The tidycat package includes the tidy_categorical() function to
expand broom::tidy() outputs for categorical parameter estimates.
See the pkgdown site for full details.
You can install the released version of tidycat from CRAN with:
install.packages("tidycat")And the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("guyabel/tidycat")The tidy_categorical() function will probably not work as expected for
non-default contrasts such as contr.helmert() and when one or more
model parameters are rank deficient. It also only supports a limited
range of models; lm() or glm() should be fine. For more complex
cases, or an alternative method to create great coefficient plots, see
the
ggcoef_model()
function in the ggstats
package, which went through a major upgrade around the same time as I
developed tidycat.
For full documentation, see the package vignette: The tidycat package: expand broom::tidy() output for categorical parameter estimates
The tidy() function in the broom package takes the messy output of
built-in functions in R, such as lm(), and turns them into tidy data
frames.
library(dplyr)
library(broom)
m1 <- mtcars %>%
mutate(transmission = recode_factor(am, `0` = "automatic", `1` = "manual")) %>%
lm(mpg ~ as.factor(cyl) + transmission + wt * as.factor(cyl), data = .)
tidy(m1)
#> # A tibble: 7 × 5
#> term estimate std.error statistic p.value
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 (Intercept) 41.5 4.54 9.14 0.00000000190
#> 2 as.factor(cyl)6 -8.66 10.4 -0.836 0.411
#> 3 as.factor(cyl)8 -16.9 5.27 -3.20 0.00374
#> 4 transmissionmanual -0.902 1.51 -0.595 0.557
#> 5 wt -6.19 1.65 -3.75 0.000937
#> 6 as.factor(cyl)6:wt 2.12 3.40 0.625 0.538
#> 7 as.factor(cyl)8:wt 3.84 1.77 2.17 0.0399The tidy_categorical() function adds
- further columns (
variable,levelandeffect) to thebroom::tidy()output to help manage categorical variables - further rows for reference category terms and a column to indicate
their location (
reference) when settinginclude_reference = TRUE(default)
It requires two inputs
- a data frame
dof parameter estimates from a model frombroom::tidy() - the corresponding model object
mpassed tobroom::tidy()
For example:
library(tidycat)
d1 <- m1 %>%
tidy(conf.int = TRUE) %>%
tidy_categorical(m = m1)
d1 %>%
select(-(3:5))
#> # A tibble: 10 × 8
#> term estimate conf.low conf.high variable level effect refer…¹
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <fct> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 (Intercept) 41.5 32.1 50.8 (Interce… (Int… main Non-Ba…
#> 2 <NA> 0 0 0 as.facto… 4 main Baseli…
#> 3 as.factor(cyl)6 -8.66 -30.0 12.7 as.facto… 6 main Non-Ba…
#> 4 as.factor(cyl)8 -16.9 -27.7 -6.00 as.facto… 8 main Non-Ba…
#> 5 <NA> 0 0 0 transmis… auto… main Baseli…
#> 6 transmissionmanual -0.902 -4.02 2.22 transmis… manu… main Non-Ba…
#> 7 wt -6.19 -9.59 -2.79 wt wt main Non-Ba…
#> 8 <NA> 0 0 0 as.facto… 4 inter… Baseli…
#> 9 as.factor(cyl)6:wt 2.12 -4.87 9.12 as.facto… 6 inter… Non-Ba…
#> 10 as.factor(cyl)8:wt 3.84 0.192 7.50 as.facto… 8 inter… Non-Ba…
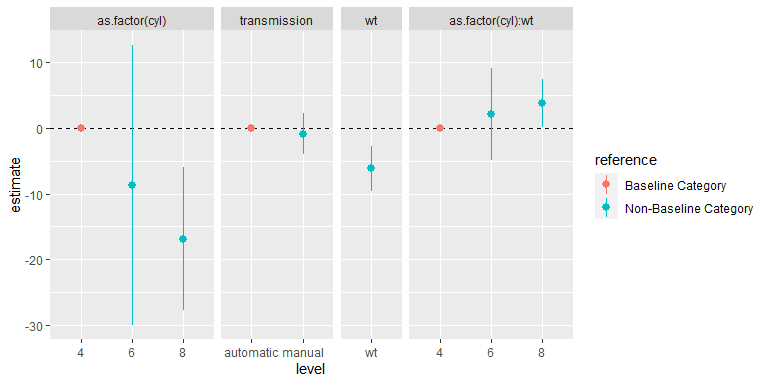
#> # … with abbreviated variable name ¹referenceThe expanded data frame from tidy_categorical() of parameter estimates
can be particularly useful for creating coefficient plots, allowing:
- grouping terms from the same categorical variable from the additional columns.
- inclusion of reference categories in a coefficient plot from the additional rows, allowing the reader to better grasp the meaning of the parameter estimates in each categorical variable.
For example:
library(forcats)
library(ggplot2)
library(ggforce)
d1 %>%
slice(-1) %>%
mutate(variable = fct_inorder(variable)) %>%
ggplot(mapping = aes(x = level, y = estimate, colour = reference,
ymin = conf.low, ymax = conf.high)) +
facet_row(facets = "variable", scales = "free_x", space = "free") +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0, linetype = "dashed") +
geom_pointrange()