|
AMD Ryzen™ AI brings the power of computing closer to you on an AI PC, unlocking a whole new level of efficiency for work, collaboration, and innovation. The RyzenAI PC comes with a dedicated AI accelerator, called the AI Engine (AIE), integrated on-chip with the CPU cores. The AMD Ryzen™ AI Software SDK enables developers to take machine learning models trained in PyTorch or TensorFlow and run them on laptops powered by Ryzen AI, which can intelligently optimize tasks and workloads, freeing-up CPU and GPU resources, and ensuring optimal performance at lower power.
AMD Ryzen™ AI Software includes the tools and runtime libraries for optimizing and deploying AI inference on AIE. Installation is as simple as downloading and running a single command. Additionally, the software comes with various pre-quantized ready to deploy models on Hugging Face model zoo. Developers can get started in building their applications within minutes unleashing the full potential of AI acceleration on Ryzen AI PCs.
In this blog, we will download a pre-trained OPT1.3B model from Hugging Face and deploy it on a Ryzen AI laptop with a Chatbot app in a simple three step process.
- Version: Ryzen AI Software Platform v1.1
- Support: AMD Ryzen 7040U, 7040HS series processors with Windows 11 OS.
- Last update: May 2024
- Prerequisites
- Step-1: Download pre-trained OPT-1.3b Model from Hugging Face
- Step-2: Quantize the downloaded model from FP32 to INT8
- Step-3: Deploy Chatbot app with the model
- License
First, make sure that the following prerequisites are met.
- AMD Ryzen AI laptop with Windows 11 OS
- Anaconda, install if needed from here
- Latest Ryzen AI AIE Driver and Software. Follow the installation here
Clone this repo or download and extract Chatbot-with-RyzenAI-1.0.zip into the root directory where you have installed the Ryzen AI SW.
git clone https://github.com/ahoquegh/Chatbot-with-RyzenAI-1.0.git
Navigate to the folder Chatbox-with-RyzenAI-1.0 and then activate the conda environment created when RyzenAI was installed. In my case it was ryzenai-1.0-20231204-120522.
cd Chatbot-with-RyzenAI-1.0
conda activate ryzenai-1.0-20231204-120522
In the packages needed for this example using the requirements.txt file and initialize the required PATH variables using the setup.bat file.
pip install -r requirements.txt
setup.bat
If you're using RyzenAI Software version 1.1, due to a change in the underlying packages, you may encounter the following error during model download. A workaround is provided in the following steps.
Error: Failed to import optimum.exporters.onnx.__main__ because of the following error (look up to see its traceback):
cannot import name 'is_torch_less_than_1_11' from 'transformers.pytorch_utils'
Edit the convert.py file that can be found in your RyzenAI environment (for example: ryzenai-1.0-20231206-161054) at:
C:\Users\<username>\miniconda3\envs\ryzenai-1.0-20231206-161054\Lib\site-packages\optimum\exporters\onnx\convert.py
- Update Line 49
- From:
from transformers.pytorch_utils import is_torch_less_than_1_11 - To:
from transformers.pytorch_utils import is_torch_greater_or_equal_than_1_12
- From:
- Update line 561
- From:
if is_torch_less_than_1_11: - To:
if is_torch_greater_or_equal_than_1_12 == False:
- From:
Now we are setup to create the Chatbot using the next 3 steps.
In this step, we will download a pre-trained OPT-1.3B model from Hugging Face. You can modify the run.py script to download a pre-trained model from your own or your company repository. OPT-1.3b is a large model, ~4GB. Download time depends on your internet speed. In my case it took ~6 minutes.
cd Chatbot-with-RyzenAI-1.0\
python run.py --model_name opt-1.3b --download
The downloaded model saves in the subdirectory \opt-1.3b_pretrained_fp32\.
Once the download is complete we quantize the model using following command:
python run.py --model_name opt-1.3b --quantize
Quantization is a two steps process. First, the FP32 model is smooth quantized to reduce accuracy loss during quantization. It essentially identifies the outliers in the activation coefficients and conditions the weights accordingly. That way, if the outliers are dropped during quantization any errors introduced is negligible. The Smooth Quant is invented by one of AMD's pioneer researchers, Dr. Song Han, he is a professor at the MIT EECS department. Below is a visual presentation of how the smooth quantization technique works.
You can learn more about the smooth quantatization technique in the paper found here. After smooth quantization, the conditioned model, along with config.json files, are saved in the folder 'opt-1.3b_smoothquant/model_onnx'.
Smooth quantization takes ~30 seconds to complete. Once done, the Optimum quantizer is used to quantize the model into INT8. The INT8 quantized model is then saved in the folder 'opt-1.3b_smoothquant\model_onnx_int8'. Quantization is an offline process. It take about 2-3 minutes to complete and needs to be done only once. Here is a screen capture of Int8 quantization log.
Next, we evaluate the quantized model and run it targeting AIE with the following command. Notice the model path is set to the location where the INT8 quatized model was saved during in the previous step.
python run.py --model_name opt-1.3b --target aie --local_path .\opt-1.3b_smoothquant\model_onnx_int8\
For the first run, the model is automatically compiled by an inline compiler. Compilation is also a two-step process:
- First, the compiler identifies the layers that can be executed in the AIE. Then, it creates sets of subgraphs, one set for AIE and the other set for CPU with the remaining layers.
- Secondly, it creates instruction sets for each of the subgraphs targeting their respective execution unit. These instructions are executed by two ONNX execution providers (EP), one for the CPU and one for the AIE.
After compilation, the compiled model is saved in the cache so that in the subsequent executions it does not need to repeat the compilation. Here is a screen capture where the model information was printed during the compilation flow.
After the compilation, the model runs on AIE and CPU. A test prompt was used for this initial run with the response from the LLM printing to the command line. Keep in mind that we downloaded and deployed a publicly available pretrained model. So the responses from the LLM may not be as expected, depending on the training data used. We strongly recommend finetuning publicly available models before production deployment.
Now, lets launch the Chatbot with the INT8 quantized model saved at the following location \opt-1.3b-smooothquant\model_onnx_int8\
python gradio_app\opt_demo_gui.py --model_file .\opt-1.3b_smoothquant\model_onnx_int8\
The Chatbot application will runs on the localhost on port 1234. To open the application, use your browser to navigate to: http://localhost:1234
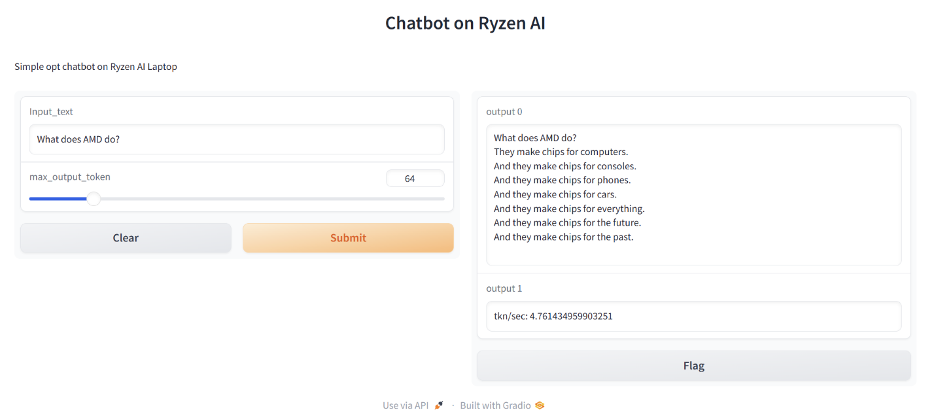
Once you've opened the application, set the max_output_token=64 and in the "Input_text box", enter the prompt: "What does AMD do?". The Chatbot outputs the response as shown below. It also calculates the KPI as token/sec. In my run it was ~4.7 tkn/sec.
The results from each input prompt will also be shown in your CLI.
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2024 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.