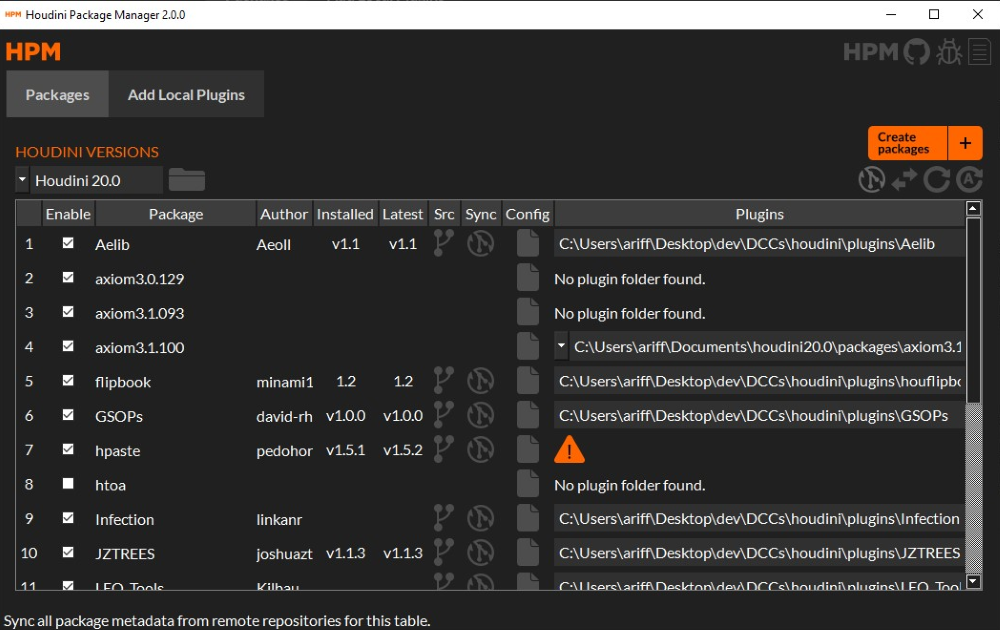
A comprehensive GUI package manager for Houdini. Manage all your plugins and create new packages with ease.
- Download the application: https://houpm.com
- Github repository: https://github.com/ariffjeff/houdini-package-manager
- PyPI repository: https://pypi.org/project/houdini-package-manager
- Download the latest version from https://houpm.com
- Unzip and store the folder anywhere you want.
- Create a shortcut of the Houdini_Package_Manager-x.y.z.exe file from the folder.
- Now you can run HPM from the shortcut, that's all there is to it!
- Windows (
.exedistributable)- Only tested on Windows 10.
- Houdini 19.5+ (older versions untested)
- A supported version of Houdini must be installed for HPM to launch successfully.
- An internet connection for the package GitHub syncing features.
- In very unlikely situations, a version >= Houdini 20.0.x with patch(es) pertaining to
hconfig.exe.- Unfortunately specific user package configurations (
.jsonfiles) cause a program calledhconfig.exethat ships with Houdini to hang and fail to return valid data, which HPM needs in order to function. I am working with SideFX to fix the issue but in this unlikely scenario HPM might fail to launch or will display that you are missing packages. Make sure you have an up to date version of Houdini with a relevant patch if this applies to you.
- Unfortunately specific user package configurations (
HPM is a Python application that basically grabs your plugins' package config files and converts them into a nice UI with a bunch of useful functionality.
- Gets Houdini's environment variable key value pairs.
- Gets the raw json package config data (some values might contain variables), typically found in
/packages. - Uses the Houdini environment variables to resolve the package config variables. The data as a whole is also simplified.
- Creates arbitrary objects from this resolved package config/plugin data.
- Converts this package/plugin data into a Pyside6 UI with accompanying functionality.
- This is all then built into an executable with
Pyinstaller.
- You can create new package configs for plugins you have downloaded to quickly get them into Houdini hassle free.
- HPM takes the plugin folder path, HDA, or script you provide it and simply creates a new package config from a template, and puts it in
/packages.
Note: This project was primarily tested with Python 3.9.10 and 3.10.10 on Windows 10.
- Install the Poetry dependency manager (using either of the CLI commands).
- Clone HPM
- Open a terminal, and
cdto it.
- Open a terminal, and
- Do
poetry install - Make your code changes and commit them
- If you're adding other files/images/vectors/etc., put them somewhere appropriate in
houdini_package_manager/resources/
- If you're adding other files/images/vectors/etc., put them somewhere appropriate in
- Version bump (optional)
- Automatic version bump:
- Do
poetry version minor. Usemajororpatchin place ofminorif appropriate. These will automatically be updated:pyproject.toml__version__in__init__.py. (if the Poetry poetry-bumpversion plugin is installed)- The relevant HTML in
houpm.com. (auto updated later bymake prepare) - The final executable and .zip file/folder names. (auto updated later by
make prepare)
- Do
- Manual version bump:
- Do
poetry version 1.2.3
- Do
- Commit the version bump later along with a new build (keep reading next steps).
- Automatic version bump:
- Do
make prepare- This does all the final build management automatically by running a bunch of other commands.
- Review these make commands only if you need to use them individually...
make testruns the project pytests. Skip them withmake prepare TEST=0make build-exebuilds the project. It will appear indist/resources/is copied to the build folder automatically so you don't have to worry about it.- The build folder and .exe name is determined by the version number set by the result of
poetry version ...(referenced in the Makefile)
make zipzips the build indist/make dist-movecreates a copy of the dist build in the HouPM website dist_hpm folder.make update-houpmupdates HPM version html in houpm website.
- Run/test the build (sanity check)
- Run the build
- Different methods:
- Go to
dist/, find the .exe and run it. - Or do
make run-exe.- Be aware this doesn't run it directly in the folder its in, which can lead to the issue of relative file paths not being able to find the files they're targetting if the paths have been set improperly... i.e. images failing to load. Make sure you set file paths with
utils.epath()which automatically handles relative paths correctly for both the dev and build environment.
- Be aware this doesn't run it directly in the folder its in, which can lead to the issue of relative file paths not being able to find the files they're targetting if the paths have been set improperly... i.e. images failing to load. Make sure you set file paths with
- Go to
- Different methods:
- If you get unexpected behavior, HPM fails to start up, or a crash:
- Check the app folder for a .log crash file.
- Crash log files are currently timestamped/created immediately upon exe run. If HPM is closed normally (not from a crash and not via the debug console) then the log file will be deleted.
- Do
make build-exe-logto make an exe that displays a debug console on run. Run the exe normally (not via amakecommand) to get the console to display. If any errors occur, you can inspect them in the console.
- Check the app folder for a .log crash file.
- Run the build
- Commit
- Commit both the version bump (mentioned before) and the new build .zip together.
- The commit message should just be the version number (e.g.
1.3.2) for convention. - Try not to commit anything else with these for simplicity.
- Tag the commit
- The tag name should be the version number (e.g.
1.3.2) for convention. - You can do this by right clicking the commit if you're using a GUI like GitHub Desktop.
- The tag name should be the version number (e.g.
- Push and pull request
- Name the pull request the version number (e.g.
1.3.2). - Merge to the relevant branch.
- Hopefully you haven't pushed directly to main.
- Name the pull request the version number (e.g.
- Create a new release
- On GitHub, go to Releases.
- Select the tag version number (e.g.
1.3.2) from the dropdown. - Name the title the same version number.
- Click
Generate release notes. - Add any extra descriptive changes for this release.
- Click publish.
- PyPI will automatically be updated with the new HPM version via a GitHub action.
- HPM should warn the user if a .json file contains the "path" in-place-of/next to "HOUDINI_PATH" key since "path" is now deprecated by SESI according to their documentation. Or just auto merge "path" value with "HOUDINI_PATH" value (ignore duplicate paths) - (changing the actual json file to remove "path" in favor of "HOUDINI_PATH"). "hpath" technically should work as well but I couldn't get it to work.
- unchecking config button dissappears plugin path, even if actual config json is not set to false
- Be able to create a default plugin folder structure from a template from HPM. (containing /otls, /scripts, /toolbar, etc.)
- Be able to migrate scripts and otls to other Houdini versions.
- allow user to configure a plugin to not apply to certain Houdini version. i.e. a plugin is obsolete in a newer Houdini version because SideFX adds a node that has the same/better functionality.
- node tree view editing of package/script/otl dependencies for each houdini version
- warning dialog for about to overwrite package config when creating a package
- allow HPM to find loose otls and scripts that aren't in a folder
- easy editing of houdini env vars
- pref pane to disable auto update
- refresh package tables when new packages created
- ability to delete package table items
- give option to use existing .json package config created by plugin dev instead of using default template
- the other meta header data
- sort table by rows
- status log history (executed actions only)
- donations link
- ability to easily set most of the top-level variables ("load_package_once", etc.)
- See what versions of houdini a package is in from a glance.
- button that finds new installs of houdini (it might already do this? or just restart the app)
- packages with houdini patch version specifications should be represented visually somehow
- proper svg color changing: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33512884/pyside-change-color-or-opacity-of-svg-in-qicon
- create tables scripts and OTLs not directly a part of any package
- search bar for packages - isolates row in table (for when you have a lot of packages)
- class
PackageConfig:- search paths for plugin HDAs (\otls)
_get_houdini_paths()does not account for linux/macospackages_table.py- utilize
_main.jsonto locate loose HDAs and scripts that aren't actual plugin packages
- utilize