A repository of different programming languages and libraries providing examples of MQTT Client implementations that integrate directly to the Link Labs MQTT User Credentials Object and MQTT ecosystem.
For additional, more generic, MQTT client examples, you can also view: emqx/MQTT-Client-Examples
- Use MQTT v5 specification.
- Use TLS encryption and port 8883 (instead of the default, unencrypted port 1883).
- Validate TLS Certificate from Certificate Authority (no key file is required).
- Use one client id per process, sharing the same client id across multiple processes will result in both processes disconnecting the other, preventing any messages from being processed by either process.
- Use the MQTT Shared Subscription topic, which appends a
$share/<share group>prefix before the MQTT topic string. This allows multiple MQTT client processes, with unique MQTT client ids to "share" the same subscription, which will balance the load of traffic between the MQTT client processes. This allows for failure tolerance in the case that a subscription service fails as well as no-downtime upgrades of services by doing a rolling update of the services. - Utilize QoS of 1 to ensure that MQTT events are received at least once (and can be possibly duplicated).
- Utilize a
clean_session=Falsewhen the desired behavior is to process the backlog of QoS 1 messages that were not received by the MQTT client implementation and are unacknowledged from the perspective of the Link Labs MQTT Broker. - Utilize a
clean_session=Truewhen the desired behavior is to drop the unacknowledged and unreceived backlog messages from the Link Labs MQTT Broker and resume processing new near real time events only.
- Utilize a
- The Link Labs MQTT Broker only allows encrypted transport via the standard port 8883, specified in the MQTT User Credentials.
- The default unencrypted port 1883 is blocked and will result in a network timeout.
- This port requires TLS to be enabled on your MQTT client.
- We also recommend validating the certificate if it is an option in your MQTT client implementation.
- Using invalid credentials: username, password, and client ID must all match what is provided by MQTT User Credentials.
- The provided MQTT User Credentials only have access to the topic given in the MQTT User Credentials.
- Some implementations attempt to subscribe to "#" or "$SYS/#", this will prevent a connection.
- The given topic is just a base topic so you can fine-tune the subscription beyond your base topic if desired.
- A client is already subscribed to the MQTT Broker utilizing the same MQTT User Credentials (Client ID).
Already using or planning to use an existing Geographic Information System, Enterprise Resource Planning, or IoT Platform? The following are some of many ready-to-configure MQTT integrations:
- ArcGIS Velocity
- AWS IoT
- Azure IoT
- Informatica
- Lenses Kafka MQTT Source Connector
- Open Automation Software
- Salesforce/Mulesoft
- SAP ABAP
- ThingsBoard
The MQTT Sink connector validates connection using a randomly generated client ID. This validation method is fine in most cases, however, issues may arise if the MQTT broker rejects clients based on client IDs.
The Link Labs MQTT Broker requires static client id configuration as a part of the client authentication. An open-source alternative would be Lenses Kafka MQTT Source Connector
Once you have been registered in the Airfinder Platform with an Organization, you will need the admin level permissions to generate MQTT Crednetials.
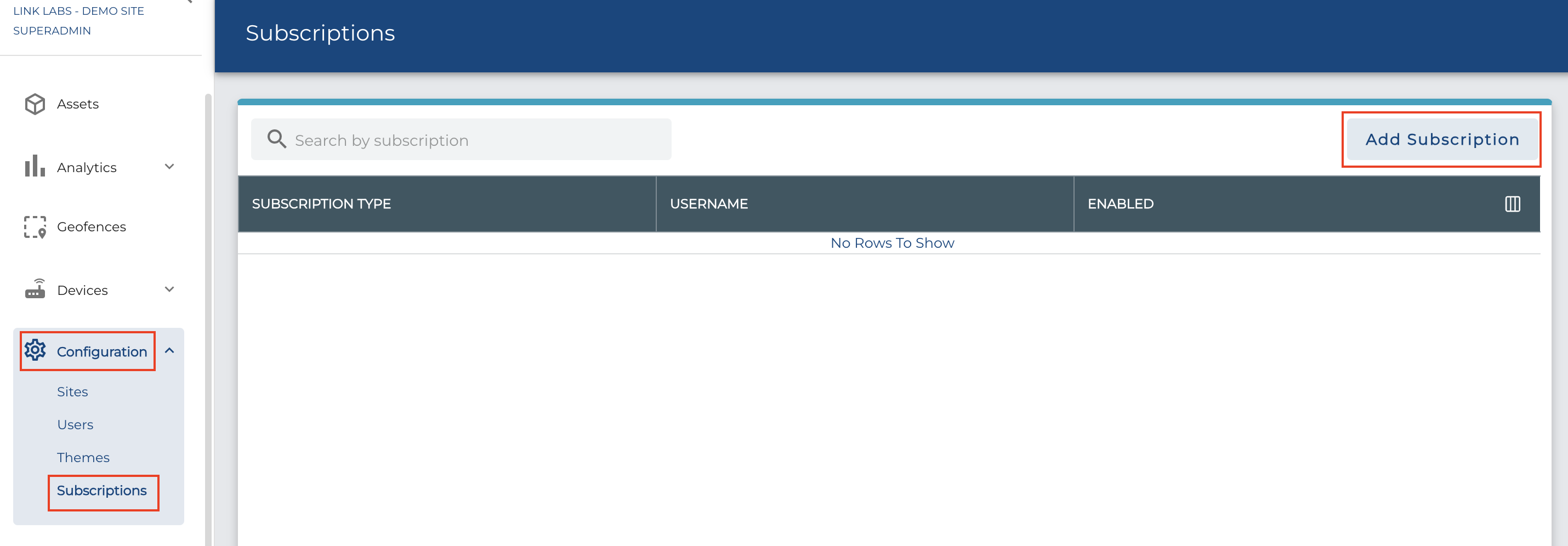
Go to the Configuration > Subscriptions menu. If this menu is not availible then your account does not have the sufficient admin level permissions.
You can view any existing credentials or "Add Subscription" to create a set of MQTT Credentials. At this point you can choose the scope of the MQTT Credentials, if the scope is for a single Airfinder Site or for the entire Organization.
To view the details of an MQTT Credentials, you can click the "..." icon and select "View Details". This will allow you to copy out individual fields or export out the entire document via the "Copy All Fields" button.
Once you "Copy All Fields", you can place that into a creds.json file within the root of the MQTT Client Example project you want to run in order to set up and run that example project.
The MQTT User Credential Swagger documentation can be found here: https://networkasset-conductor.link-labs.com/networkAsset/docs.html#!/airfinder-mqttuser-controller
To utilize this API you must have an Organization level admin permission, the API accepts BasicAuth and OAuth2 (with client configuration). You must also know your Organization ID, which can be found with this endpoint: GET https://networkasset-conductor.link-labs.com/networkAsset/airfinder/organizations
When you have the organization ID you can retrieve the MQTT Credentials with
curl -X GET "https://networkasset-conductor.link-labs.com/networkAsset/airfinder/mqttUsers?organizationId=<organization id>" \
-H "Authorization: basic <Basic Auth>"