Fortinet FortiManager Address, Group and Package Update (AGPU) module for Consul Terraform Sync (CTS)
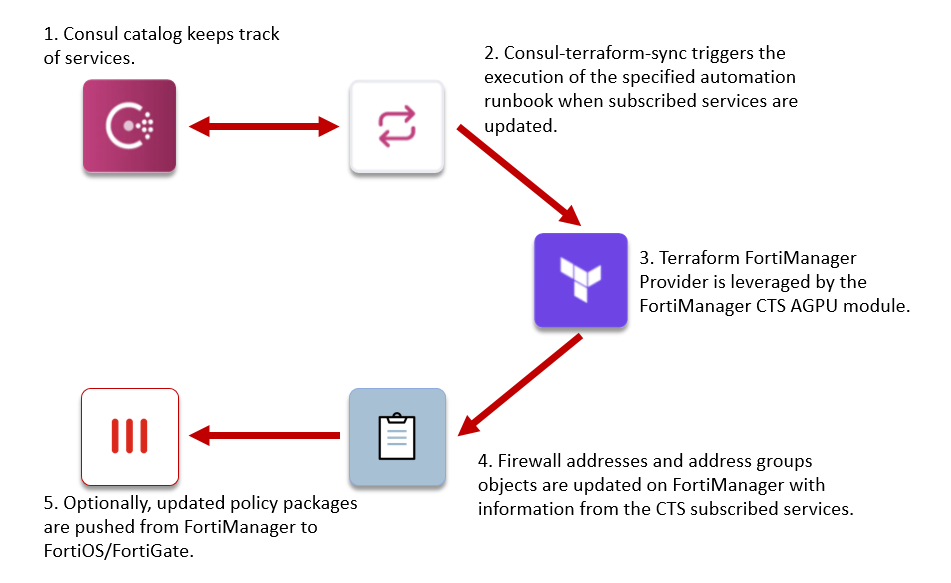
This Terraform module connects to FortiManager and creates Firewall addresses for each Consul service and updates address groups based on service names. Each address group will include all firewall addresses with the service names in variable addrgrp_name_map. Using the module in automation with Consul Terraform Sync will dynamically add or remove service instances from the address group based on Consul service discovery.
This way FortiManager will be configured with the dynamically learned services IP addresses and push them to the managed FortiOS/FortiGate devices, thus allowing FortiOS/FortiGate to implement Firewall policies based on dynamically learned service information.
Using this Terraform module in conjunction with consul-terraform-sync enables teams to reduce manual ticketing processes and automate Day-2 operations related to application scale up/down in a way that is both declarative and repeatable across the organization and across multiple FortiManager and their managed FortiOS/FortiGate devices.
The module dynamically creates, updates, and deletes Firewall address and address group based on service id and address.
Firewall address groups will be created based on the keys of variable addrgrp_name_map. The argument of member will be modified based on the services that each address group name is mapped to. Argument member will be set to none if all mapped services are removed. All address groups will never be deleted to avoid potential error that would occur when the address groups are referenced by other resources.
If install_package is set to Yes, once there are some changes on services, the module will update the relevant firewall addresses and address groups and then trigger FortiManager to install the policy package automatically into the Installation Targets.
If there is a missing feature or a bug - - open an issue
The consul-terraform-sync runs as a daemon that enables a publisher-subscriber paradigm between Consul and FortiManager based devices to support Network Infrastructure Automation (NIA).
-
consul-terraform-sync subscribes to updates from the Consul catalog and executes one or more automation "tasks" with appropriate value of service variables based on those updates. consul-terraform-sync leverages Terraform as the underlying automation tool and utilizes the Terraform provider ecosystem to drive relevant change to the network infrastructure.
-
Each task consists of a runbook automation written as a compatible Terraform module using resources and data sources for the underlying network infrastructure provider.
Please refer to this link for getting started with consul-terraform-sync
-
Install Consul and run a consul client. Please refer to this Consul CLI Quick Start
-
Install consul-terraform-sync. Please refer to this Install Consul-Terraform-Sync
-
In FortiManager, no address group should exist with the same names as specified in variable
addrgrp_name_map -
Firewall address
noneshould exists and be configured with0.0.0.0/32 -
If policy package installation is to be automatically performed, FortiManager needs to be managing the Installation Targets
| Ecosystem | Version |
|---|---|
| consul | >= 1.7 |
| consul-terraform-sync | >= 0.1.0 |
| terraform | >= 0.14 |
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| fortinetdev/fortimanager | >= 1.3.5 |
This module is meant for use with consul-terraform-sync >= 0.1.0 and Terraform >= 0.14 and fortimanager provider versions >= 1.3.5
-> The maximum number of supported address group member depends on the model of the managed FortiGate and version of FortiOS. The maximum address group member each address group will support can be validated on the FortiOS maximum values document under the firewall.addrgrp:member object.
In order to use this module, you will need to install consul-terraform-sync, create a "task" with this Terraform module as a source within the task, and run consul-terraform-sync.
The users can subscribe to the services in the consul catalog and define the Terraform module which will be executed when there are any updates to the subscribed services using a "task".
~> Note: It is recommended to have the consul-terraform-sync config guide for reference.
-
Download the consul-terraform-sync on a node which is highly available (prefrably, a node running a consul client)
-
Add consul-terraform-sync to the PATH on that node
-
Check the installation
$ consul-terraform-sync --version consul-terraform-sync v0.1.1 (4dc13b5) Compatible with Terraform >= 0.13.0, < 0.15 -
Create a config file <YOUR_CONFIG>.hcl, and a variable file <YOUR_VARIABLE>.tfvars if needed. Please note that this just an example.
task.hcl
log_level = "info" consul { address = <Consul agent address> # e.g. "localhost:8500" } driver "terraform" { log = true version = "0.14.0" required_providers { fortimanager = { source = "fortinetdev/fortimanager" } } } terraform_provider "fortimanager" { hostname = <FortiManager address> insecure = "true" username = <Your username> # Your FortiManager device username password = <Your password> # Your FortiManager device password scopetype = <Your scopetype> # Scope of application of those resources managed by the provider. Default value is adom. adom = <Your adom> # Adom of the resources managed by the provider. Valid only when the scopetype set to adom. Default value is root. } task { name = <Task name> # "CTS-test" description = <Description of the task> #"Dynamic manage FortiManager Firewall address and address group by Consul_Terraform_Sync" source = "github.com/fortinetdev/terraform-fortimanager-cts-agpu" # to be updated providers = ["fortimanager"] services = <List of services> # e.g. ["finance_workstations", "windows10", "windows11"] variable_files = <List of variable files for this module with full path> # e.g. ["/opt/fmg-consul/consul_test.tfvars"] }
consul_test.tfvars
package="<YOUR_PACKAGE_NAME>" install_package="No" addrgrp_name_map = { "<Address group name 1>" : <List of services>, # e.g. "cts-finance" : ["finance_workstations"], "<Address group name 2>" : <List of services> # e.g. "cts-windows" : ["windows10", "windows11"] } -
Start consul-terraform-sync
$ consul-terraform-sync -config-file <YOUR CONFIG>.hclFor example:
$ consul-terraform-sync -config-file tasks.hcl
consul-terraform-sync is now subscribed to the Consul catalog. Any updates to the services identified in the task will result in updating the service groups in the FortiManager device
~> Note: If you are interested in how consul-terraform-sync works, please refer to this section.
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required | Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| addrname_prefix | Prefix added to each address name | string |
"" | No | N/A |
| addrname_sufix | Sufix added to each address name | string |
"" | No | N/A |
| net_mask | Net mask for firewall address | string |
"255.255.255.255" | No | N/A |
| package | Package name for target device | string |
"default" | Yes | N/A |
| scopetype | The scope of application of the resource | string |
"inherit" | No | inherit: The scopetype of the provider will be inherited, and adom will also be inherited;global: Set the scope of application of resources to global;adom: Set the scope of application of resources to adom; |
| adom | ADOM name | string |
"root" | Yes | N/A |
| install_package | Flag of whether install package to device automatically | string |
"No" | Yes | Yes: Install package to device when services are changed;No: Do not install package to device; |
| addrgrp_name_map | Map of Firewall Address Group name to services | string |
N/A | Yes | N/A |
| services | Consul services monitored by consul-terraform-sync | map( |
N/A | Yes | N/A |
There are 2 aspects of consul-terraform-sync.
-
Updates from Consul catalog: In the backend, consul-terraform-sync creates a blocking API query session with the Consul agent indentified in the config to get updates from the Consul catalog. Consul-terraform-sync will get an update for the services in the consul catalog when any of the following service attributes are created, updated or deleted. These updates include service creation and deletion as well.
- service id
- service name
- service kind
- service address
- service port
- service meta
- service tags
- service namespace
- service status
- node
- node id
- node address
- node datacenter
- node tagged addresses
- node meta
- cts_user_defined_meta
-
Managing the entire Terraform workflow: If a task is defined, one or more services are associated with the task, provider is declared in the task and a Terraform module is specified using the source field of the task, the following sequence of events will occur:
- consul-terraform-sync will install the required version of Terraform.
- consul-terraform-sync will install the required version of the Terraform provider defined in the config file and declared in the "task".
- A new directory "sync-tasks" with a sub-directory corresponding to each "task" will be created. This is the reason for having strict guidelines around naming.
- Each sub-directory corresponds to a separate Terraform workspace.
- Within each sub-directory corresponding a task, consul-terraform-sync will template a main.tf, variables.tf, variables.module.tf, terraform.tfvars, provider.tfvars, and terraform.tfvars.tmpl.
-
main.tf:
- This file contains declaration for the required terraform and provider versions based on the task definition.
- In addition, this file has the module (identified by the 'source' field in the task) declaration with the input variables
- Consul K/V is used as the backend state for this Terraform workspace.
Example generated main.tf file:
# This file is generated by Consul Terraform Sync. # # The HCL blocks, arguments, variables, and values are derived from the # operator configuration for Sync. Any manual changes to this file # may not be preserved and could be overwritten by a subsequent update. # # Task: CTS-test # Description: Consul_Terraform_Sync test for FMG terraform { required_version = ">= 0.13.0, < 0.15" required_providers { fortimanager = { source = "fortinetdev/fortimanager" } } backend "consul" { address = "localhost:8500" gzip = true path = "consul-terraform-sync/terraform" } } provider "fortimanager" { adom = var.fortimanager.adom hostname = var.fortimanager.hostname insecure = var.fortimanager.insecure password = var.fortimanager.password scopetype = var.fortimanager.scopetype username = var.fortimanager.username } # Consul_Terraform_Sync test for FMG module "CTS-test" { source = "fortinetdev/cts-agpu/fortimanager" services = var.services addrgrp_name_map = var.addrgrp_name_map install_package = var.install_package package = var.package }
-
variables.tf:
- This is
variables.tffile defined in the module.
Example generated
variables.tffile:# This file is generated by Consul Terraform Sync. # # The HCL blocks, arguments, variables, and values are derived from the # operator configuration for Sync. Any manual changes to this file # may not be preserved and could be overwritten by a subsequent update. # # Task: CTS-test # Description: Consul_Terraform_Sync test for FMG # Service definition protocol v0 variable "services" { description = "Consul services monitored by Consul Terraform Sync" type = map( object({ id = string name = string kind = string address = string port = number meta = map(string) tags = list(string) namespace = string status = string node = string node_id = string node_address = string node_datacenter = string node_tagged_addresses = map(string) node_meta = map(string) cts_user_defined_meta = map(string) }) ) } variable "fortimanager" { default = null description = "Configuration object for fortimanager" sensitive = true type = object({ adom = string hostname = string insecure = string password = string scopetype = string username = string }) }
- This is
-
variables.module.tf:
- This is
variables.module.tffile defined in the module.
Example generated
variables.module.tffile:# This file is generated by Consul Terraform Sync. # # The HCL blocks, arguments, variables, and values are derived from the # operator configuration for Sync. Any manual changes to this file # may not be preserved and could be overwritten by a subsequent update. # # Task: CTS-test # Description: Consul_Terraform_Sync test for FMG variable "addrgrp_name_map" { default = null type = object({ cts-finance = tuple([string]) cts-windows = tuple([string, string]) }) } variable "install_package" { default = null type = string } variable "package" { default = null type = string }
- This is
-
terraform.tfvars:
- This is the most important file generated by consul-terraform-sync.
- This variables file is generated with the most updated values from Consul catalog for all the services identified in the task.
- consul-terraform-sync updates this file with the latest values when the corresponding service gets updated in Consul catalog.
Example terraform.tfvars file:
# This file is generated by Consul Terraform Sync. # # The HCL blocks, arguments, variables, and values are derived from the # operator configuration for Sync. Any manual changes to this file # may not be preserved and could be overwritten by a subsequent update. # # Task: CTS-test # Description: Consul_Terraform_Sync test for FMG services = { "finance_workstations-1.xing-virtual-machine.dc1" : { id = "finance_workstations-1" name = "finance_workstations" kind = "" address = "192.168.5.11" port = 0 meta = {} tags = [] namespace = null status = "passing" node = "xing-virtual-machine" node_id = "71043c58-114a-1422-d459-61935d186aea" node_address = "127.0.0.1" node_datacenter = "dc1" node_tagged_addresses = { lan = "127.0.0.1" lan_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1" wan = "127.0.0.1" wan_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1" } node_meta = { consul-network-segment = "" } cts_user_defined_meta = {} }, "finance_workstations-2.xing-virtual-machine.dc1" : { id = "finance_workstations-2" name = "finance_workstations" kind = "" address = "192.168.5.12" port = 0 meta = {} tags = [] namespace = null status = "passing" node = "xing-virtual-machine" node_id = "71043c58-114a-1422-d459-61935d186aea" node_address = "127.0.0.1" node_datacenter = "dc1" node_tagged_addresses = { lan = "127.0.0.1" lan_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1" wan = "127.0.0.1" wan_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1" } node_meta = { consul-network-segment = "" } cts_user_defined_meta = {} }, "windows10-1.xing-virtual-machine.dc1" : { id = "windows10-1" name = "windows10" kind = "" address = "192.168.6.11" port = 0 meta = {} tags = [] namespace = null status = "passing" node = "xing-virtual-machine" node_id = "71043c58-114a-1422-d459-61935d186aea" node_address = "127.0.0.1" node_datacenter = "dc1" node_tagged_addresses = { lan = "127.0.0.1" lan_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1" wan = "127.0.0.1" wan_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1" } node_meta = { consul-network-segment = "" } cts_user_defined_meta = {} }, "windows11-1.xing-virtual-machine.dc1" : { id = "windows11-1" name = "windows11" kind = "" address = "192.168.7.11" port = 0 meta = {} tags = [] namespace = null status = "passing" node = "xing-virtual-machine" node_id = "71043c58-114a-1422-d459-61935d186aea" node_address = "127.0.0.1" node_datacenter = "dc1" node_tagged_addresses = { lan = "127.0.0.1" lan_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1" wan = "127.0.0.1" wan_ipv4 = "127.0.0.1" } node_meta = { consul-network-segment = "" } cts_user_defined_meta = {} } }
-
providers.tfvars:
- This variables file is generated with the configurations from user.
Example providers.tfvars file:
# This file is generated by Consul Terraform Sync. # # The HCL blocks, arguments, variables, and values are derived from the # operator configuration for Sync. Any manual changes to this file # may not be preserved and could be overwritten by a subsequent update. # # Task: CTS-test # Description: Consul_Terraform_Sync test for FMG fortimanager = { adom = "<Your adom>" hostname = "<Your hostname or IP>" insecure = "true" password = "<Your password>" scopetype = "<Your scopetype>" username = "<Your username>" }
-
terraform.tfvars.tmpl:
- This file is generated with the configurations from user.
Example terraform.tfvars.tmpl file:
# This file is generated by Consul Terraform Sync. # # The HCL blocks, arguments, variables, and values are derived from the # operator configuration for Sync. Any manual changes to this file # may not be preserved and could be overwritten by a subsequent update. # # Task: CTS-test # Description: Consul_Terraform_Sync test for FMG services = { {{- with $srv := service "finance_workstations" }} {{- $last := len $srv | subtract 1}} {{- range $i, $s := $srv}} "{{ joinStrings "." .ID .Node .Namespace .NodeDatacenter }}" : { {{ HCLService $s | indent 4 }} } {{- if (ne $i $last)}},{{end}} {{- end}} {{- end}}{{- with $beforeSrv := service "finance_workstations" }} {{- with $afterSrv := service "windows10" }},{{end}} {{- end}} {{- with $srv := service "windows10" }} {{- $last := len $srv | subtract 1}} {{- range $i, $s := $srv}} "{{ joinStrings "." .ID .Node .Namespace .NodeDatacenter }}" : { {{ HCLService $s | indent 4 }} } {{- if (ne $i $last)}},{{end}} {{- end}} {{- end}}{{- with $beforeSrv := service "windows10" }} {{- with $afterSrv := service "windows11" }},{{end}} {{- end}} {{- with $srv := service "windows11" }} {{- $last := len $srv | subtract 1}} {{- range $i, $s := $srv}} "{{ joinStrings "." .ID .Node .Namespace .NodeDatacenter }}" : { {{ HCLService $s | indent 4 }} } {{- if (ne $i $last)}},{{end}} {{- end}} {{- end}} }
-
Network Infrastructure Automation (NIA) compatible modules are built to utilize the above service variables
-
- consul-terraform-sync manages the entire Terraform workflow of plan, apply and destroy for all the individual workspaces corresponding to the defined "tasks" based on the updates to the services for those tasks.
In summary, consul-terraform-sync triggers a Terraform workflow (plan, apply, destroy) based on updates it detects from Consul catalog.