-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Browse files
Browse the repository at this point in the history
* [Item62] 다른 타입이 적절하다면 문자열 사용을 피하라 * [Item67] 최적화는 신중히 하라
- Loading branch information
1 parent
99bdc4c
commit 77f66ad
Showing
2 changed files
with
210 additions
and
0 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,152 @@ | ||
|
|
||
| ### 문자열은 다른 타입을 대신하기 부적절 | ||
|
|
||
| - 입력받을 데이터가 진짜 문자열인 경우에만 사용하는것이 좋다. | ||
| - 적절한 타입이 있다면 그것을 사용하고 없다면 새로운 타입을 하나 만들어서 사용하자. | ||
| - 되도록이면, 문자열 사용을 피하자. | ||
| - 문자열은 실수의 가능성이 있음. (오타가 있어도 컴파일러가 확인할 방법이 없음) | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| public static final int APPLE_FUJI = 0; | ||
| public static final int APPLE_PIPPIN = 1; | ||
| public static final int APPLE_GRANNY_SMITH = 2; | ||
|
|
||
| public static final int ORANGE_NAVEL = 0; | ||
| public static final int ORANGE_TEMPLE = 1; | ||
| public static final int ORANGE_BLOOD = 2; | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| - 타입의 안전성을 보장할 수 없으며 접두어를 사용하여 이름 충돌을 방지 | ||
| - 프로그램이 깨지기 쉽다. | ||
| - 평범한 상수를 나열한 것뿐이라 컴파일하면 그 값이 클라이언트(API가 적용된 클래스: 코드, 프로그램) 파일에 그대로 새겨진다. | ||
| - 즉, API의 상수 값이 바뀌면 클라이언트도 재컴파일을 해야만 한다. | ||
| - 정수 상수는 문자열로 출력하기 까다롭다 | ||
| - 상수의 의미를 출력하는 것은 좋지만 이를 하드 코딩 해야한다는 점 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 열거 타입 사용하기 | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| public enum Apple { FUJI, PIPPIN, GRANNY_SMITH } | ||
| public enum Orange { NAVEL, TEMPLE, BLOOD } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## 문자열은 혼합 타입을 대신하기에 적합하지 않다. | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| String compoundKey = className + "#" + i.next(); | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| - className, i.next() 에서 "#" 이 쓰이면 혼란스러울 것 | ||
| - String과 String을 더하는 행위는 메모리 할당과 해제를 발생시키며, 매번 파싱해야 하는 문제(문자열 연결은 느리니 주의하라), 또한 equals, toString, CompareTo 를 사용할 수 없고, String Class 가 제공하는 메서드만 사용해야 한다. | ||
| - 차라리 두 요소를 병합해서 관리하는 클래스를 만드는 것이 낫다. | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| public class studyInfo { | ||
| private String team; | ||
| private int itemNum; | ||
| private static class compoundKey{ | ||
| private String team; | ||
| private int itemNum; | ||
|
|
||
| public compoundKey(String team, int itemNum) { | ||
| this.team = team; | ||
| this.itemNum = itemNum; | ||
| } | ||
| public studyInfo compound(){ | ||
| return new studyInfo(this); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| private studyInfo(compoundKey compoundKey){ | ||
| team = compoundKey.team; | ||
| itemNum = compoundKey.itemNum; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public static void main(String[] args) { | ||
| ArrayList<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList<>(List.of(60,61,62)); | ||
| Iterator<Integer> i = itemList.iterator(); | ||
|
|
||
| studyInfo student1 = new studyInfo.compoundKey("B팀",i.next()).compound(); | ||
| studyInfo student2 = new studyInfo.compoundKey("A팀",i.next()).compound(); | ||
| studyInfo student3 = new studyInfo.compoundKey("B팀",i.next()).compound(); | ||
|
|
||
| System.out.println("student1: " + student1.team + " 아이템 " + student1.itemNum); | ||
| System.out.println("student2: " + student1.team + " 아이템 " + student2.itemNum); | ||
| System.out.println("student3: " + student1.team + " 아이템 " + student3.itemNum); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 문자열은 권한을 표시하기에 적합하지 않다. | ||
|
|
||
| #### ThreadLocal이란? | ||
|
|
||
| - 일반 변수의 경우 : 수명이 코드 블록 내에서만 가능하다 | ||
| - 스레드 지역 변수 설계 : 각 스레드가 자신만의 변수를 갖게 해주는 기능 | ||
| - 자바2 이전에는 이를 개발자가 직접 설계했고, 클라이언트가 제공한 문자열 키로 지역변수를 식별하기까지 했다. | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| public class ThreadLocal { | ||
| private ThreadLocal() { } | ||
|
|
||
| public static void set(String key, Object value); // 현 스레드의 값을 키로 구분해 저장 | ||
|
|
||
| public static Object get(String key); // (키가 가리키는) 현 스레드의 값을 반환한다 | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| - 스레드 구분용 문자열 키가 전역 이름 공간에서 공유된다는 문제점 | ||
| - 두 클라이언트가 서로 소통하지 못해 같은 키를 쓰기로 결정했다면, 의도하지 않게 같은 변수를 공유하게 된다 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| - 악의적인 클라이언트라면 의도적으로 같은 키를 사용하여 다른 클라이언트의 값을 획득할 수도 있다. | ||
| - 이런 경우에는 String으로 권한을 구분하는 것이 아니라 별도의 타입을 만들어 해결해야 한다. | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| public class ThreadLocal { | ||
| private ThreadLocal() { | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public static class Key { | ||
| Key() { | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public staatic getKey() { | ||
| return Key; | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public static void set(Key key, Object value); | ||
|
|
||
| public static Object get(Key key); | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| - set, get메서드는 정적 메서드일 이유가 없으니 Key 클래스의 인스턴스 메서드로 옮긴다. | ||
| - Key는 더 이상 스레드 지역변수를 구분하기 위한 키가 아니라, 그 자체가 스레드 지역변수가 된다. | ||
| - 결과적으로 지금 톱레벨 클래스인 ThreadLocal은 별달리 하는 일이 없어지므로 치워버리고, 중첩 클래스 Key의 이름을 ThreadLocal로 바꾼다. | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| // Key -> ThreadLocal | ||
| public final class ThreadLocal { | ||
| public ThreadLocal() { | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| public void set(Object value); | ||
|
|
||
| public Object get(); | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| - API에서는 get으로 얻은 Object를 실제 타입으로 형변환해 써야 해서 타입 안전하지 않다. | ||
| - ThreadLocal을 매개변수화 타입으로 선언하여 문제를 해결한다. | ||
| - java.lang.ThreadLocal처럼 구성하여 문자열 기반 API의 문제를 해결 | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| public final class ThreadLocal<T> { | ||
| public ThreadLocal(); | ||
|
|
||
| public void set(T value); | ||
|
|
||
| public T get(); | ||
| } | ||
| ``` |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,58 @@ | ||
| # 최적화는 신중히 하라 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| ### 빠른 프로그램보다는 좋은 프로그램를 작성하라 | ||
|
|
||
| - 성능보다는 구캡슐화가 잘 된, 다른 모듈과 결합성이 낮은 아키텍처를 설계할 것 | ||
| - 성능같은 구현 상의 문제는 나중에 최적화해서 해결할 수 있지만, 아키텍처의 결함은 시스템 전체를 다시 작성하지 않고는 해결하기 불가능할 수 있습니다 | ||
| ### 설계 단계에서 성능을 염두해야한다. | ||
|
|
||
| - 완성후 가장 변경하기 힘든거는 컴포넌트, 외부 시스템과 소통 방식,API, 네트워크 프로토콜, 영구 저장 데이터 포맷 (인터페이스) | ||
| - 시스템 성능저하 가져올 수 있음 | ||
| ### API를 설계할 때 성능에 주는 영향을 고려하라. | ||
| - 퍼블릭 타입을 변경가능하게 만드는 것은 불필요한 방어적 복사(defensive copying)을 요구한다. | ||
| - 합성이 적절해 보이는 설계에 상속을 사용하는 것은 슈퍼 클래스와 서브 클래스의 결합도를 상승한다. (성능을 물려받음) | ||
| - 구체적인 구현 타입 보다는 인터페이스를 사용 - 구현체에 종속 방지 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| #### java.awt.Component Class | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| public abstract class Component implements ImageObserver, MenuContainer, Serializable | ||
| { | ||
| public Dimension getSize() { | ||
| return size(); | ||
| } | ||
|
|
||
| @Deprecated | ||
| public Dimension size() { | ||
| return new Dimension(width, height); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ### 좋은 API 설계가 좋은 성능 | ||
| - 성능을 올리기 위해서 API를 변형하지 말 것 | ||
| - 추상화 격차가 크기 때문에 코드를 최적화 한다고 해서 성능이 개선될 수 있을지 모른다. | ||
| - 자바는 C와 C++보다 최적화의 영향을 측정하는 것이 중요 | ||
| - 알고리즘을 잘 고르는 것만으로도 큰 성능이 개선 | ||
| - 성능을 최적화 하면 프로파일링 도구를 활용해서 측정해보아야 한다. | ||
| - 프로파일링 도구(소스 레벨의 분석을 위한 툴)로 JMH, JProbe, ej-technologies, JProfiler를 활용할 수 있음 | ||
| - Intellj의 프로파일링 도구 https://madplay.github.io/post/intellij-idea-profiling-tools | ||
|
|
||
| ### Intellij IDEA Ultimate Profiling | ||
|
|
||
| 사용방법 : https://blog.jetbrains.com/idea/2020/03/profiling-tools-and-intellij-idea-ultimate/ | ||
|
|
||
| 사용방법2 : https://blog.jetbrains.com/idea/2022/01/fixing-the-parrot-party/ | ||
|
|
||
| - 애플리케이션의 실행 방식과 메모리, CPU 리소스가 할당되는 방식에 대한 분석을 제공하는 Async Profiler | ||
|
|
||
| - 애플리케이션이 실행되는 동안 JVM에서 발생한 이벤트에 대한 정보를 수집하는 모니터링 도구인 Java Flight Recorder | ||
| 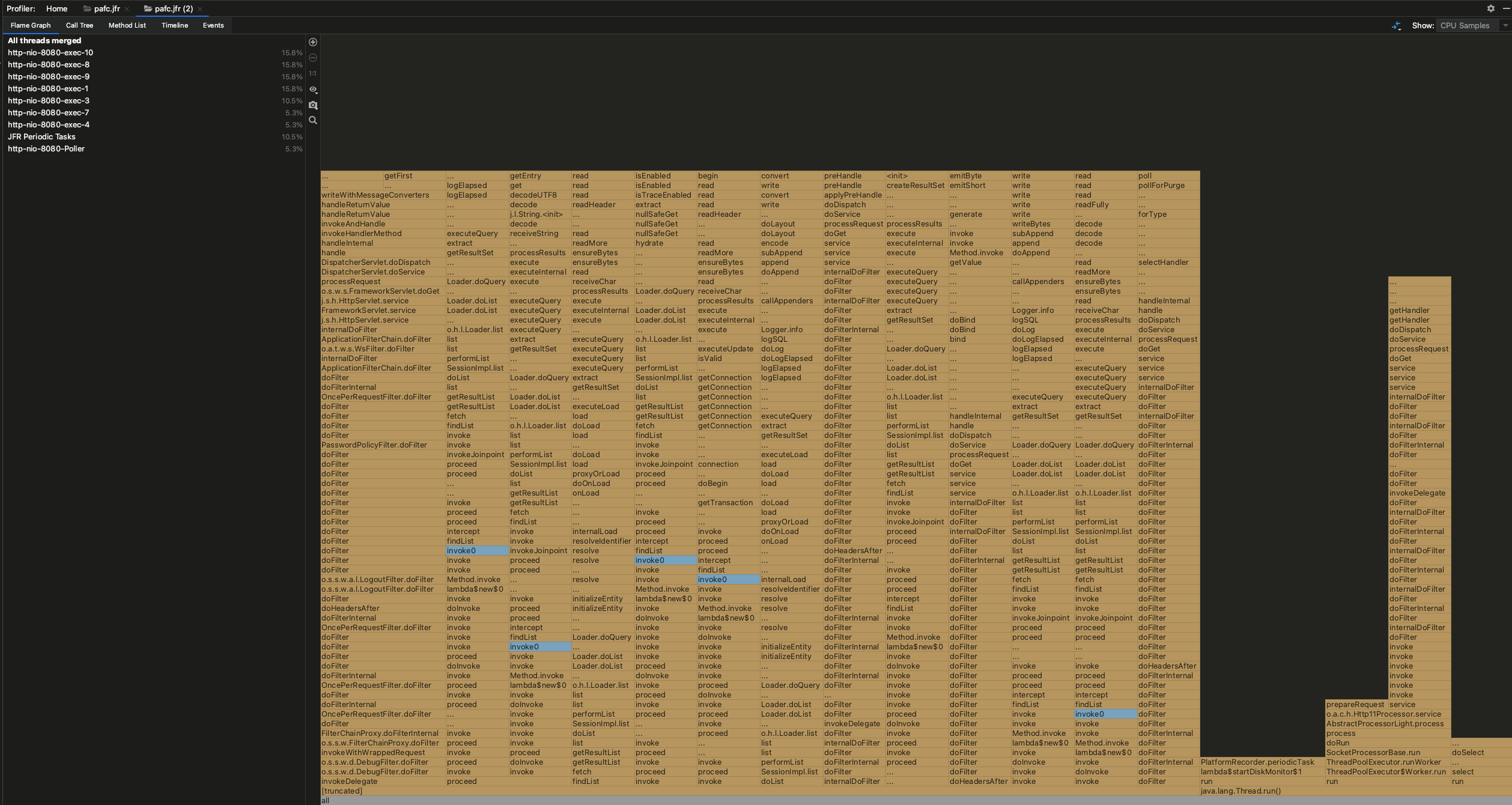 | ||
|
|
||
| - 애플리케이션의 특정 시점의 스냅샷으로 메모리를 분석하거나 Analyze memory snapshots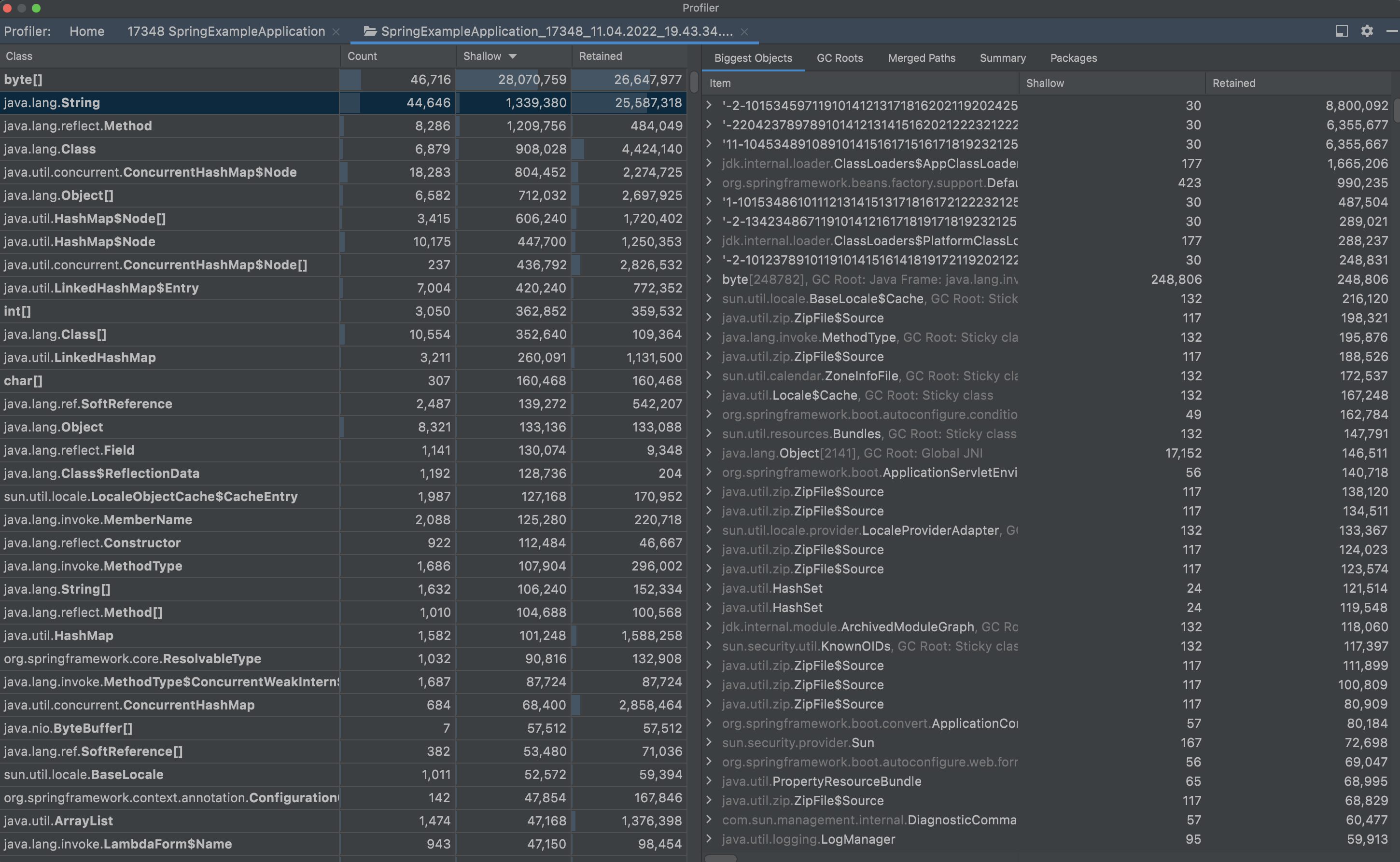 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| - 애플리케이션이 실행되는 도중에도 CPU와 메모리 현황을 실시간으로 확인할 수 있는 기능 CPU and memory live charts | ||
| - 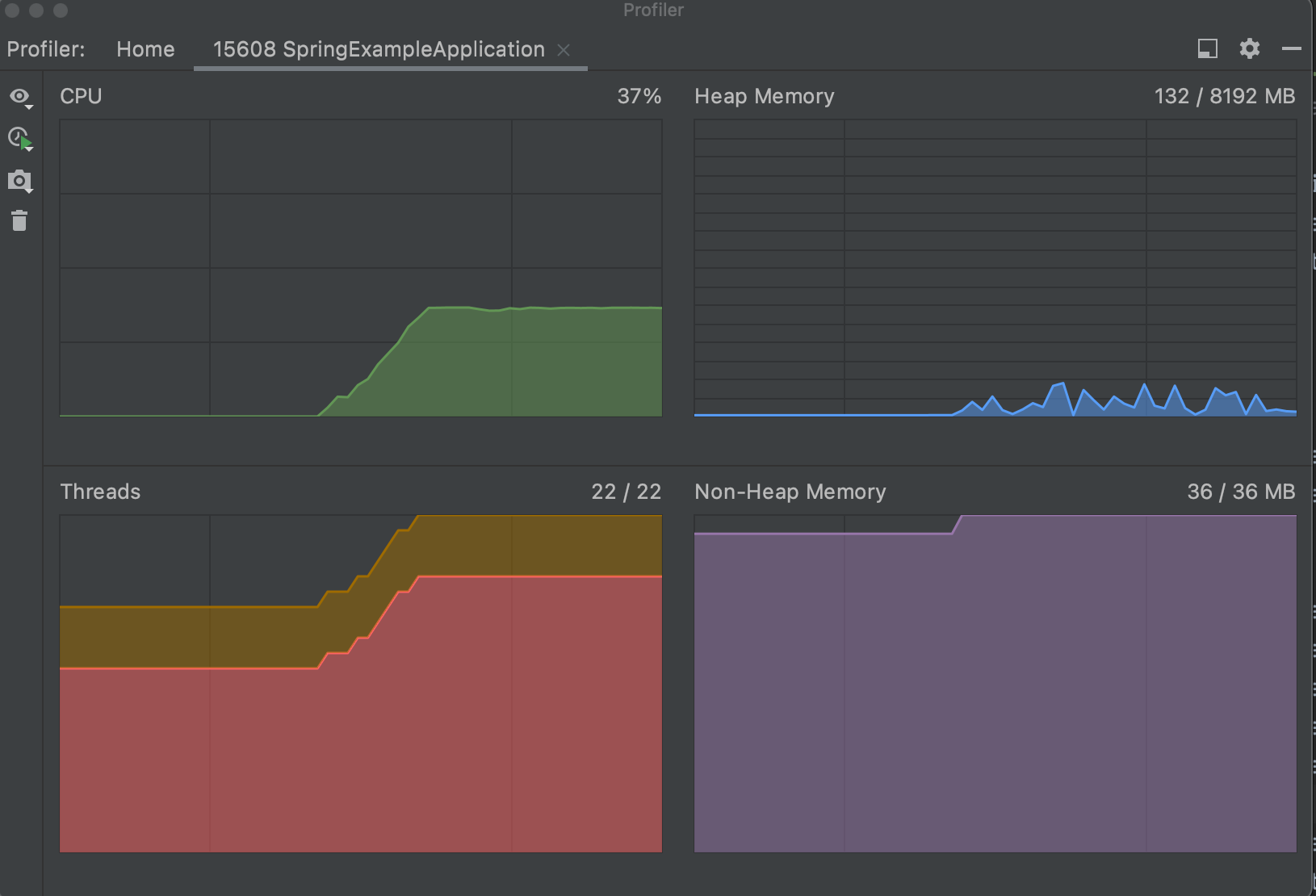 |