Open-source LoRaWAN Server that integrates both the network-server and the application-server. This is useful for application providers that operate their own LoRa network, or for device and application developers.
The server:
- Implements the LoRaWAN Specification v1.0.1
- Communicates with (any number of) remote LoRaWAN gateways. It currently supports:
- All gateways based on the Packet Forwarder, such as the Semtech LoRa demo kit, LoRa Lite Gateway, LORANK-8, or MultiConnect Conduit.
- Performs all required encryption and integrity checks.
- Supports relaxed frame-counter check for simple ABP devices.
- Invokes internal modules with application logic. It provides examples for:
- Invokes external applications. It currently supports connections via:
- WebSocket protocol RFC6455
- MQTT v3.1/v3.1.1, including applications hosted in Amazon AWS IoT, IBM Watson IoT Platform, MathWorks ThingSpeak, Microsoft Azure IoT Hub or Adafruit IO
- Handles (any number of) Class A or Class C devices.
- Supports both the node activation by personalization (ABP) and the over-the-air activation (OTAA).
- Supports both unconfirmed and confirmed data uplink and downlink.
- Supports multicast to user-defined groups.
- Supports EU 863-870, US 902-928, CN 779-787, EU 433, AU 915-928, CN 470-510 and KR 920-923 band.
- Provides a network management interface.
- Displays device battery and connectivity status.
- Supports both manual and automatic configuration of TX power and data rate (ADR).
- Runs on all major operating systems, including Windows, Linux, OS X and Solaris, even on embedded systems like OpenWrt or in a Docker container.
- Does not crash as it's implemented in Erlang, which is designed for building fault-tolerant systems.
- Is free, distributed under the MIT license.
The server aims to be an all-in-one software package for small private LoRa networks. However:
- You still need to buy your LoRaWAN Gateway.
- You will need to deploy and maintain it yourself. (With my support.)
- It will probably never support the sophisticated management features of the commercial-grade network-servers.
The maximum amount of gateways, devices and nodes the server can support depends on the server load and hardware performance. There are no hard limits.
The API may change and some functions may not be implemented. To ask questions or request features please join the lorawan-server mailing list. We will gladly assist you. If you find a bug, you may also add an Issue.
The lorawan-server includes all functions required to run a private LoRa network. It integrates your LoRaWAN network directly with your backend IT systems. The server is provided as a comprehensive package with a single configuration file and a single administration tool. You only need to install the Erlang/OTP 19 or later.
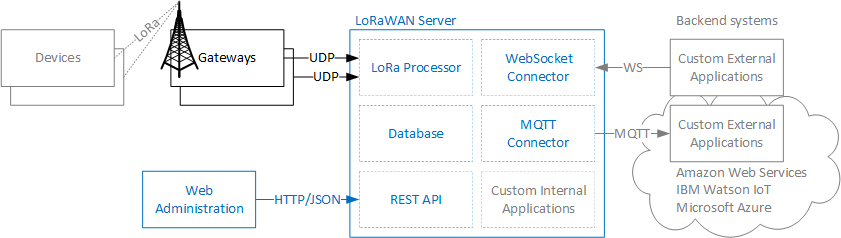
The main components of the lorawan-server are shown in the following figure:
The server behaviour is described in the Communication Guide.
The Installation Instructions describe how to build, install and configure the server. You can use a Debian package, download the binary release and run it manually or build the server from source codes.
Run the lorawan-server release by:
cd lorawan-server
bin/lorawan-serverDon't forget to set the server address and port (by default 1680) in the LoRaWAN gateways you want to use with the server.
You can terminate the lorawan-server by:
bin/lorawanctl stopYou can administrate and manage the server via a set of web-pages or via a REST API as described in the Administration Guide and in the Adaptive Data Rate (ADR) Guide.
By default you can access the administration at http://server:8080, using "admin" as both username and password. After the installation you have to:
- Add LoRaWAN gateways you want to use.
- Configure each device you want to use, either as a personalized device (ABP) or as an over-the-air activated (OTAA) device.
You can integrate lorawan-server with external applications using the WebSocket interface as described in the WebSocket Guide, or using MQTT as described in the Backend Administration. Instructions on how to integrate with some major clouds such as AWS or Azure are provided in the Integration Guide.
You can also use the internal web server and develop internal applications, which may offer custom REST APIs. The lorawan-server is designed to be highly extensible. I encourage you to Learn You Some Erlang and develop your own modules.
To implement an internal application you need to create a new module implementing the
lorawan_application behaviour as described in the
Custom Application Guide and Development Guide.
If the server doesn't do what you expect, please review the server logs and consult the Troubleshooting Instructions for the most common problems.
If the problem persists, please verify you have the latest version. I recommend to always use the latest release. If you use the latest sources, please verify the "build" icon above is green and then try upgrading by running:
cd lorawan-server
git pull
make upgrade
make releaseIf the "build" icon above is red, please wait few minutes (or hours) until it gets green again.
If nothing helps, please contact the lorawan-server mailing list or review the existing issues to verify the problem was not already reported and then create new issue.
The server is used (both commercially and non-commercially) by various companies and institutions. It was mentioned by the following blogs and articles:
- Three reasons for creating an Open Source LoRaWan server
- LoraWAN server running on OpenWrt/LEDE
- Espruino RN2483 LoRa Modules
Please let me know if you use the lorawan-server and want to be listed here.
The lorawan-server is distributed under the terms of the MIT License. See the LICENSE.
Copyright (c) 2016-2017 Petr Gotthard
 KMLE is working on the challenge of
helping customers optimize the way they work by digitizing the workplace
and their workflows.
KMLE is working on the challenge of
helping customers optimize the way they work by digitizing the workplace
and their workflows.