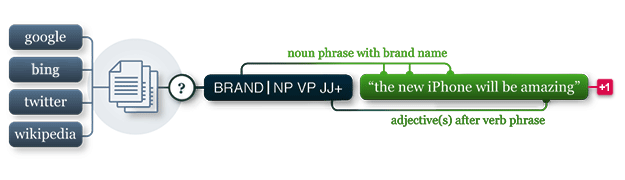
Pattern is a web mining module for Python. It has tools for:
- Data Mining: web services (Google, Twitter, Wikipedia), web crawler, HTML DOM parser
- Natural Language Processing: part-of-speech taggers, n-gram search, sentiment analysis, WordNet
- Machine Learning: vector space model, clustering, classification (KNN, SVM, Perceptron)
- Network Analysis: graph centrality and visualization.
It is well documented and bundled with 50+ examples and 350+ unit tests. The source code is licensed under BSD and available from http://www.clips.ua.ac.be/pages/pattern.
2.6
BSD, see LICENSE.txt for further details.
The setup can be simple. For example if you wanted to setup for collecting data from twitter you should only need to update the API key with your API key. The file you need to update is pattern/web/api.py. The license setting for twitter (license["Twitter"]) needs to be changed. Update the four lines to reflect the values you have for the twitter App api key you have.
This example trains a classifier on adjectives mined from Twitter. First, tweets that contain hashtag #win or #fail are collected. For example: "$20 tip off a sweet little old lady today #win". The word part-of-speech tags are then parsed, keeping only adjectives. Each tweet is transformed to a vector, a dictionary of adjective → count items, labeled WIN or FAIL. The classifier uses the vectors to learn which other tweets look more like WIN or more like FAIL.
from pattern.web import Twitter
from pattern.en import tag
from pattern.vector import KNN, count
twitter, knn = Twitter(), KNN()
for i in range(1, 3):
for tweet in twitter.search('#win OR #fail', start=i, count=100):
s = tweet.text.lower()
p = '#win' in s and 'WIN' or 'FAIL'
v = tag(s)
v = [word for word, pos in v if pos == 'JJ'] # JJ = adjective
v = count(v) # {'sweet': 1}
if v:
knn.train(v, type=p)
print knn.classify('sweet potato burger')
print knn.classify('stupid autocorrect')http://www.clips.ua.ac.be/pages/pattern
De Smedt, T., Daelemans, W. (2012). Pattern for Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 13, 2031–2035.
The source code is hosted on GitHub and contributions or donations are welcomed, see the developer documentation. If you use Pattern in your work, please cite our reference paper.
Pattern is bundled with the following data sets, algorithms and Python packages:
- Beautiful Soup, Leonard Richardson
- Brill tagger, Eric Brill
- Brill tagger for Dutch, Jeroen Geertzen
- Brill tagger for German, Gerold Schneider & Martin Volk
- Brill tagger for Spanish, trained on Wikicorpus (Samuel Reese & Gemma Boleda et al.)
- Brill tagger for French, trained on Lefff (Benoît Sagot & Lionel Clément et al.)
- Brill tagger for Italian, mined from Wiktionary
- English pluralization, Damian Conway
- Spanish verb inflection, Fred Jehle
- French verb inflection, Bob Salita
- Graph JavaScript framework, Aslak Hellesoy & Dave Hoover
- LIBSVM, Chih-Chung Chang & Chih-Jen Lin
- LIBLINEAR, Rong-En Fan et al.
- NetworkX centrality, Aric Hagberg, Dan Schult & Pieter Swart
- PDFMiner, Yusuke Shinyama
- Python docx, Mike Maccana
- PyWordNet, Oliver Steele
- simplejson, Bob Ippolito
- spelling corrector, Peter Norvig
- Universal Feed Parser, Mark Pilgrim
- WordNet, Christiane Fellbaum et al.
Authors:
- Tom De Smedt ([email protected])
- Walter Daelemans ([email protected])
Contributors (chronological):
- Frederik De Bleser
- Jason Wiener
- Daniel Friesen
- Jeroen Geertzen
- Thomas Crombez
- Ken Williams
- Peteris Erins
- Rajesh Nair
- F. De Smedt
- Radim Řehůřek
- Tom Loredo
- John DeBovis
- Thomas Sileo
- Gerold Schneider
- Martin Volk
- Samuel Joseph
- Shubhanshu Mishra
- Robert Elwell
- Fred Jehle
- Antoine Mazières + fabelier.org
- Rémi de Zoeten + closealert.nl
- Kenneth Koch
- Jens Grivolla
- Fabio Marfia
- Steven Loria
- Colin Molter + tevizz.com
- Peter Bull
- Maurizio Sambati
- Dan Fu
- Salvatore Di Dio
- Vincent Van Asch
- Frederik Elwert