There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n and n - 1 edges. You are given the integer n. The parent node of a node with a label v is the node with the label floor (v / 2). The root of the tree is the node with the label 1.
- For example, if
n = 7, then the node with the label3has the node with the labelfloor(3 / 2) = 1as its parent, and the node with the label7has the node with the labelfloor(7 / 2) = 3as its parent.
You are also given an integer array queries. Initially, every node has a value 0 on it. For each query queries[i], you should flip all values in the subtree of the node with the label queries[i].
Return the total number of nodes with the value 1 after processing all the queries.
Note that:
- Flipping the value of a node means that the node with the value
0becomes1and vice versa. floor(x)is equivalent to roundingxdown to the nearest integer.
Example 1:
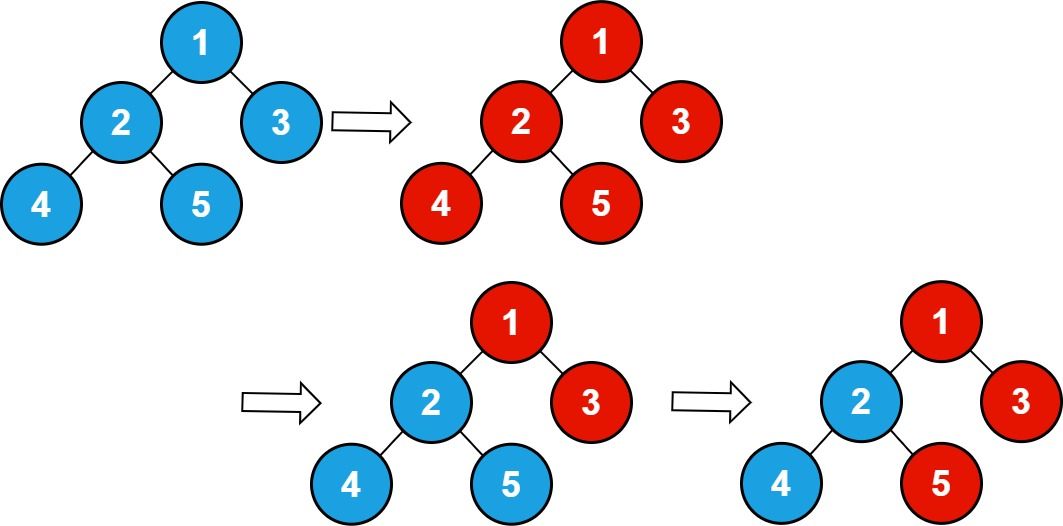
Input: n = 5 , queries = [1,2,5] Output: 3 Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree structure and its status after performing the queries. The blue node represents the value 0, and the red node represents the value 1. After processing the queries, there are three red nodes (nodes with value 1): 1, 3, and 5.
Example 2:
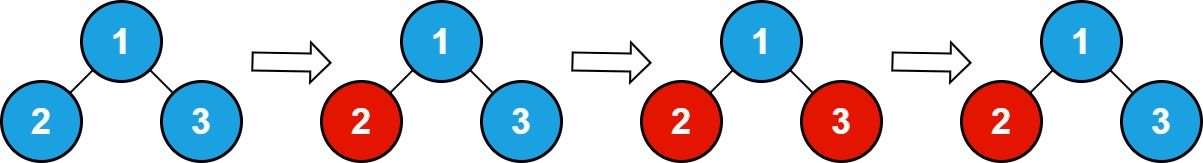
Input: n = 3, queries = [2,3,3] Output: 1 Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree structure and its status after performing the queries. The blue node represents the value 0, and the red node represents the value 1. After processing the queries, there are one red node (node with value 1): 2.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1051 <= queries.length <= 1051 <= queries[i] <= n
class Solution:
def numberOfNodes(self, n: int, queries: List[int]) -> int:
def dfs(i):
if i > n:
return
tree[i] ^= 1
dfs(i << 1)
dfs(i << 1 | 1)
tree = [0] * (n + 1)
cnt = Counter(queries)
for i, v in cnt.items():
if v & 1:
dfs(i)
return sum(tree)class Solution {
private int[] tree;
public int numberOfNodes(int n, int[] queries) {
tree = new int[n + 1];
int[] cnt = new int[n + 1];
for (int v : queries) {
++cnt[v];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i) {
if (cnt[i] % 2 == 1) {
dfs(i);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i) {
ans += tree[i];
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i) {
if (i >= tree.length) {
return;
}
tree[i] ^= 1;
dfs(i << 1);
dfs(i << 1 | 1);
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numberOfNodes(int n, vector<int>& queries) {
vector<int> tree(n + 1);
vector<int> cnt(n + 1);
for (int v : queries) ++cnt[v];
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (i > n) return;
tree[i] ^= 1;
dfs(i << 1);
dfs(i << 1 | 1);
};
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i) {
if (cnt[i] & 1) {
dfs(i);
}
}
return accumulate(tree.begin(), tree.end(), 0);
}
};func numberOfNodes(n int, queries []int) int {
tree := make([]int, n+1)
cnt := make([]int, n+1)
for _, v := range queries {
cnt[v]++
}
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(i int) {
if i > n {
return
}
tree[i] ^= 1
dfs(i << 1)
dfs(i<<1 | 1)
}
for i, v := range cnt {
if v%2 == 1 {
dfs(i)
}
}
ans := 0
for _, v := range tree {
ans += v
}
return ans
}