "high"
}
val sqlfunc = udf(coder)
carDataFrame.withColumn("First", sqlfunc(col("speed"))).show()

Returns a new DataFrame with a column renamed.
empDataFrame2.withColumnRenamed("id", "employeeId").show()
Returns a new DataFrame with a column dropped.
carDataFrame.drop("speed").show()

Returns a new DataFrame that contains only the unique rows from this DataFrame. This is an alias for distinct.
carDataFrame.dropDuplicates().show()

describe returns a DataFrame containing information such as number of non-null entries (count),mean, standard deviation, and minimum and maximum value for each numerical column.
carDataFrame.describe("speed").show()

SparkSQL supports two different types methods for converting existing RDDs into DataFrames:
The Scala interface for Spark SQL supports automatically converting an RDD containing case classes to a DataFrame. The case class defines the schema of the table. The names of the arguments to the case class are read using reflection and they become the names of the columns. RDD can be implicitly converted to a DataFrame and then be registered as a table. Tables can be used in subsequent SQL statements.
def main(args: Array[String]) {
/**
* Create RDD and Apply Transformations
*/
val fruits = sc.textFile("src/main/resources/fruits.txt")
.map(_.split(","))
.map(frt => Fruits(frt(0).trim.toInt, frt(1), frt(2).trim.toInt))
.toDF()
/**
* Store the DataFrame Data in a Table
*/
fruits.registerTempTable("fruits")
/**
* Select Query on DataFrame
*/
val records = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM fruits")
/**
* To see the result data of allrecords DataFrame
*/
records.show()
}
}
case class Fruits(id: Int, name: String, quantity: Int)
Creating DataFrame is through programmatic interface that allows you to construct a schema and then apply it to an existing RDD. DataFrame can be created programmatically with three steps. We Create an RDD of Rows from an Original RDD. Create the schema represented by a StructType matching the structure of Rows in the RDD created in Step first. Apply the schema to the RDD of Rows via createDataFrame method provided by SQLContext.
object ProgrammaticallySchema {
val sc = SparkCommon.sparkContext
val schemaOptions = Map("header" -> "true", "inferSchema" -> "true")
//sc is an existing SparkContext.
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
// Create an RDD
val fruit = sc.textFile("src/main/resources/fruits.txt")
// The schema is encoded in a string
val schemaString = "id name"
// Generate the schema based on the string of schema
val schema =
StructType(
schemaString.split(" ").map(fieldName => StructField(fieldName, StringType, true)))
schema.foreach(println)
// Convert records of the RDD (fruit) to Rows.
val rowRDD = fruit.map(_.split(",")).map(p => Row(p(0), p(1).trim))
rowRDD.foreach(println)
// Apply the schema to the RDD.
val fruitDataFrame = sqlContext.createDataFrame(rowRDD, schema)
fruitDataFrame.foreach(println)
// Register the DataFrames as a table.
fruitDataFrame.registerTempTable("fruit")
/**
* SQL statements can be run by using the sql methods provided by sqlContext.
*/
val results = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM fruit")
results.show()
}
}

Spark SQL supports a number of structured data sources. These sources include Hive tables, JSON, and Parquet files.Spark SQL supports operating on a variety of data sources through the DataFrame interface. A DataFrame can be operated on as normal RDDs and can also be registered as a temporary table. Registering a DataFrame as a table allows you to run SQL queries over its data.
Here we include some basic examples of structured data processing using DataFrames. As an example, the following creates a DataFrame based on the content of a JSON file. Read a JSON document named cars.json with the following content and generate a table based on the schema in the JSON document.
[{"itemNo" : 1, "name" : "ferrari", "speed" : 259 , "weight": 800}, {"itemNo" : 2, "name" : "jaguar", "speed" : 274 , "weight":998}, {"itemNo" : 3, "name" : "mercedes", "speed" : 340 , "weight": 1800}, {"itemNo" : 4, "name" : "audi", "speed" : 345 , "weight": 875}, {"itemNo" : 5, "name" : "lamborghini", "speed" : 355 , "weight": 1490}]
object DataFrameOperations {
val sc = SparkCommon.sparkContext
/**
* Use the following command to create SQLContext.
*/
val ssc = SparkCommon.sparkSQLContext
val schemaOptions = Map("header" -> "true", "inferSchema" -> "true")
def main(args: Array[String]) {
/**
* Create the DataFrame
*/
val cars = "src/main/resources/cars.json"
/**
* read the JSON document
* Use the following command to read the JSON document named cars.json.
* The data is shown as a table with the fields − itemNo, name, speed and weight.
*/
val carDataFrame: DataFrame = ssc.read.format("json").options(schemaOptions).load(cars)
/**
* Show the Data
* If you want to see the data in the DataFrame, then use the following command.
*/
carDataFrame.show()
/**
* printSchema Method
* If you want to see the Structure (Schema) of the DataFrame, then use the following command
*/
carDataFrame.printSchema()
/**
* Select Method
* Use the following command to fetch name-column among three columns from the DataFrame
*/
carDataFrame.select("name").show()
/**
* Filter used to
* cars whose speed is greater than 300 (speed > 300).
*/
carDataFrame.filter(empDataFrame("speed") > 300).show()
/**
* groupBy Method
* counting the number of cars who are of the same speed.
*/
carDataFrame.groupBy("speed").count().show()
}
}
If you want to see the data in the DataFrame, then use the following command.
carDataFrame.show()
If you want to see the Structure (Schema) of the DataFrame, then use the following command
carDataFrame.printSchema()

Use the following command to fetch name-column among three columns from the DataFrame
carDataFrame.select("name").show()
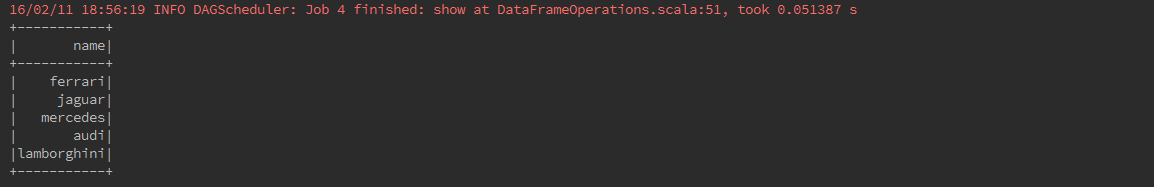
Use the following command to filter whose speed is greater than 300 (speed > 300)from the DataFrame
carDataFrame.filter(carDataFrame("speed") > 300).show()

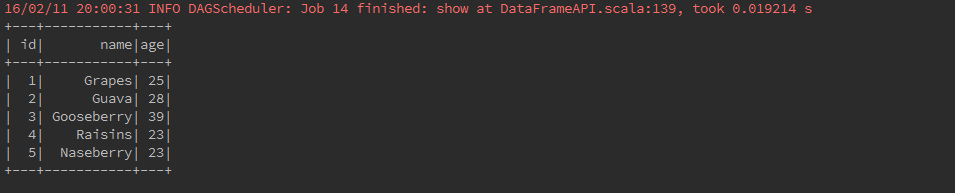
As an example, the following creates a DataFrame based on the content of a text file. Read a text document named fruits.txt with the following content and generate a table based on the schema in the text document.
1, Grapes, 25
2, Guava, 28
3, Gooseberry, 39
4, Raisins, 23
5, Naseberry, 23 val fruits = sc.textFile("src/main/resources/fruits.txt")
.map(_.split(","))
.map(frt => Fruits(frt(0).trim.toInt, frt(1), frt(2).trim.toInt))
.toDF()
/**
* Store the DataFrame Data in a Table
*/
fruits.registerTempTable("fruits")
/**
* Select Query on DataFrame
*/
val records = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM fruits")
/**
* To see the result data of allrecords DataFrame
*/
records.show()
}
}
case class Fruits(id: Int, name: String, quantity: Int)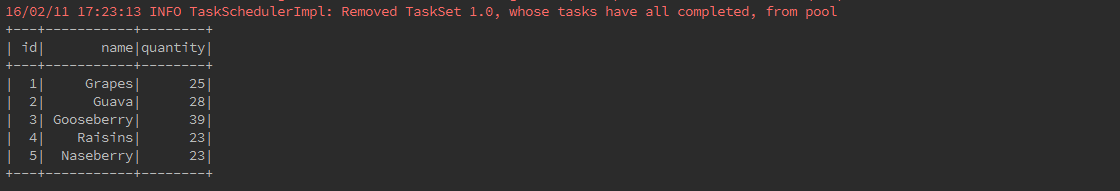
As an example, the following creates a DataFrame based on the content of a CSV file. Read a csv document named cars.csv with the following content and generate a table based on the schema in the csv document.
year,make,model,comment,blank
"2012","Tesla","S","No comment",
1997,Ford,E350,"Go get one now they are going fast",
2015,Chevy,Voltobject csvFile {
val sc = SparkCommon.sparkContext
val sqlContext = SparkCommon.sparkSQLContext
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val df = sqlContext.read
.format("com.databricks.spark.csv")
.option("header", "true") // Use first line of all files as header
.option("inferSchema", "true") // Automatically infer data types
.load("src/main/resources/cars.csv")
df.show()
df.printSchema()
val selectedData = df.select("year", "model")
selectedData.write
.format("com.databricks.spark.csv")
.option("header", "true")
.save(s"src/main/resources/${UUID.randomUUID()}")
println("OK")
}
}
Dataset is a new experimental interface that tries to provide the benefits of RDDs (strong typing, ability to use powerful lambda functions) with the benefits of Spark SQL’s optimized execution engine. Dataset can be constructed from JVM objects and then manipulated using functional transformations (map, flatMap, filter, etc.).
A Dataset is a strongly-typed, immutable collection of objects that are mapped to a relational schema. Datasets are similar to RDDs, however, instead of using Java Serialization they use a specialized Encoder to serialize the objects for processing or transmitting over the network. Dataset API is a new concept called an encoder, which is responsible for converting between JVM objects and tabular representation. Dataset support for automatically generating encoders for a wide variety of types, including primitive types (e.g. String, Integer, Long), Scala case classes, and Java Beans. Here we are using text document named test_file.txt with the following content and generate a table based on the schema in the text document.
JSON is a popular semistructured data format. The simplest way to load JSON data is
by loading the data as a text file and then mapping over the values with a JSON
parser. Likewise, we can use our preferred JSON serialization library to write out the
values to strings, which we can then write out.
In Java and Scala we can also work
with JSON data using a custom Hadoop format.
“JSON” on page 172 also shows how to
load JSON data with Spark SQL.
package com.tutorial.sparksql
import com.tutorial.utils.SparkCommon
object CreatingDatasets {
val sc = SparkCommon.sparkContext
val sqlContext = new org.apache.spark.sql.SQLContext(sc)
def main(args: Array[String]) {
import sqlContext.implicits._
val lines = sqlContext.read.text("src/main/resources/test_file.txt").as[String]
val words = lines
.flatMap(_.split(" "))
.filter(_ != "")
.groupBy(_.toLowerCase)
.count()
.show()
}
}

Encoders are also created for case classes.
case class Cars(name: String, kph: Long)
val ds = Seq(Cars("lamborghini", 32)).toDS()
ds.show()
DataFrames can be converted to a Dataset by providing a class. Mapping will be done by name.
case class Cars(name: String, kph: Long)
val car = sqlContext.read.json("src/main/resources/cars.json").as[Cars]
car.show()
