There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n and n - 1 edges. You are given the integer n. The parent node of a node with a label v is the node with the label floor (v / 2). The root of the tree is the node with the label 1.
- For example, if
n = 7, then the node with the label3has the node with the labelfloor(3 / 2) = 1as its parent, and the node with the label7has the node with the labelfloor(7 / 2) = 3as its parent.
You are also given an integer array queries. Initially, every node has a value 0 on it. For each query queries[i], you should flip all values in the subtree of the node with the label queries[i].
Return the total number of nodes with the value 1 after processing all the queries.
Note that:
- Flipping the value of a node means that the node with the value
0becomes1and vice versa. floor(x)is equivalent to roundingxdown to the nearest integer.
Example 1:
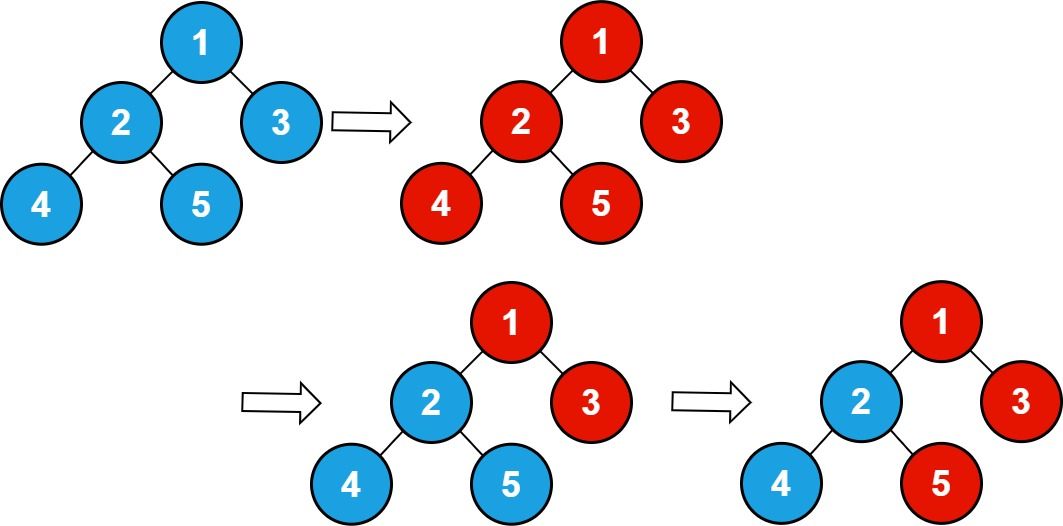
Input: n = 5 , queries = [1,2,5] Output: 3 Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree structure and its status after performing the queries. The blue node represents the value 0, and the red node represents the value 1. After processing the queries, there are three red nodes (nodes with value 1): 1, 3, and 5.
Example 2:
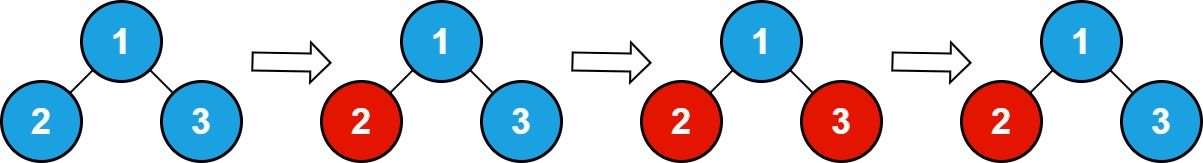
Input: n = 3, queries = [2,3,3] Output: 1 Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree structure and its status after performing the queries. The blue node represents the value 0, and the red node represents the value 1. After processing the queries, there are one red node (node with value 1): 2.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1051 <= queries.length <= 1051 <= queries[i] <= n
方法一:模拟
根据题意,我们可以模拟每次查询的过程,即将查询节点及其子树的节点值反转。最后统计节点值为 1 的节点个数即可。
这里有一个优化点,每个节点及其对应的子树,如果经过了偶数次查询,那么节点值不会发生变化,因此我们可以记录每个节点的查询次数,对于奇数次查询的节点及其子树,才进行反转。
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def numberOfNodes(self, n: int, queries: List[int]) -> int:
def dfs(i):
if i > n:
return
tree[i] ^= 1
dfs(i << 1)
dfs(i << 1 | 1)
tree = [0] * (n + 1)
cnt = Counter(queries)
for i, v in cnt.items():
if v & 1:
dfs(i)
return sum(tree)class Solution {
private int[] tree;
public int numberOfNodes(int n, int[] queries) {
tree = new int[n + 1];
int[] cnt = new int[n + 1];
for (int v : queries) {
++cnt[v];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i) {
if (cnt[i] % 2 == 1) {
dfs(i);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i) {
ans += tree[i];
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i) {
if (i >= tree.length) {
return;
}
tree[i] ^= 1;
dfs(i << 1);
dfs(i << 1 | 1);
}
}class Solution {
public:
int numberOfNodes(int n, vector<int>& queries) {
vector<int> tree(n + 1);
vector<int> cnt(n + 1);
for (int v : queries) ++cnt[v];
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int i) {
if (i > n) return;
tree[i] ^= 1;
dfs(i << 1);
dfs(i << 1 | 1);
};
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i) {
if (cnt[i] & 1) {
dfs(i);
}
}
return accumulate(tree.begin(), tree.end(), 0);
}
};func numberOfNodes(n int, queries []int) int {
tree := make([]int, n+1)
cnt := make([]int, n+1)
for _, v := range queries {
cnt[v]++
}
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(i int) {
if i > n {
return
}
tree[i] ^= 1
dfs(i << 1)
dfs(i<<1 | 1)
}
for i, v := range cnt {
if v%2 == 1 {
dfs(i)
}
}
ans := 0
for _, v := range tree {
ans += v
}
return ans
}