The python client is deprecated, until such time that the community wishes to update it to work with the latest API's
casperlabs-client is a Python package consisting of
- a client library
casperlabs_clientthat can be used to interact with a CasperLabs node via its gRPC API and - a command line interface (CLI) script with the same name:
casperlabs_client.
Note, the name of the package available on PyPi is casperlabs-client (with hyphen),
but the name of the library as well as the CLI is written with underscore: casperlabs_client.
These instructions are for Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04. Note: The default versions of Python are different for both versions of Ubuntu. These steps are required prior to activating the Python environment every time the client is used.
casperlabs-client is a Python 3.7+ module, it does not support Python 2.7.
sudo apt install gcc python3.7 python3.7-dev
virtualenv -p python3.7 env
sudo apt install gcc python3.8 python3.8-dev
virtualenv -p python3.8 env
Each time you use the virtual environment you need to activate it. This is done with a script inside the env directory you created.
source env/bin/activate
You will need to do this for the install below, but also each time you open a new terminal to run the casperlabs_client once installed.
After activating the Python environment, install the casperlabs_client package with
python -m pip install casperlabs-client
Install Python 3 with brew: https://docs.python-guide.org/starting/install3/osx/
Next, type the following commands in the Terminal:
brew update
brew upgrade
pip install casperlabs-client
To install casperlabs-client on Windows 10 you need to install latest Python 3.7,
it is currently not possible to install it on Python 3.8 due to
grpc/grpc#20831
It is recommended to install Python from the python.org website: https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/
If you install Python from the Windows Store
you will need to manually add the Scripts folder of your Python installation to your Path
in order to have the casperlabs_client command line tool
available on the command line without providing full path to it.
This will be located in a path similar to this:
C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Local\Packages\PythonSoftwareFoundation.Python.3.x_qbz5n2kfra8p0\LocalCache\local-packages\Python37\Scripts>
You also need to install free Microsoft Visual Studio C++ 14.0.
Get it with "Build Tools for Visual Studio 2019":
https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/
(All downloads -> Tools for Visual Studio 2019 -> Build tools for Visual Studio 2019).
This is required by the pyblake2 extension module.
After installing the above prerequisites you can install the casperlabs-client package by
typing the following on the command line:
C:\Users\alice>python -m pip install casperlabs-client
The package casperlabs-client includes command line interface (CLI)
script called casperlabs_client.
Type casperlabs_client --help to see short synopsis with a list of
available commands
$ casperlabs_client --help
usage: casperlabs_client [--help] [-h HOST] [-p PORT]
[--port-internal PORT_INTERNAL] [--node-id NODE_ID]
[--certificate-file CERTIFICATE_FILE] [--version]
{account-hash,balance,deploy,keygen,make-deploy,query-state,send-deploy,show-block,show-blocks,show-deploy,show-deploys,show-peers,sign-deploy,stream-events,transfer,validator-keygen,vdag}
...
$ casperlabs_client deploy --help
To see available API functions, their parameters and documentation,
see source.
The API functions are marked with @api decorator.
After installing casperlabs-client you can start interacting with
CasperLabs Testnet.
import casperlabs_client
client = casperlabs_client.CasperLabsClient('deploy.casperlabs.io', 40401)
block_info = next(client.show_blocks(1, full_view=False))
for bond in block_info.summary.header.state.bonds:
print(f'{bond.validator_public_key.hex()}: {bond.stake.value}')When executed the script should print a list of bonded validators' public keys and their stake:
89e744783c2d70902a5f2ef78e82e1f44102b5eb08ca6234241d95e50f615a6b: 5000000000
1f66ea6321a48a935f66e97d4f7e60ee2d7fc9ccc62dfbe310f33b4839fc62eb: 8000000000
569b41d574c46390212d698660b5326269ddb0a761d1294258897ac717b4958b: 4000000000
d286526663ca3766c80781543a148c635f2388bfe128981c3e4ac69cea88dc35: 3000000000
Note, you will also see a warning:
WARNING:root:Creating insecure connection to deploy.casperlabs.io:40401 (<class 'casperlabs_client.casper_pb2_grpc.CasperServiceStub'>)
Currently it is possible to connect from client to node without SSL encryption, which is what the above example code does.
In the future encryption will become obligatory and you will have to pass a certificate_path to the CasperLabsClient constructor.
The warning about insecure connection is meant to remind about this.
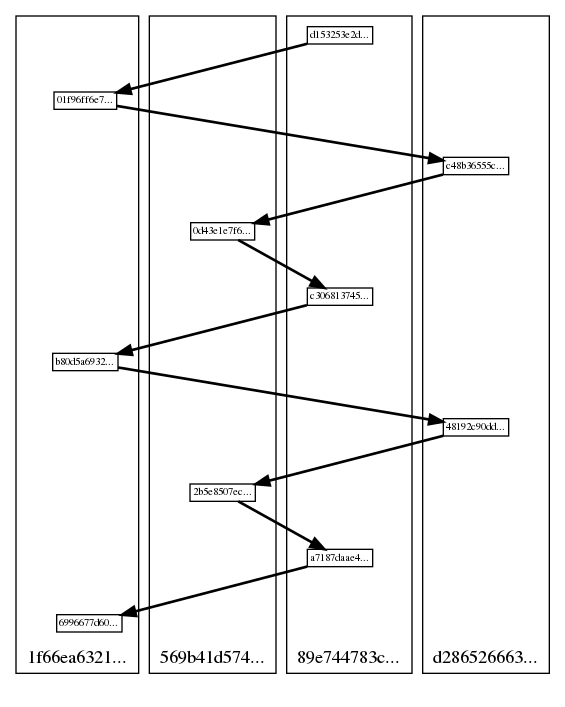
casperlabs_client has vdag command that can be used to visualize DAG.
If you want to use it you need to first install Graphviz,
the free graph visualization software.
For example:
casperlabs_client --host deploy.casperlabs.io vdag --depth 10 --out dag.png
will produce an image file similar to the one below:
Small boxes represent blocks, labeled with short prefixes of their block hashes. Blocks are aligned in "lanes" representing validators that created them. Bold arrows point to main parents of blocks.
To deploy a smart contract to CasperLabs Testnet you have to first:
-
Create an account using CasperLabs Explorer and transfer (free) tokens to the account from the faucet.
An account address is a hash of public key in hex format such as:
f2cbd19d054bd2b2c06ea26714275271663a5e4503d5d059de159c3b60d81ab7 -
Compile a contract to the WASM format, see CasperLabs contract examples to see example contracts and instructions on how to compile them.
To deploy a compiled contract from your account address, with client as CasperLabsClient instance:
response = client.deploy(from_addr="f2cbd19d054bd2b2c06ea26714275271663a5e4503d5d059de159c3b60d81ab7",
payment_amount=1000000,
session="helloname.wasm",
private_key="path/to/private.pem")Return values of the API functions defined in the CasperLabsClient are generally deserialized gRPC response objects
of the corresponding requests defined in the node's gRPC service, see
casper.proto.
Response to requests like show_blocks or show_deploys is a stream of objects.
Corresponding Python API functions return generator objects:
for block in client.show_blocks(depth=10):
print (block.blockHash)Some requests' response objects (see their definitions in casper.proto ) have fields indicating success.
InternalError is the only exception that user code can expect to be thrown by the API.