-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 887
v2_0_cpp_object
msgpack::object is a kind of variant type. The internal type of the msgpack::object is corresponding to the msgpack format. Here is the list of types.
| MessagePack type | msgpack-c type |
|---|---|
| nil | msgpack::type::NIL |
| boolean | msgpack::type::BOOLEAN |
| uint | msgpack::type::POSITIVE_INTEGER |
| int | msgpack::type::NEGATIVE_INTEGER |
| float 32 | msgpack::type::FLOAT32 |
| float 64 | msgpack::type::FLOAT64 |
| str | msgpack::type::STR |
| bin | msgpack::type::BIN |
| ext | msgpack::type::EXT |
| array | msgpack::type::ARRAY |
| map | msgpack::type::MAP |
You can get the type of msgpack::object via type member variable.
If the type of msgpack::object is array or map, the object has children. So msgpack::object is a composite structure.
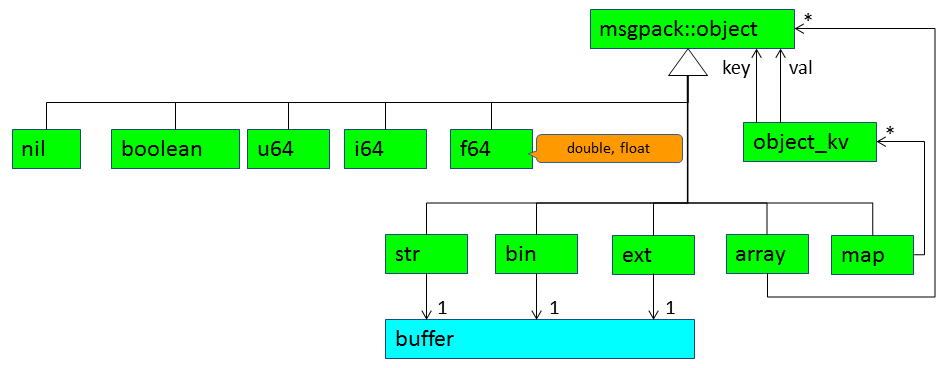
When the type of msgpack::object is str, bin, or ext, the msgpack::object might have a reference of external memory.
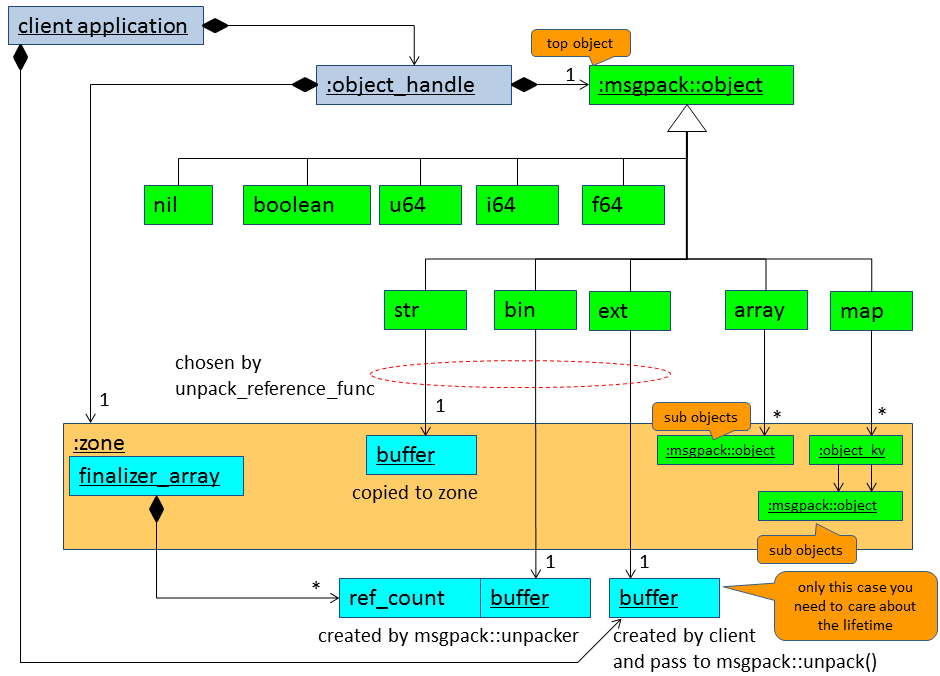
When you use msgpack::unpacker, msgpack::object_handle manages all allocated memories. Treat msgpack::object_handle as a smart pointer.
When you use msgpack::unpack() function without unpack_referenc_func, msgpack::object_handle manages all allocated memories. If you give a custom unpack_referenc_func that returns true, you need to keep the lifetime of the data that you passed to msgpack::unpack() while the unpacked msgpack::object_handle exists.
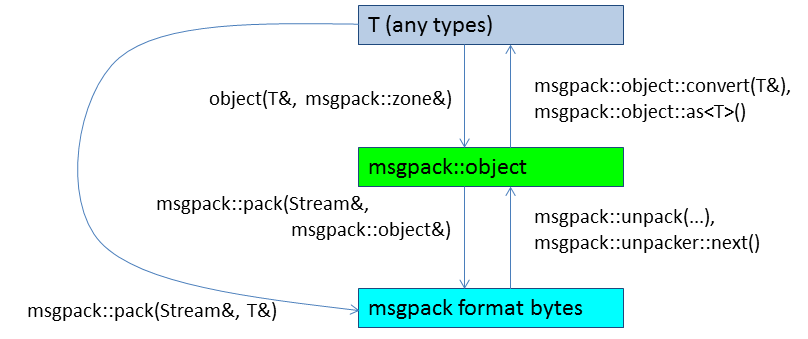
When you unpack msgpack format data, you get msgpack::object from msgpack::object_handle. Then you get various types values from msgpack::object. If you want to convert to custom types from msgpack::object, see adaptor.
You can create a msgpack::object from a various type value using the following constructor. If you want to create a msgpack::object from a custom type, see https://github.com/redboltz/msgpack-c/wiki/v2_0_cpp_adaptor#object and https://github.com/redboltz/msgpack-c/wiki/v2_0_cpp_adaptor#object_with_zone
template <typename T>
object(const T& v, zone& z);You need pass a zone. When the object contains array and/or map, child objects are allocated in the zone. A value that has the type corresponding to str and bin, the contents of the value is copied to the zone with one exception. The exception is msgpack::type::raw_ref. When you call msgpack::object constructor with raw_ref as follows:
msgpack::object obj(msgpack::type::raw_ref(data, size), zone);The data is NOT copied to the zone.
-
Home
- Q&A
- v2.0.x or later
- v1.1.x - v1.4.x
- v1.0.x