CoyPU Knowledge Graph (KG) contains a huge amount of data about all the countries worldwide, including each country's performance based on thousands of indicators presented in the World Bank datasets. An indicator refers to a specific metric measuring a particular aspect of economic, social, or environmental development. We aim to detect communities of Country-Indicator and predict relationships between them.
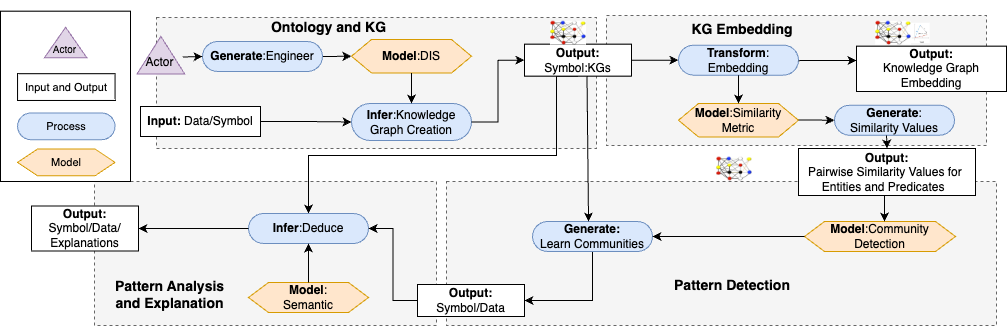
We follow a hybrid AI framework that employs inductive learning to identify a partitioning of nodes within a KG. The proposed framework comprises four design patterns describing the sub-systems that implement the tasks mentioned above toward solving the problem of detecting communities. The following figure shows the framework comprising a basic vocabulary and four design patterns.
The first pattern, Ontology and KG, involves the process of Knowledge Graph Creation, which performs a bottom-up evaluation of the mapping rules to generate the CoyPU KG. The second pattern, KG Embedding and Large Language Model (LLM), represents the system that learns the k-dimensional vector representations of entities and relations. This design pattern combines embeddings generated from methods that extract contextual knowledge from structured and unstructured data (LLM), integrating the two perspectives. The next design pattern, Pattern Detection, follows a community detection algorithm to partition the Country-Indicator into a set of communities. Finally, Pattern Analysis and Explanation, designs a system for explaining knowledge captured by the detected communities using statistical and symbolic statements. Our system efficiently partitions Country-Indicator communities through a hybrid AI approach, leveraging knowledge captured comprehensively.
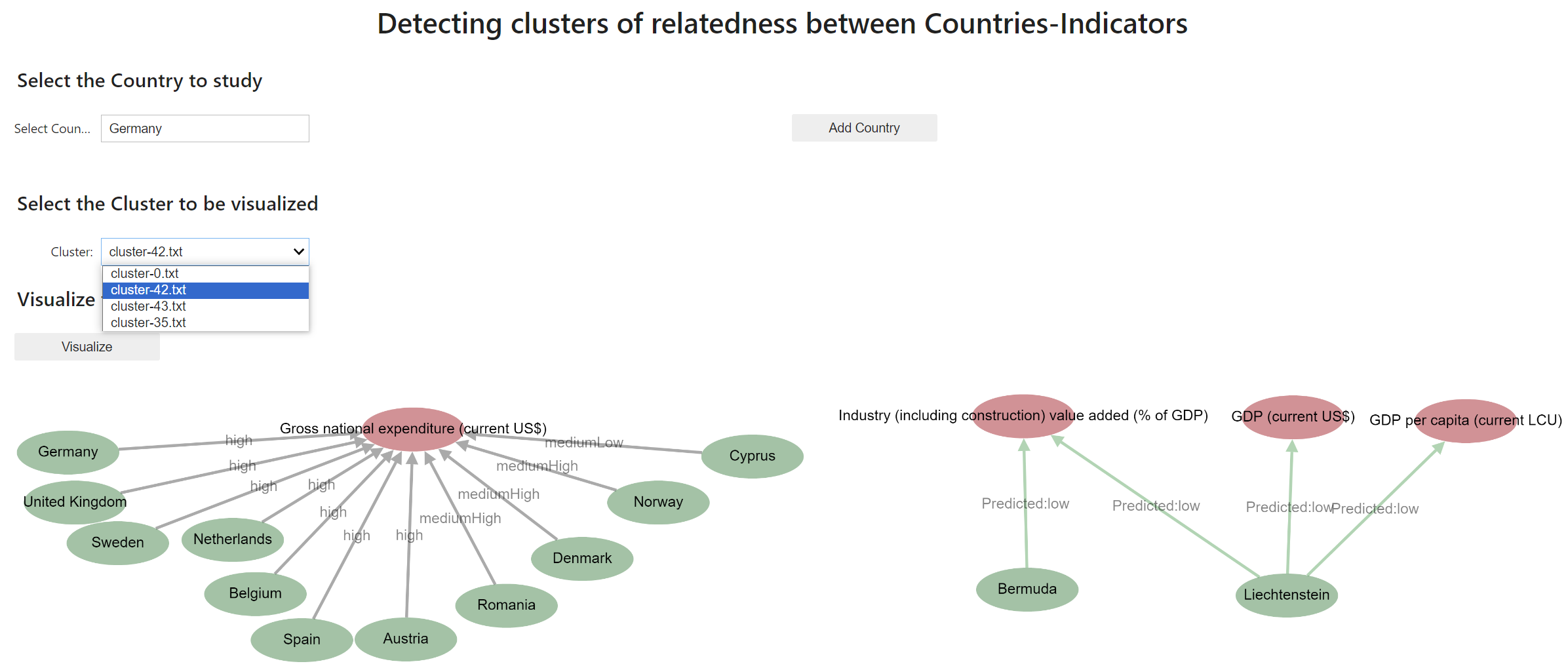
Use Case 1: Given a country and a specific year, identify its communities of relatedness between Countries-Indicators and predict relationships.
Given the input country, Germany, and the year 2022, the hybrid AI framework detects four clusters where Germany is involved. The following figure visualizes a cluster, with red nodes representing the indicators and green nodes representing the countries.
We can observe that those countries are similar based on the performance of the indicator Gross National Expenditure. Furthermore, in green, the cluster contains links predicted between two countries and three economic indicators.
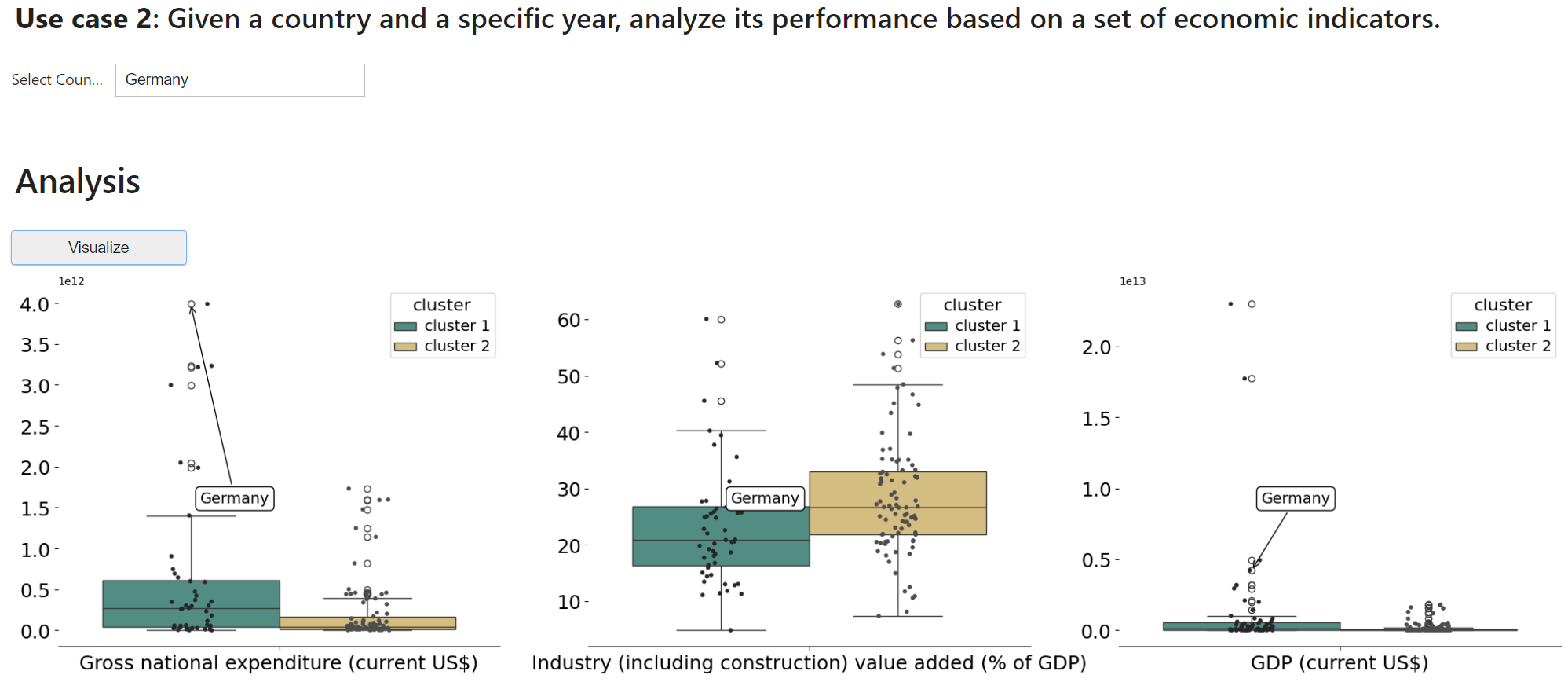
Use Case 2: Given a country and a specific year, analyze its performance based on a set of economic indicators.
Given the input country, Germany and the year 2022, the hybrid AI framework employs inductive learning to identify a partitioning of nodes within a KG. Then, the framework analyzes the country's performance for each community of countries based on Gross national expenditure, Industry value added, and Gross domestic product (GDP). The next figure displays the framework result, which detects two clusters of countries. Each point in the first box plot represents the gross national expenditure of a country where Germany has the highest value. Germany is in the top of the third quartile for industry value added, and Germany also has a high GDP value.
The demo demonstrates the ability to predict relationships within these communities, providing valuable insights into the global development indicators. Furthermore, the users understand the economic landscape comprehensively, allowing for informed decision-making and policy insights.