This repository contains all the Python Notebooks from the "Visualizing Mathematics and its Applications" the Illinois Geometry Lab (IGL) high school camp.
Topics: Evolutionary Biology, Prisoner's Dilemma, Reinforcement Learning, Q-Learning, Moran Processes.
Evolutionary game theory studies how the processes and patterns of evolution change populations over time. Each individual in the population is represented by a player. Game Theory allows us to determine the best outcome for the players by using mathematical models and algorithms. This theory is applicable to many fields such as economics and social sciences.
We focused on the Prisoner's Dilemma, which states the following situation:
- The police captures two suspects and accuses them of a crime.
- The police know they do not have enough evidence to convict either of the suspects of the crime they are accused of committing, but do have enough to convict them both of a lesser crime.
- The police make each of the suspects, individually, an offer captured by the payoff matrix below.
With this payoff matrix, we see that the best individual outcome is to defect while the best collective outcome is to cooperate.
To understand the evolution of cooperation, we simulated the behavior of players when presented with the choice to cooperate or defect and visualized the outcomes.
By repeating these scenarios, we saw different strategies for the player emerge over time (eg. Tit for Tat).
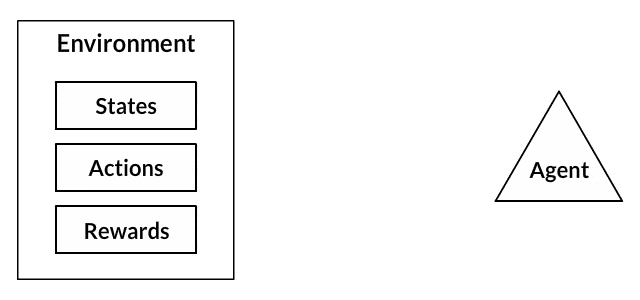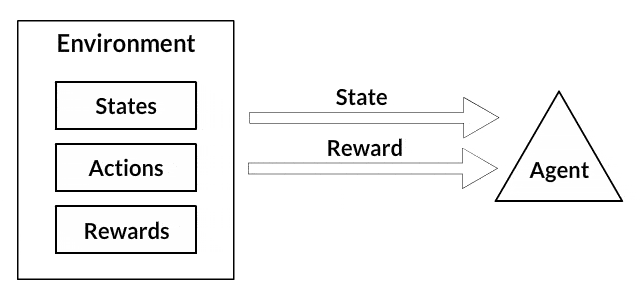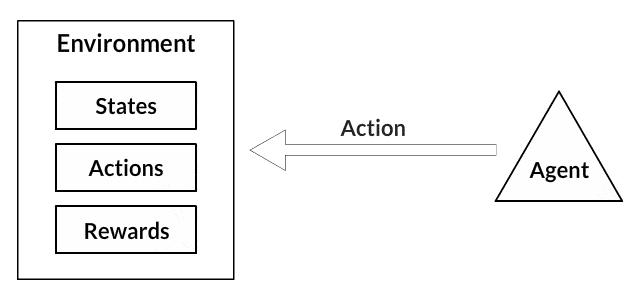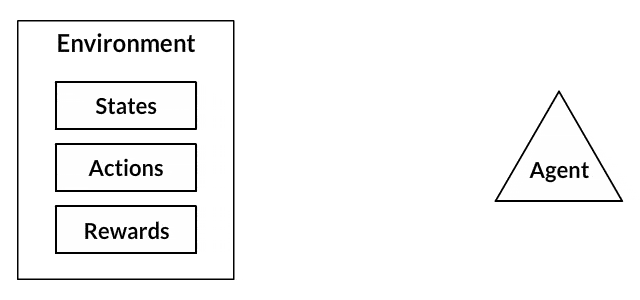
In addition, we used a Q-learning, a reinforcement learning algorithm, to determine the best strategies in a game based on past experience, by considering a set of states, actions, and rewards made by an agent (player).
Using this algorithm, we were able to compare the outcome of Q-learners with different player behaviors (eg. Arrogant, Risky, Cautious, and Hesitant).
- Arrogant Q-learner: This Q learner jumps to quick conclusions and cares about the future.
- Cautious Q-learner: This Q learner is slower to come to conclusions and wants to look ahead more.
- Hesitant Q-learner: This Q learner is slower to come to conclusions and does not look ahead much.
- Risky Q-learner: This Q learner is quick to come to conclusions and doesn’t care about the future.