-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 102
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Merge branch 'master' into dns-providers
- Loading branch information
Showing
767 changed files
with
17,998 additions
and
16,141 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,57 @@ | ||
| --- | ||
| title: Structured DNS Errors (SDE) | ||
| sidebar_position: 5 | ||
| --- | ||
|
|
||
| With the release of AdGuard DNS v2.10, AdGuard has become the first public DNS resolver to implement support for [*Structured DNS Errors* (SDE)](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-dnsop-structured-dns-error/09/), an update to [RFC 8914](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc8914/). This feature allows DNS servers to provide detailed information about blocked websites directly in the DNS response, rather than relying on generic browser messages. In this article, we'll explain what *Structured DNS Errors* are and how they work. | ||
|
|
||
| ## What Structured DNS Errors are | ||
|
|
||
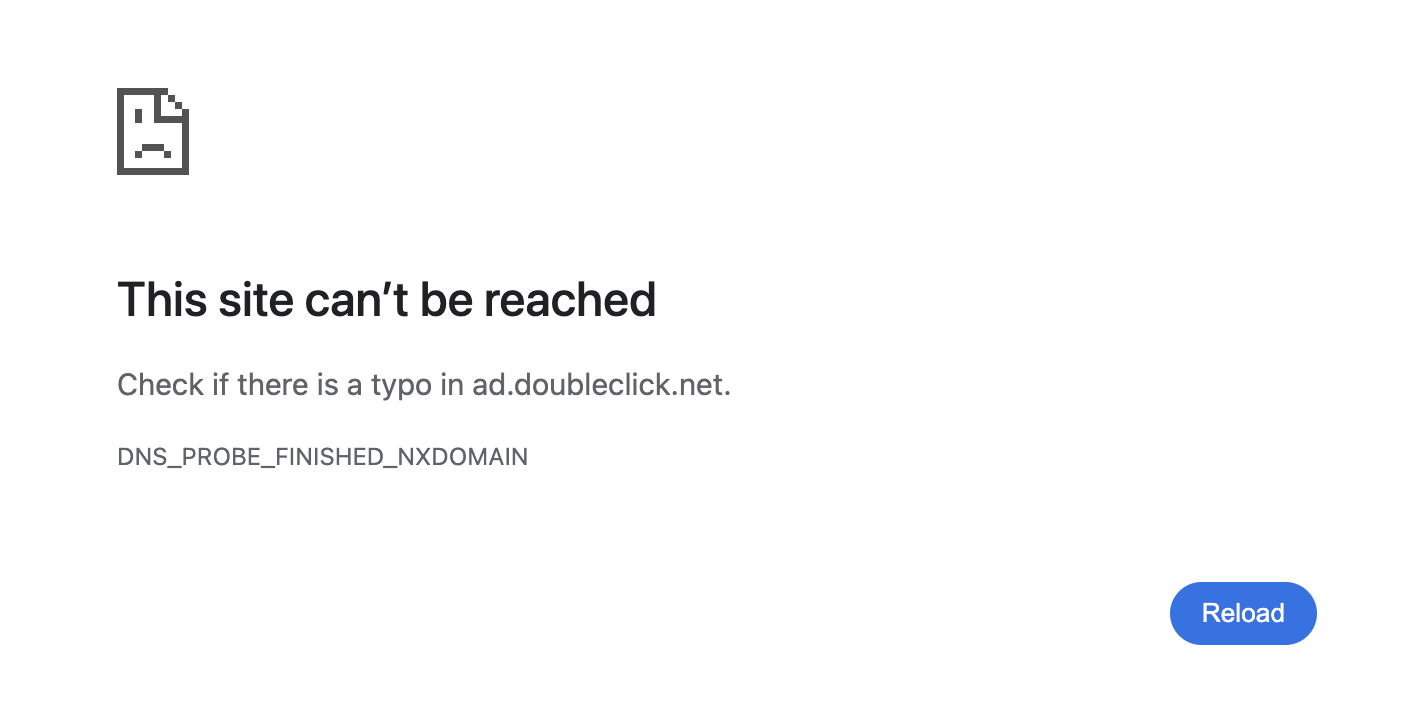
| When a request to an advertising or tracking domain is blocked, the user may see blank spaces on a website or may not even notice that DNS filtering has occurred. However, if an entire website is blocked at the DNS level, the user will be completely unable to access the page. When trying to access a blocked website, the user may see a generic "This site can't be reached" error displayed by the browser. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| Such errors don't explain what happened and why. This leaves users confused about why a website is inaccessible, often leading them to assume that their Internet connection or DNS resolver is broken. | ||
|
|
||
| To clarify this, DNS servers could redirect users to their own page with an explanation. However, HTTPS websites (which are the majority of websites) would require a separate certificate. | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| There’s a simpler solution: [Structured DNS Errors (SDE)](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-dnsop-structured-dns-error/09/). The concept of SDE builds on the foundation of [*Extended DNS Errors* (RFC 8914)](https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/rfc8914/), which introduced the ability to include additional error information in DNS responses. The SDE draft takes this a step further by using [I-JSON](https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7493) (a restricted profile of JSON) to format the information in a way that browsers and client applications can easily parse. | ||
|
|
||
| The SDE data is included in the `EXTRA-TEXT` field of the DNS response. It contains: | ||
|
|
||
| - `j` (justification): Reason for blocking | ||
| - `c` (contact): Contact information for inquiries if the page was blocked by mistake | ||
| - `o` (organization): Organization responsible for DNS filtering in this case (optional) | ||
| - `s` (suberror): The suberror code for this particular DNS filtering (optional) | ||
|
|
||
| Such a system enhances transparency between DNS services and users. | ||
|
|
||
| ### What is required to implement Structured DNS Errors | ||
|
|
||
| Although AdGuard DNS has implemented support for Structured DNS Errors, browsers currently do not natively support parsing and displaying SDE data. For users to see detailed explanations in their browsers when a website is blocked, browser developers need to adopt and support the SDE draft specification. | ||
|
|
||
| ### AdGuard DNS demo extension for SDE | ||
|
|
||
| To showcase how Structured DNS Errors work, AdGuard DNS has developed a demo browser extension that shows how *Structured DNS Errors* could work if browsers supported them. If you try to visit a website blocked by AdGuard DNS with this extension enabled, you will see a detailed explanation page with the information provided via SDE, such as the reason for blocking, contact details, and the organization responsible. | ||
|
|
||
| 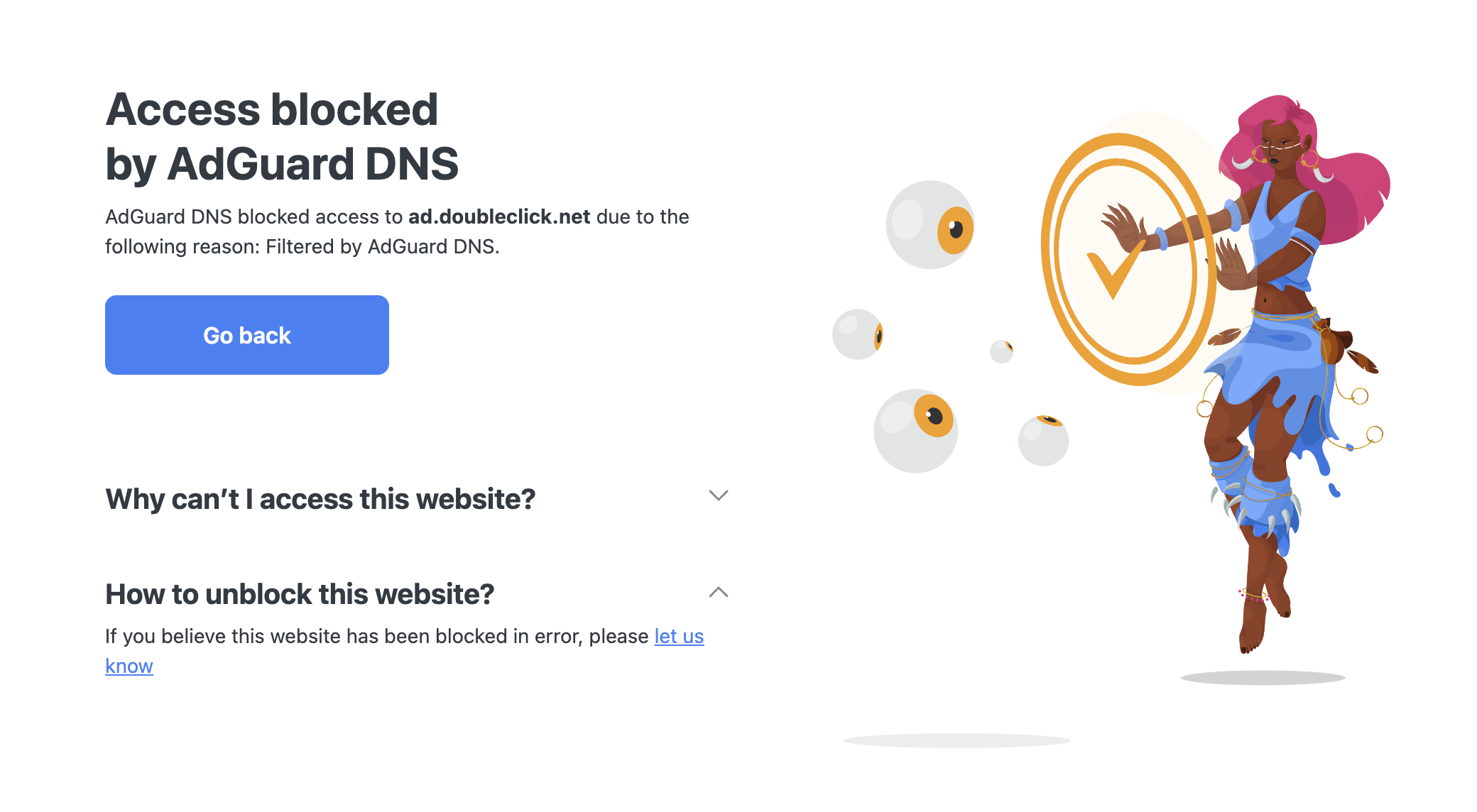 | ||
|
|
||
| You can install the extension from the [Chrome Web Store](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/oeinmjfnchfhaabhchfjkbdpmgeageen) or from [GitHub](https://github.com/AdguardTeam/dns-sde-extension/). | ||
|
|
||
| If you want to see what it looks like at the DNS level, you can use the `dig` command and look for `EDE` in the output. | ||
|
|
||
| ```text | ||
| % dig @94.140.14.14 'ad.doubleclick.net' A IN +ednsopt=15:0000 | ||
| ... | ||
| ;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION: | ||
| ; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1232 | ||
| ; EDE: 17 (Filtered): ({"j":"Filtered by AdGuard DNS","o":"AdGuard DNS","c":["mailto:[email protected]"]}) | ||
| ;; QUESTION SECTION: | ||
| ;ad.doubleclick.net. IN A | ||
| ... | ||
| ``` |
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -5,9 +5,7 @@ sidebar_position: 3 | |
|
|
||
| ## What linked IPs are and why they are useful | ||
|
|
||
| Not all devices can support encrypted DNS protocols. In this case, users should consider setting up unencrypted DNS. | ||
|
|
||
| You can use a **linked IP address**: in this setup, the service will consider all standard DNS queries coming from that IP address and for that specific device. The only requirement for a linked IP address is that it must be a residential IP. | ||
| Not all devices support encrypted DNS protocols. In this case, you should consider setting up unencrypted DNS. For example, you can use a **linked IP address**. The only requirement for a linked IP address is that it must be a residential IP. | ||
|
|
||
| :::note | ||
|
|
||
|
|
@@ -16,7 +14,9 @@ A **residential IP address** is assigned to a device connected to a residential | |
| ::: | ||
|
|
||
| Sometimes, a residential IP address may already be in use, and if you try to connect to it, AdGuard DNS will prevent the connection. | ||
|
|
||
| 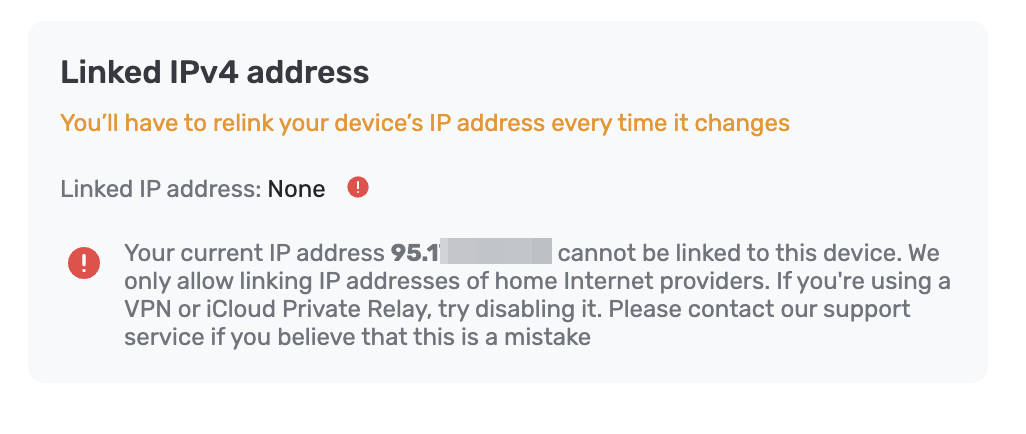 | ||
|
|
||
| If that happens, please reach out to support at [[email protected]](mailto:[email protected]), and they’ll assist you with the right configuration settings. | ||
|
|
||
| ## How to set up linked IP | ||
|
|
@@ -27,11 +27,12 @@ The following instructions explain how to connect to the device via **linking IP | |
| 1. Add a new device or open the settings of a previously connected device. | ||
| 1. Go to *Use DNS server addresses*. | ||
| 1. Open *Plain DNS server addresses* and connect the linked IP. | ||
|
|
||
| 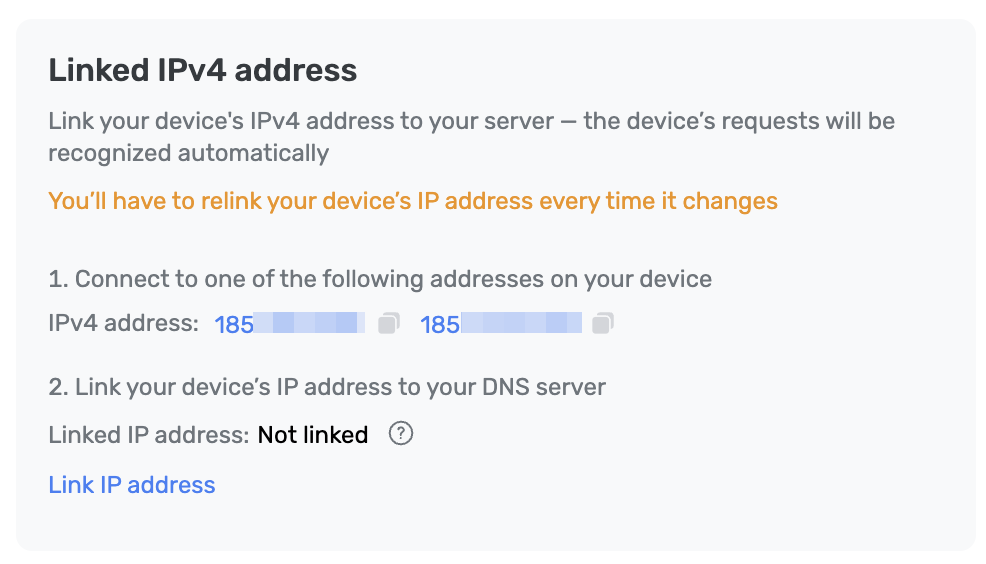 | ||
|
|
||
| ## Dynamic DNS: Why it is useful | ||
|
|
||
| Every time a device connects to the network, it gets a new dynamic IP address. When a device disconnects, the DHCP server reassigns IP addresses to the remaining devices. This means dynamic IP addresses can change frequently and unpredictably. Consequently, you'll need to update settings whenever the device is rebooted or the network changes. | ||
| Every time a device connects to the network, it gets a new dynamic IP address. When a device disconnects, the DHCP server can assign the released IP address to another device on the network. This means dynamic IP addresses change frequently and unpredictably. Consequently, you'll need to update settings whenever the device is rebooted or the network changes. | ||
|
|
||
| To automatically keep the linked IP address updated, you can use DNS. AdGuard DNS will regularly check the IP address of your DDNS domain and link it to your server. | ||
|
|
||
|
|
@@ -49,11 +50,14 @@ This way, you won’t have to manually update the associated IP address each tim | |
| - Go to *Router settings* → *Network* | ||
| - Locate the DDNS or the *Dynamic DNS* section | ||
| - Navigate to it and verify that the settings are indeed supported. *This is just an example of what it may look like. It may vary depending on your router* | ||
|
|
||
| 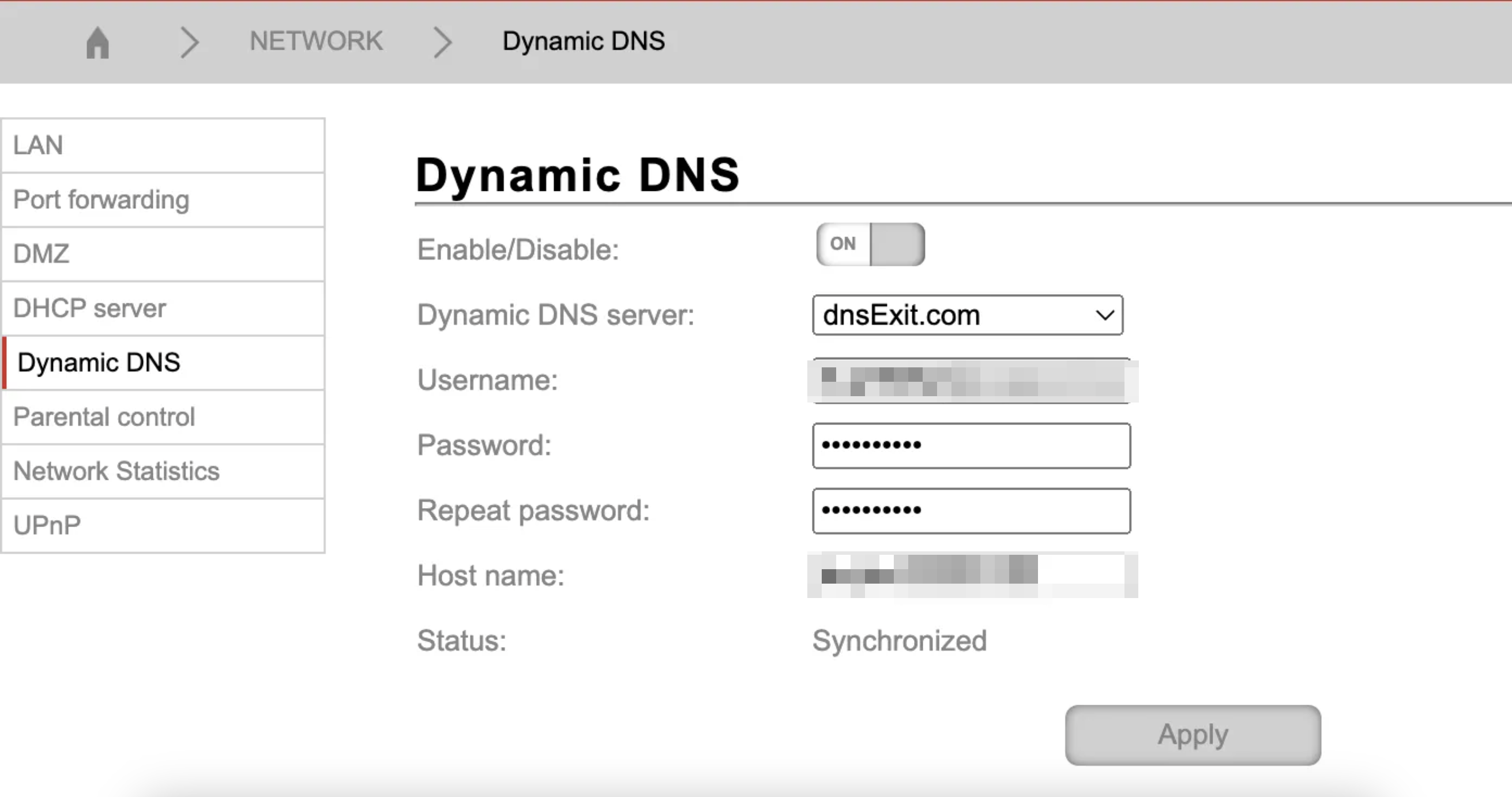 | ||
|
|
||
| 1. Register your domain with a popular service like [DynDNS](https://dyn.com/remote-access/), [NO-IP](https://www.noip.com/), or any other DDNS provider you prefer. | ||
| 1. Enter the domain in your router settings and sync the configurations. | ||
| 1. Go to the Linked IP settings to connect the address, then navigate to *Advanced Settings* and click *Configure DDNS*. | ||
| 1. Input the domain you registered earlier and click *Configure DDNS*. | ||
|
|
||
| 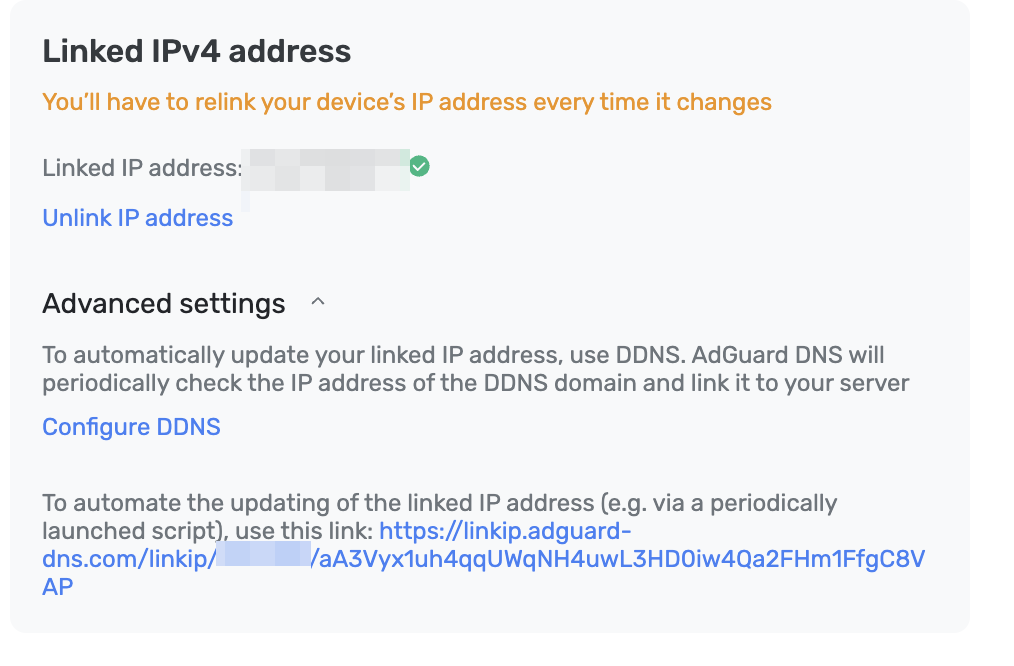 | ||
|
|
||
| All done, you've successfully set up DDNS! | ||
|
|
||
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
Oops, something went wrong.