双指针主要用于遍历数组,两个指针指向不同的元素,从而协同完成任务。
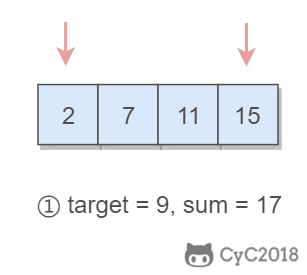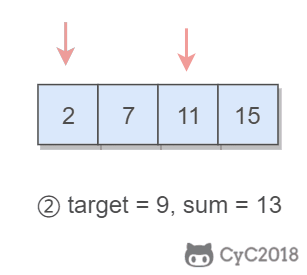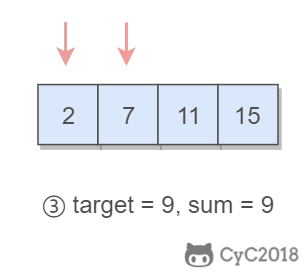
167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted (Easy)
Input: numbers={2, 7, 11, 15}, target=9
Output: index1=1, index2=2题目描述:在有序数组中找出两个数,使它们的和为 target。
使用双指针,一个指针指向值较小的元素,一个指针指向值较大的元素。指向较小元素的指针从头向尾遍历,指向较大元素的指针从尾向头遍历。
- 如果两个指针指向元素的和 sum == target,那么得到要求的结果;
- 如果 sum > target,移动较大的元素,使 sum 变小一些;
- 如果 sum < target,移动较小的元素,使 sum 变大一些。
数组中的元素最多遍历一次,时间复杂度为 O(N)。只使用了两个额外变量,空间复杂度为 O(1)。
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
if (numbers == null) return null;
int i = 0, j = numbers.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = numbers[i] + numbers[j];
if (sum == target) {
return new int[]{i + 1, j + 1};
} else if (sum < target) {
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return null;
}633. Sum of Square Numbers (Easy)
Input: 5
Output: True
Explanation: 1 * 1 + 2 * 2 = 5题目描述:判断一个非负整数是否为两个整数的平方和。
可以看成是在元素为 0~target 的有序数组中查找两个数,使得这两个数的平方和为 target,如果能找到,则返回 true,表示 target 是两个整数的平方和。
本题和 167. Two Sum II - Input array is sorted 类似,只有一个明显区别:一个是和为 target,一个是平方和为 target。本题同样可以使用双指针得到两个数,使其平方和为 target。
本题的关键是右指针的初始化,实现剪枝,从而降低时间复杂度。设右指针为 x,左指针固定为 0,为了使 02 + x2 的值尽可能接近 target,我们可以将 x 取为 sqrt(target)。
因为最多只需要遍历一次 0~sqrt(target),所以时间复杂度为 O(sqrt(target))。又因为只使用了两个额外的变量,因此空间复杂度为 O(1)。
public boolean judgeSquareSum(int target) {
if (target < 0) return false;
int i = 0, j = (int) Math.sqrt(target);
while (i <= j) {
int powSum = i * i + j * j;
if (powSum == target) {
return true;
} else if (powSum > target) {
j--;
} else {
i++;
}
}
return false;
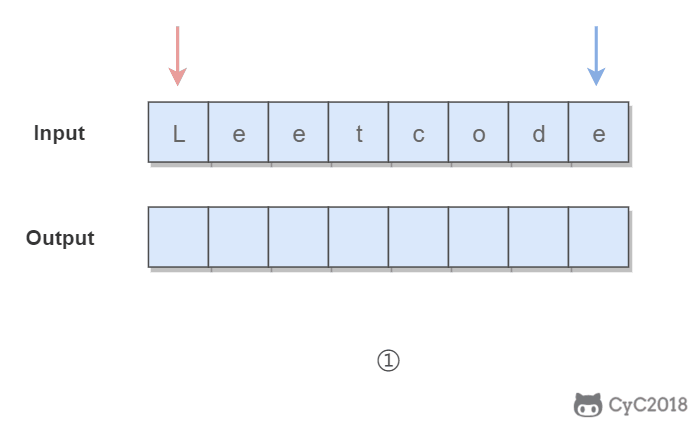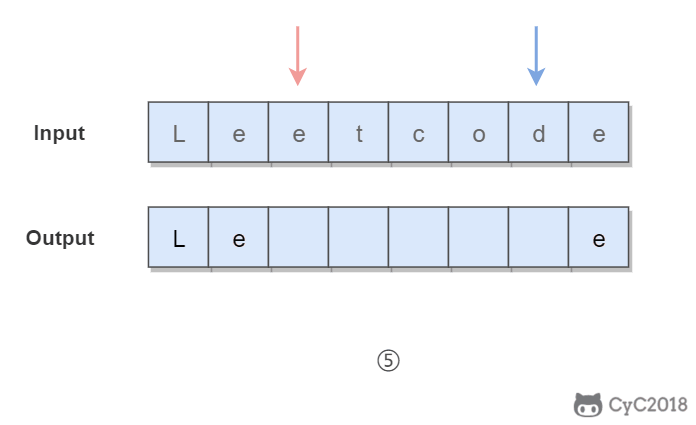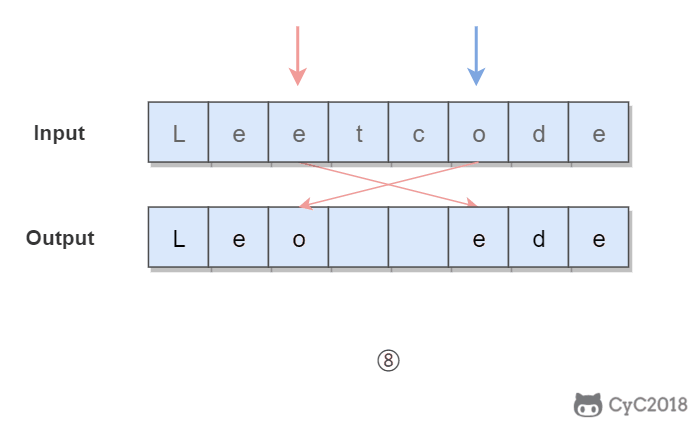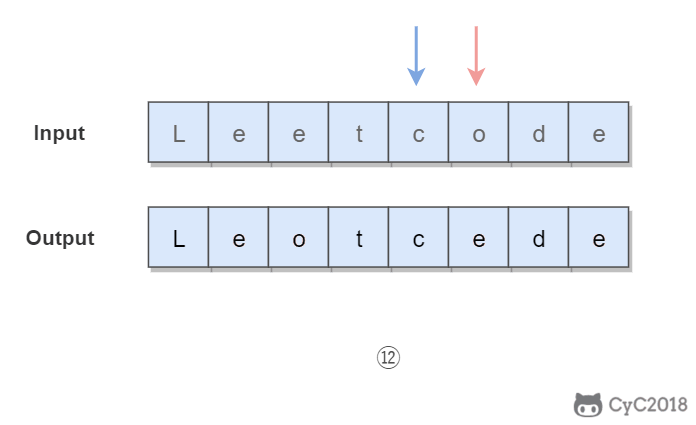
}345. Reverse Vowels of a String (Easy)
Given s = "leetcode", return "leotcede".使用双指针,一个指针从头向尾遍历,一个指针从尾到头遍历,当两个指针都遍历到元音字符时,交换这两个元音字符。
为了快速判断一个字符是不是元音字符,我们将全部元音字符添加到集合 HashSet 中,从而以 O(1) 的时间复杂度进行该操作。
- 时间复杂度为 O(N):只需要遍历所有元素一次
- 空间复杂度 O(1):只需要使用两个额外变量
private final static HashSet<Character> vowels = new HashSet<>(
Arrays.asList('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U'));
public String reverseVowels(String s) {
if (s == null) return null;
int i = 0, j = s.length() - 1;
char[] result = new char[s.length()];
while (i <= j) {
char ci = s.charAt(i);
char cj = s.charAt(j);
if (!vowels.contains(ci)) {
result[i++] = ci;
} else if (!vowels.contains(cj)) {
result[j--] = cj;
} else {
result[i++] = cj;
result[j--] = ci;
}
}
return new String(result);
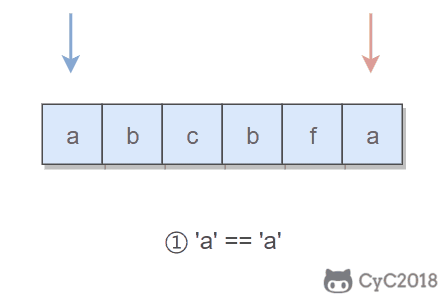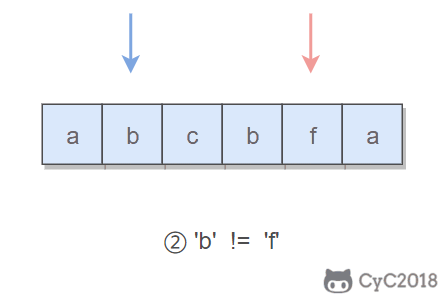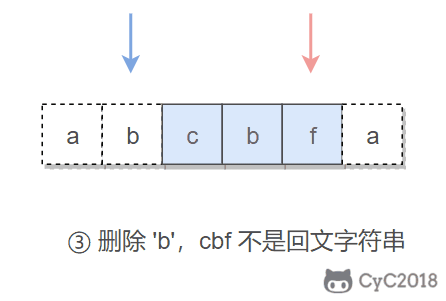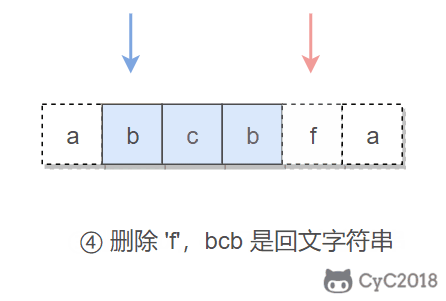
}680. Valid Palindrome II (Easy)
Input: "abca"
Output: True
Explanation: You could delete the character 'c'.题目描述:可以删除一个字符,判断是否能构成回文字符串。
所谓的回文字符串,是指具有左右对称特点的字符串,例如 "abcba" 就是一个回文字符串。
使用双指针可以很容易判断一个字符串是否是回文字符串:令一个指针从左到右遍历,一个指针从右到左遍历,这两个指针同时移动一个位置,每次都判断两个指针指向的字符是否相同,如果都相同,字符串才是具有左右对称性质的回文字符串。
本题的关键是处理删除一个字符。在使用双指针遍历字符串时,如果出现两个指针指向的字符不相等的情况,我们就试着删除一个字符,再判断删除完之后的字符串是否是回文字符串。
在判断是否为回文字符串时,我们不需要判断整个字符串,因为左指针左边和右指针右边的字符之前已经判断过具有对称性质,所以只需要判断中间的子字符串即可。
在试着删除字符时,我们既可以删除左指针指向的字符,也可以删除右指针指向的字符。
public boolean validPalindrome(String s) {
for (int i = 0, j = s.length() - 1; i < j; i++, j--) {
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
return isPalindrome(s, i, j - 1) || isPalindrome(s, i + 1, j);
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int i, int j) {
while (i < j) {
if (s.charAt(i++) != s.charAt(j--)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}88. Merge Sorted Array (Easy)
Input:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]题目描述:把归并结果存到第一个数组上。
需要从尾开始遍历,否则在 nums1 上归并得到的值会覆盖还未进行归并比较的值。
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int index1 = m - 1, index2 = n - 1;
int indexMerge = m + n - 1;
while (index2 >= 0) {
if (index1 < 0) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums2[index2--];
} else if (index2 < 0) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums1[index1--];
} else if (nums1[index1] > nums2[index2]) {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums1[index1--];
} else {
nums1[indexMerge--] = nums2[index2--];
}
}
}141. Linked List Cycle (Easy)
使用双指针,一个指针每次移动一个节点,一个指针每次移动两个节点,如果存在环,那么这两个指针一定会相遇。
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode l1 = head, l2 = head.next;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null && l2.next != null) {
if (l1 == l2) {
return true;
}
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next.next;
}
return false;
}524. Longest Word in Dictionary through Deleting (Medium)
Input:
s = "abpcplea", d = ["ale","apple","monkey","plea"]
Output:
"apple"
题目描述:删除 s 中的一些字符,使得它构成字符串列表 d 中的一个字符串,找出能构成的最长字符串。如果有多个相同长度的结果,返回字典序的最小字符串。
通过删除字符串 s 中的一个字符能得到字符串 t,可以认为 t 是 s 的子序列,我们可以使用双指针来判断一个字符串是否为另一个字符串的子序列。
public String findLongestWord(String s, List<String> d) {
String longestWord = "";
for (String target : d) {
int l1 = longestWord.length(), l2 = target.length();
if (l1 > l2 || (l1 == l2 && longestWord.compareTo(target) < 0)) {
continue;
}
if (isSubstr(s, target)) {
longestWord = target;
}
}
return longestWord;
}
private boolean isSubstr(String s, String target) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < s.length() && j < target.length()) {
if (s.charAt(i) == target.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
i++;
}
return j == target.length();
}283. Move Zeroes (Easy)力扣
Given an integer array nums, move all 0's to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
Note that you must do this in-place without making a copy of the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0,1,0,3,12]
Output: [1,3,12,0,0]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0]
Output: [0]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104
-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
使用双指针,左指针指向当前已经处理好的序列的尾部,右指针指向待处理序列的头部。
右指针不断向右移动,每次右指针指向非零数,则将左右指针对应的数交换,同时左指针右移。

注意到以下性质:
左指针左边均为非零数;
右指针左边直到左指针处均为零。
因此每次交换,都是将左指针的零与右指针的非零数交换,且非零数的相对顺序并未改变。
class Solution:
def moveZeroes(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
n = len(nums)
left = right = 0
while right < n:
if nums[right] != 0:#调换位置时关键是右边不为0
nums[left], nums[right] = nums[right], nums[left]
left += 1
right += 1复杂度分析:
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为序列长度。每个位置至多被遍历两次。
空间复杂度:O(1)。只需要常数的空间存放若干变量。