Using AI models to infer patient phenotypes from identified named entities (instances of biomedical concepts).
This repo has been migrated without history from the safehaven_mini branch in https://git.ecdf.ed.ac.uk/SMI/nlp2phenome.git
which itself was tracking upstream https://github.com/CogStack/nlp2phenome. All future updates will be made only in the repo
and not pushed back to gitlab or CogStack.
Contents:
- training models from user data (supplied by eHOST annotations)
- learning applied to future database queries to improve the results
Using natural language processing(NLP) to identify mentions of biomedical concepts from free text medical records is just the first step. There is often a gap between NLP results and what the clinical study is after. For example, a radiology report does not contain the term - ischemic stroke. Instead, it reports the patient had blocked arteries and stroke. To infer the "unspoken" ischemic stroke, a mechanism is needed to do such inferences from NLP identifiable mentions of blocked arteries and stroke. nlp2phenome is designed for doing this extra step from NLP to patient phenome.
nlp2phenome was developed for a stroke subtyping study using NLP on radiology reports in Edinburgh University led by Dr Will Whitely. It is based on top of SemEHR results. It identified 2,922 mentions of 32 types of phenotypes from 266 radiology reports and achieved an average F1: 0.929; Precision: 0.925; Recall: 0.939.
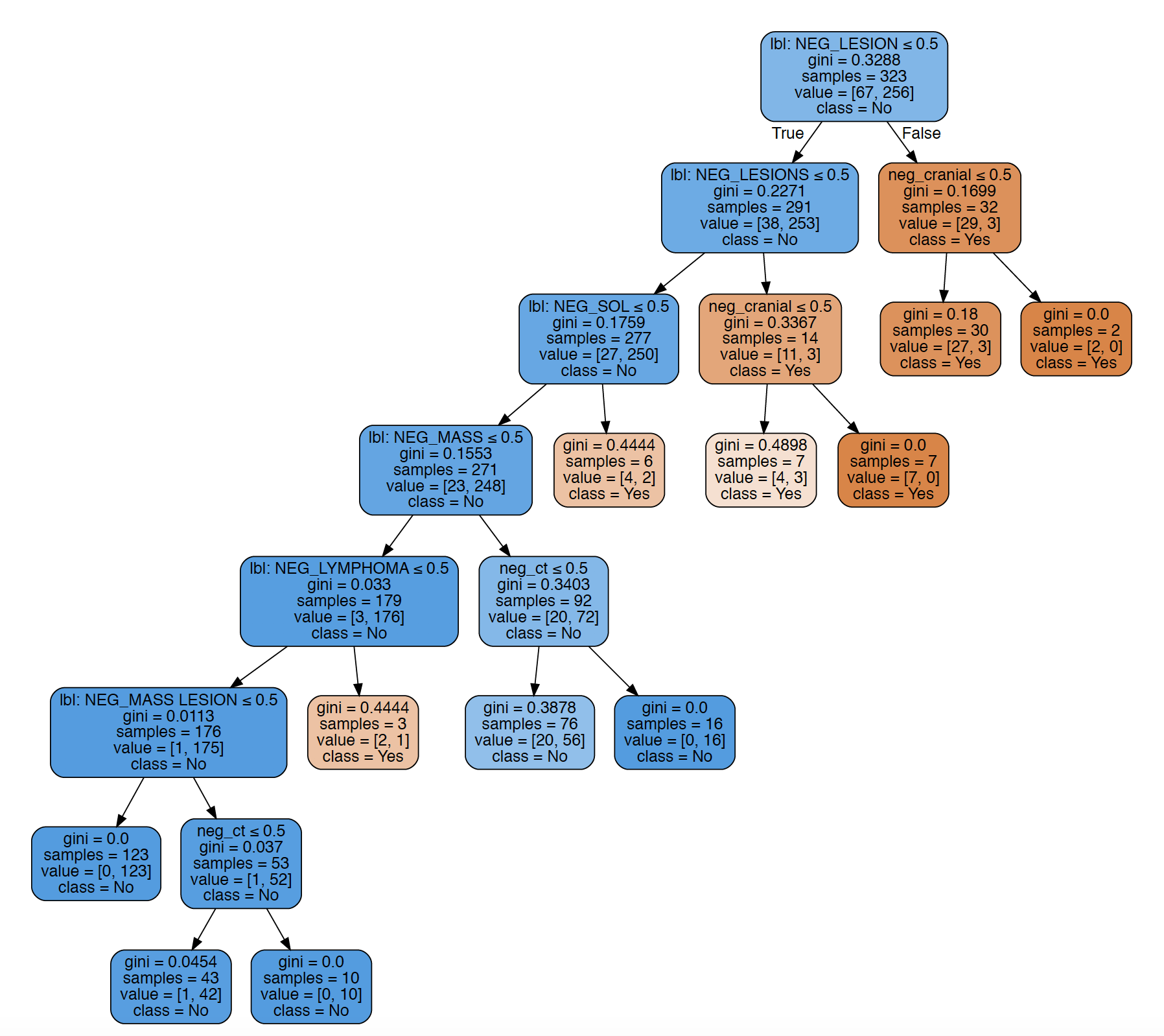
It uses various transparant machine learning models (e.g. decision tree, random forest) to learn the inference from NLP results to more insightful clinical phenotypes (such as subtypes of stroke). The image below is a decision tree learnt for negated tumour from radiology reports. Surprisingly, with specific feature selection methods, decision tree models outperforms the popular neural network based method. The other advantage is that the visualised decision trees can be verified or matched with clinical experts, or even compared to clinical guidelines. A working paper in progress, will update with a link soon.
Two datasets (radiology reports) collected in Scotland
- Edinburgh Stroke Study training data (364 reports), testing data (266 reports)
- Tayside radiology reports (300 reports)
- config your configuration file. Please see
./settings/sample_setting_kfold_learning.jsonfor reference.
{
"kfold": 10, // the fold for learning
"corpus_folder": "/data/annotated_data/corpus", // the folder containing full text documents
"gold_folder": "/data/annotated_data/gold", // the folder containing the labelled/annotated data
"semehr_folder": "/data/semehr_results", // the folder containing baseline SemEHR results
"working_folder": "/data/learning", // the working folder to store intermidieate data files
"concept_mapping_file": "./settings/empty_concept_mapping.json", // the mapping file to map UMLS CUI to phenotypes
"learning_model_dir": "./models", // where the machine learning models are stored
"entity_types_file": "./settings/better_worse_entity_types.txt", // the list of phenotypes to be worked on
"ignore_mapping_file": "./settings/ignore_mapping.json", // a json based mapping file to ignore certain CUI mappings
"min_sample_size": 25, // minimal number of samples to train a model, if the sample size is less than this number, a counting based stats will be used to assess the correctness of baseline results rather than a machine learning model
"gold_file_pattern": "%s.txt.knowtator.xml", // the annotation file pattern, %s identifies the unique id that will be used to find SemEHR result file and full text file in respective folders
"eHostGD": true // whether use eHOST annotation, only other format supported is EDiR from Edinburgh Informatics
}entity_types_file- each study is to identify a set of phenotypes (e.g., diseases, symptoms or other biomedical mentions). This file is a plain text file to list all the names ofphenotypesin a format of one phenotype per line. Check entity_types_phenotypes_stroke_sample.txt as an example.concept_mapping_file- for each phenotype defined above, it needs to be mapped to one or several ontology concepts (e.g., UMLS CUI). This is a json file. It is a json dictionary, where the key is thephenotypename and the value is an array. Each element in the array takes the form ofCONPCET_ID\tLabel\tSemantic Type-tabkey separated tuple. The first component is most important and the last two are for display purpose only. Check concept_mapping_stroke_sample.json as an example.ignore_mapping_file- this is a json dictionary for removing particular concepts (and customised dictionary terms) from the mappings of phenotypes as defined inconcept_mapping_file. The key isphenotypename and the value is an array containing either concept IDs from the ontology used (e.g., UMLS) or the customised dictionary term. This file is only needed when theconcept_mapping_fileis automatically generated from some learning data and it requires some fine-tuning.
- run it by
python run_learning.py YOUR_LEARNING_CONFIG_FILEPlease contact SMI rather than the original author.
This repo was hosted at https://git.ecdf.ed.ac.uk/SMI/nlp2phenome.git
tracking upstream https://github.com/CogStack/nlp2phenome
using git remote add upstream https://github.com/CogStack/nlp2phenome
and git checkout -t upstream/safehaven_mini
so remember to fetch upstream and push origin.
Now (2022-11) this repo is self-contained.