The diameter of a tree is the number of edges in the longest path in that tree.
There is an undirected tree of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given a 2D array edges where edges.length == n - 1 and edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return the diameter of the tree.
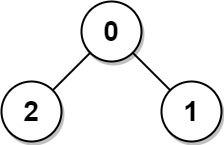
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: The longest path of the tree is the path 1 - 0 - 2.
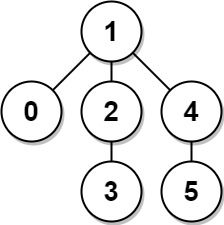
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,4],[4,5]] Output: 4 Explanation: The longest path of the tree is the path 3 - 2 - 1 - 4 - 5.
Constraints:
n == edges.length + 11 <= n <= 1040 <= ai, bi < nai != bi
class Solution:
def treeDiameter(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(u, t):
nonlocal ans, vis, d, next
if vis[u]:
return
vis[u] = True
for v in d[u]:
dfs(v, t + 1)
if ans < t:
ans = t
next = u
d = defaultdict(set)
vis = [False] * (len(edges) + 1)
for u, v in edges:
d[u].add(v)
d[v].add(u)
ans = 0
next = 0
dfs(edges[0][0], 0)
vis = [False] * (len(edges) + 1)
dfs(next, 0)
return ansclass Solution {
private Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> g;
private boolean[] vis;
private int next;
private int ans;
public int treeDiameter(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length;
ans = 0;
g = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] e : edges) {
g.computeIfAbsent(e[0], k -> new HashSet<>()).add(e[1]);
g.computeIfAbsent(e[1], k -> new HashSet<>()).add(e[0]);
}
vis = new boolean[n + 1];
next = edges[0][0];
dfs(next, 0);
vis = new boolean[n + 1];
dfs(next, 0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int u, int t) {
if (vis[u]) {
return;
}
vis[u] = true;
if (ans < t) {
ans = t;
next = u;
}
for (int v : g.get(u)) {
dfs(v, t + 1);
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, unordered_set<int>> g;
vector<bool> vis;
int ans;
int next;
int treeDiameter(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].insert(e[1]);
g[e[1]].insert(e[0]);
}
int n = edges.size();
ans = 0;
vis.resize(n + 1);
next = edges[0][0];
dfs(next, 0);
vis.assign(vis.size(), false);
dfs(next, 0);
return ans;
}
void dfs(int u, int t) {
if (vis[u]) return;
vis[u] = true;
if (ans < t) {
ans = t;
next = u;
}
for (int v : g[u]) dfs(v, t + 1);
}
};func treeDiameter(edges [][]int) int {
n := len(edges)
g := make(map[int][]int)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])
g[e[1]] = append(g[e[1]], e[0])
}
vis := make(map[int]bool, n+1)
ans := 0
next := edges[0][0]
var dfs func(u, t int)
dfs = func(u, t int) {
if vis[u] {
return
}
vis[u] = true
if ans < t {
ans = t
next = u
}
if vs, ok := g[u]; ok {
for _, v := range vs {
dfs(v, t+1)
}
}
}
dfs(next, 0)
vis = make(map[int]bool, n+1)
dfs(next, 0)
return ans
}