“Technology advanced enough is indistinguishable from magic.”
--Arthur C. Clarke (author of 2001: A Space Odyssey)
The link to the book's pretrained models may not work. Download all pretained models at Manning website https://www.manning.com/books/learn-generative-ai-with-pytorch?ar=true&lpse=A&ar=true&lpse=A
Learn Generative AI with PyTorch aims to guide you through the creation of various content (shapes, numbers, images, text, and music) from scratch. It begins with simple models, helping readers build foundational deep learning skills before advancing to more complex challenges. All generative models in this book are deep neural networks. The book starts with a comprehensive deep learning project in PyTorch, ideal for those new to the field. Each chapter is carefully structured to build upon the previous one. You'll first create basic content like shapes, numbers, and images using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) with straightforward architectures. As you progress, the complexity increases, culminating in building state-of-the-art models like Transformers and Diffusion Models.
Learn Generative AI with PyTorch is designed for machine learning enthusiasts and data scientists in various business fields who possess intermediate Python programming skills. This book aims to teach generative AI techniques for creating novel and innovative content, such as images, text, patterns, numbers, shapes, and audio, to enhance both their employers' businesses and their own careers. While many free learning materials are available online covering individual topics, this book consolidates everything into a clear, easy-to-follow, and up-to-date format, making it an invaluable resource for anyone aspiring to become an expert in generative AI.
The book has 16 chapters, organized into four parts.
Part I introduces you to generative AI and deep learning with PyTorch.
• Chapter 1 explains what generative AI is and the rationale behind selecting PyTorch over other AI frameworks like TensorFlow for building generative models in this book.
• Chapter 2 uses PyTorch to create deep neural networks to perform binary and multi-category classifications so that you become well-versed in deep learning and classification tasks. The intention is to get you ready for the upcoming chapters, where you use deep neural networks in PyTorch to create various generative models.
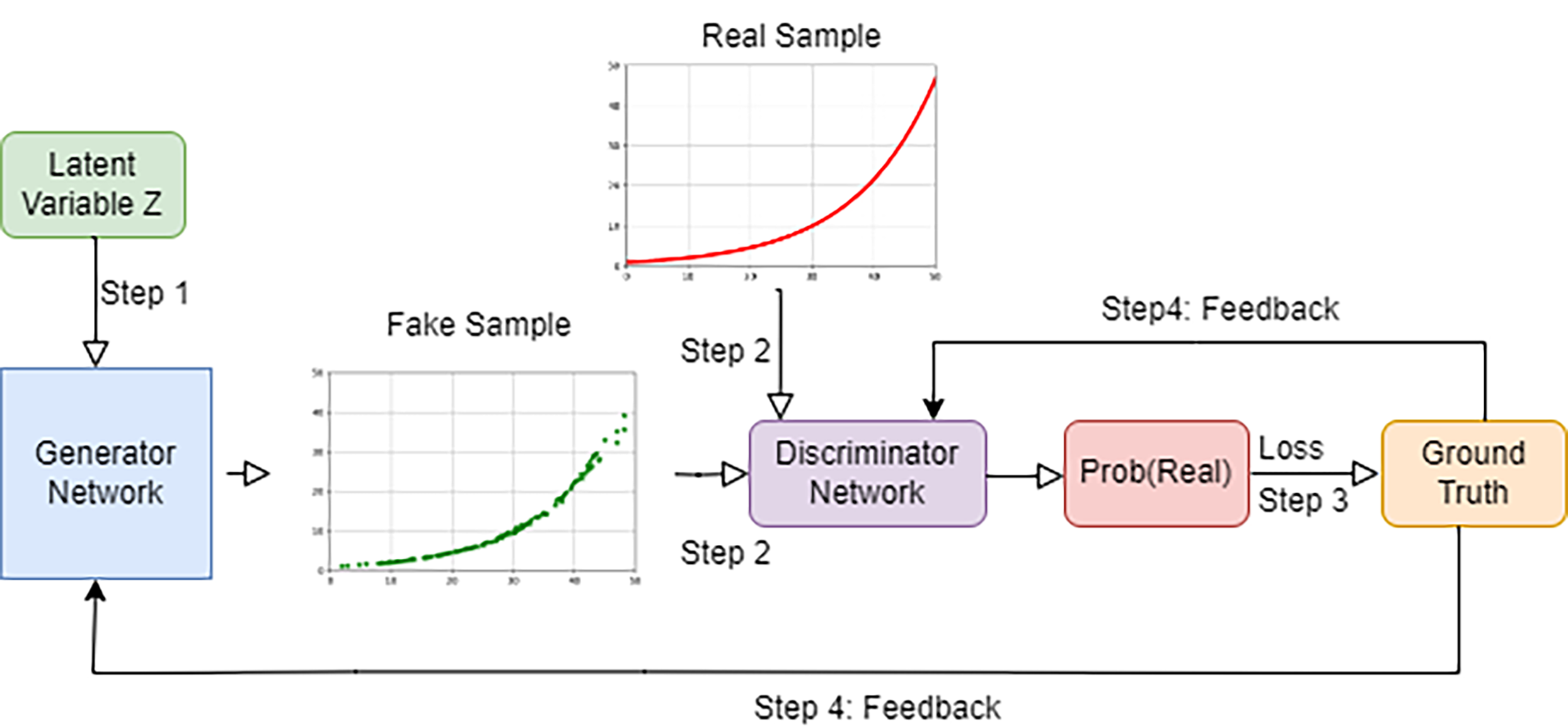
• Chapter 3 introduces you to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). You learn to use GANs to generate shapes and sequences of numbers with certain patterns.
Part II covers image generation.
• Chapter 4 discusses how to build and train GANs to generate high-resolution color images. In particular, you’ll learn to use convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to capture spatial features in images. You’ll also learn to use transposed convolutional layers to upsample and generate high-resolution feature maps in images.
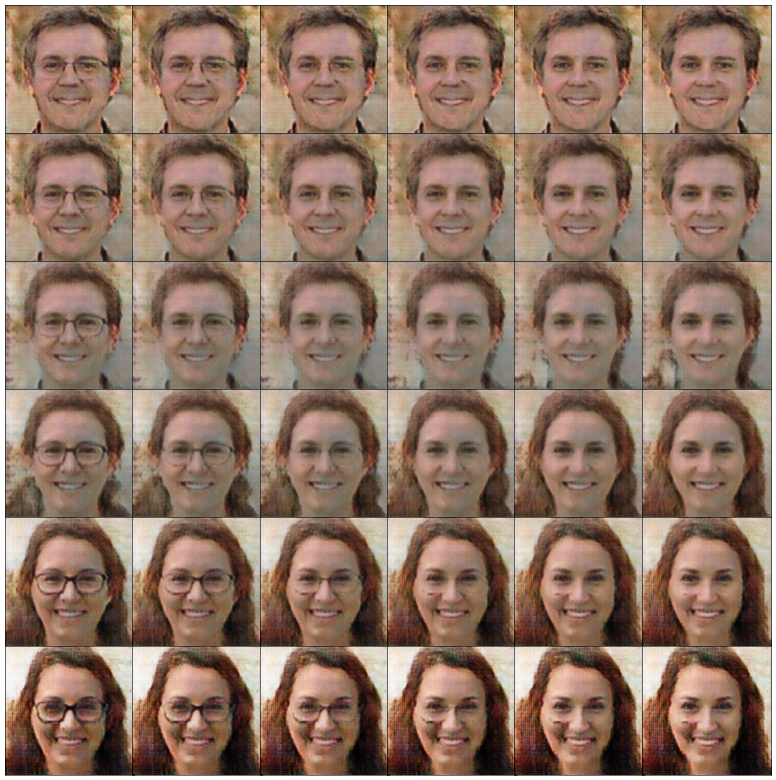
• Chapter 5 details two ways to select characteristics in generated images. The first method involves selecting specific vectors in the latent space. The second method uses a conditional GAN, where you build and train a GAN with labeled data.
• Chapter 6 teaches you how to use a CycleGAN to translate images between two domains such as images with black hair and images with blond hair, or horse images and zebra images.
• Chapter 7 explains how to generate high-resolution images using another generative model: autoencoders (AEs) and their variant, variational autoencoders (VAEs).
Part III dives into natural language processing (NLP) and text generation.
• Chapter 8 discusses text generation with a recurrent neural network (RNN). Along the way, you learn how tokenization and word embedding work. You’ll also learn to generate text autoregressively with the trained model and how to use temperature and top-K sampling to control the creativity of the generated text.
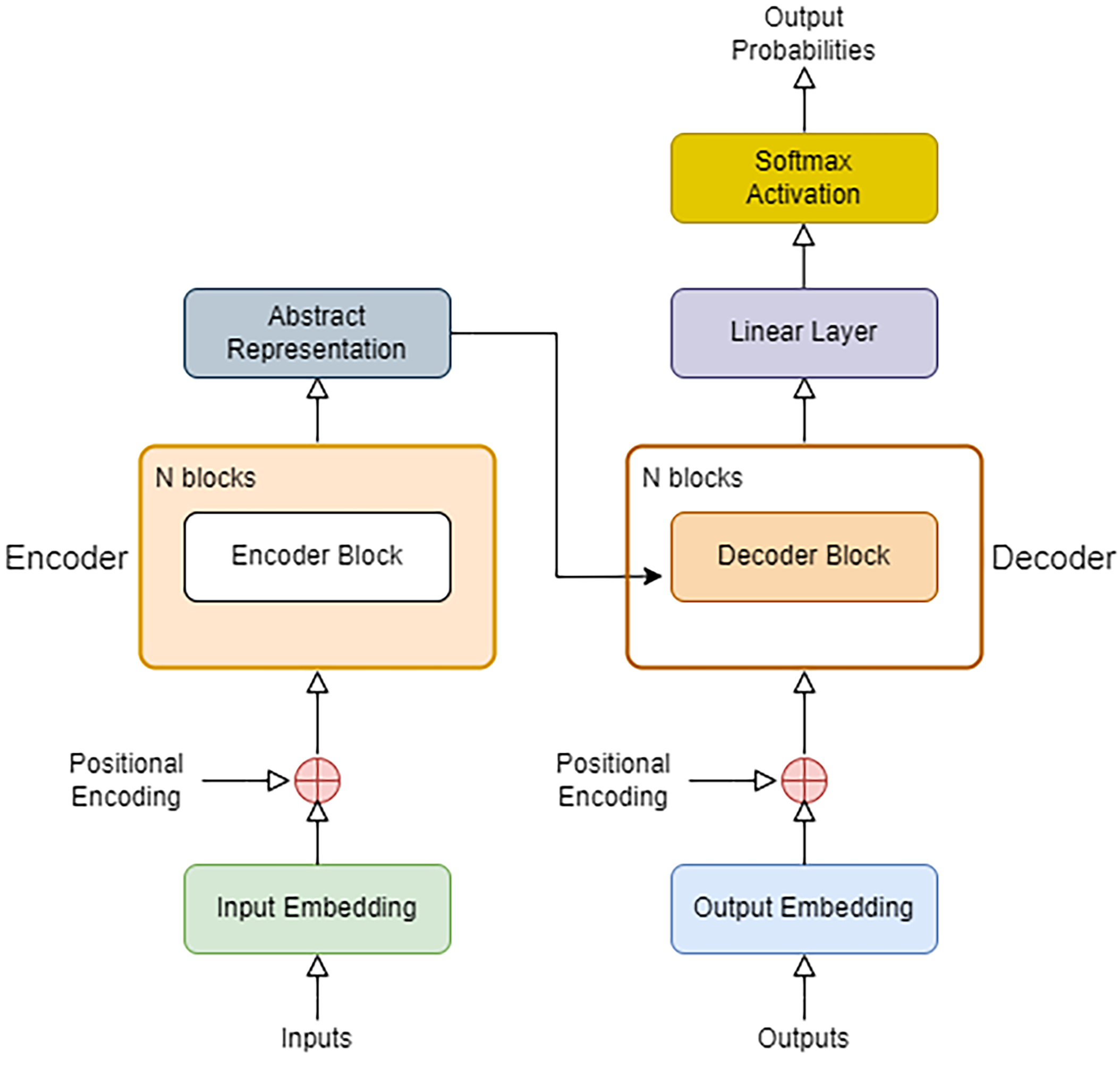
• Chapter 9 builds a Transformer from scratch, based on the paper Attention Is All You Need, to translate between any two languages. You’ll implement line by line the multi-head attention mechanism and an encoder-decoder Transformer.
• Chapter 10 trains the Transformer you built in Chapter 9 with over 47,000 pairs of English-to-French translations. You’ll learn to translate common English phrases to French with the trained model.
• Chapter 11 builds GPT-2XL, the largest version of GPT-2, from scratch. After that, you’ll learn how to extract the pre-trained weights from Hugging Face and load them to your own GPT-2 model to generate text.
• Chapter 12 constructs a scaled-down version of the GPT model with approximately five million parameters so that you can train it on a regular computer. You’ll use three novels by Ernest Hemingway as the training data. The trained model can generate text in Hemingway style.
Part IV discusses some practical applications of the generative models in the book and the most recent developments in the field of generative AI.
• Chapter 13 builds and trains a MuseGAN to generate music. MuseGAN treats a piece of music as a multi-dimensional object akin to an image. The generator produces a complete piece of music and submits it to the critic for evaluation. The generator then modifies the music based on the critic's feedback until it closely resembles real music from the training dataset. Listen to an example of the generated music: https://gattonweb.uky.edu/faculty/lium/ml/MuseGAN_song.mp3
• Chapter 14 takes a different approach to AI music creation. Instead of treating a piece of music as a multi-dimensional object, you treat it as a sequence of musical events. You'll then apply techniques from text generation to predict the next element in a sequence. Listen to an example of the generated music: https://gattonweb.uky.edu/faculty/lium/ml/musicTrans.mp3
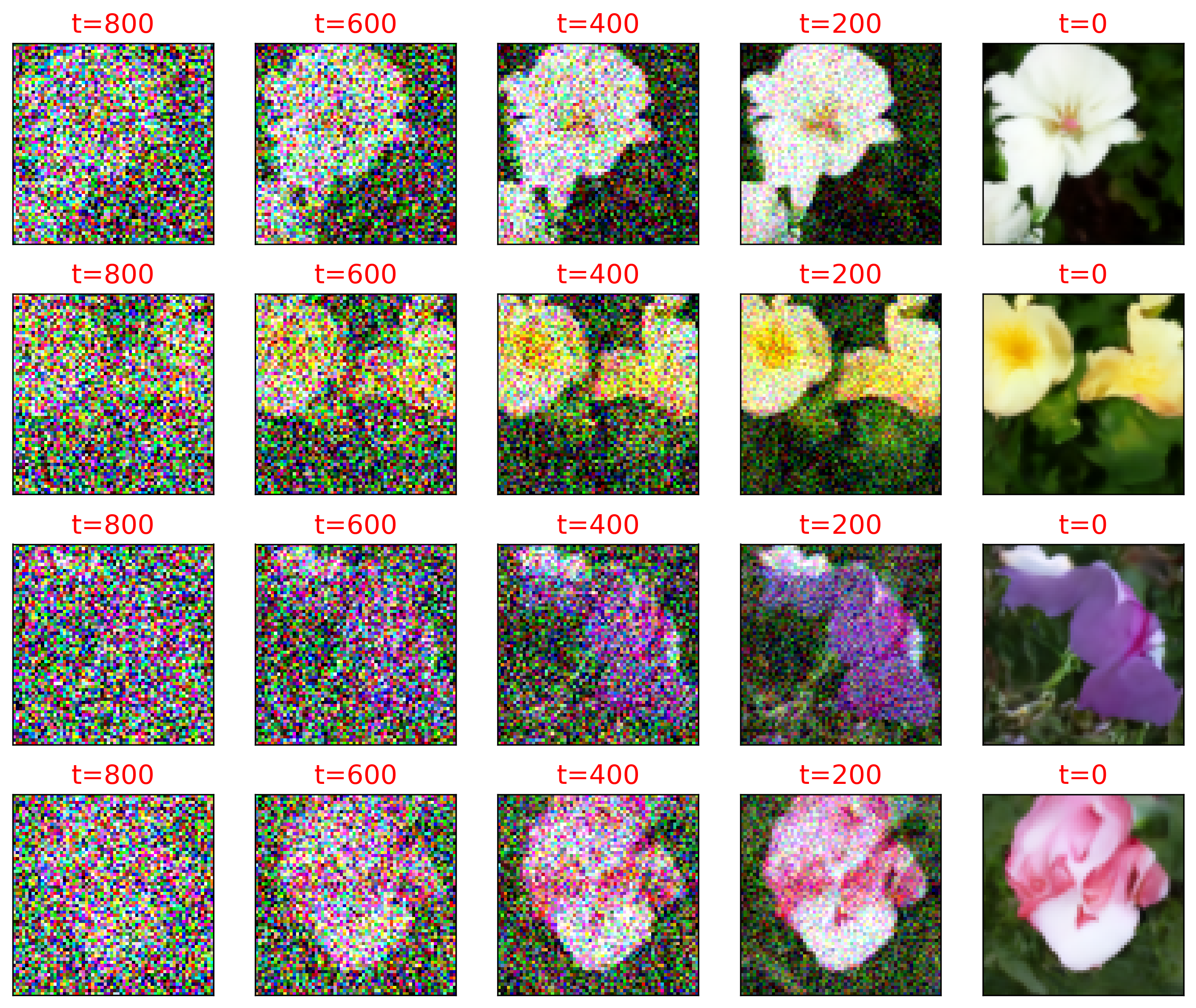
• Chapter 15 introduces you to diffusion models, which form the foundation of all leading text-to-image Transformers (such as DALL-E or Imagen). You’ll build and train a diffusion model to generate high-resolution flower images.
• Chapter 16 ends the book with a project in which you use the LangChain library to combine pre-trained large language models (LLMs) with Wolfram Alpha and Wikipedia APIs to create a zero-shot know-it-all personal assistant.
The appendix discusses how to install PyTorch on your computer, with or without a Compute Unified Device Architecture (CUDA)-enabled GPU.
All Python programs in this book are available for download at the book’s GitHub repository https://github.com/markhliu/DGAI. The programs are organized by chapters with each chapter in a single Jupyter Notebook file. See the Appendix of the book on how to install Python, PyTorch, and Jupyter Notebook on your computer.