This is the official implementation for the NeurIPS paper:
Lingjiao Chen, Matei Zaharia, James Zou, Estimating and Explaining Model Performance When Both Covariates and Labels Shift, NeurIPS 2022.
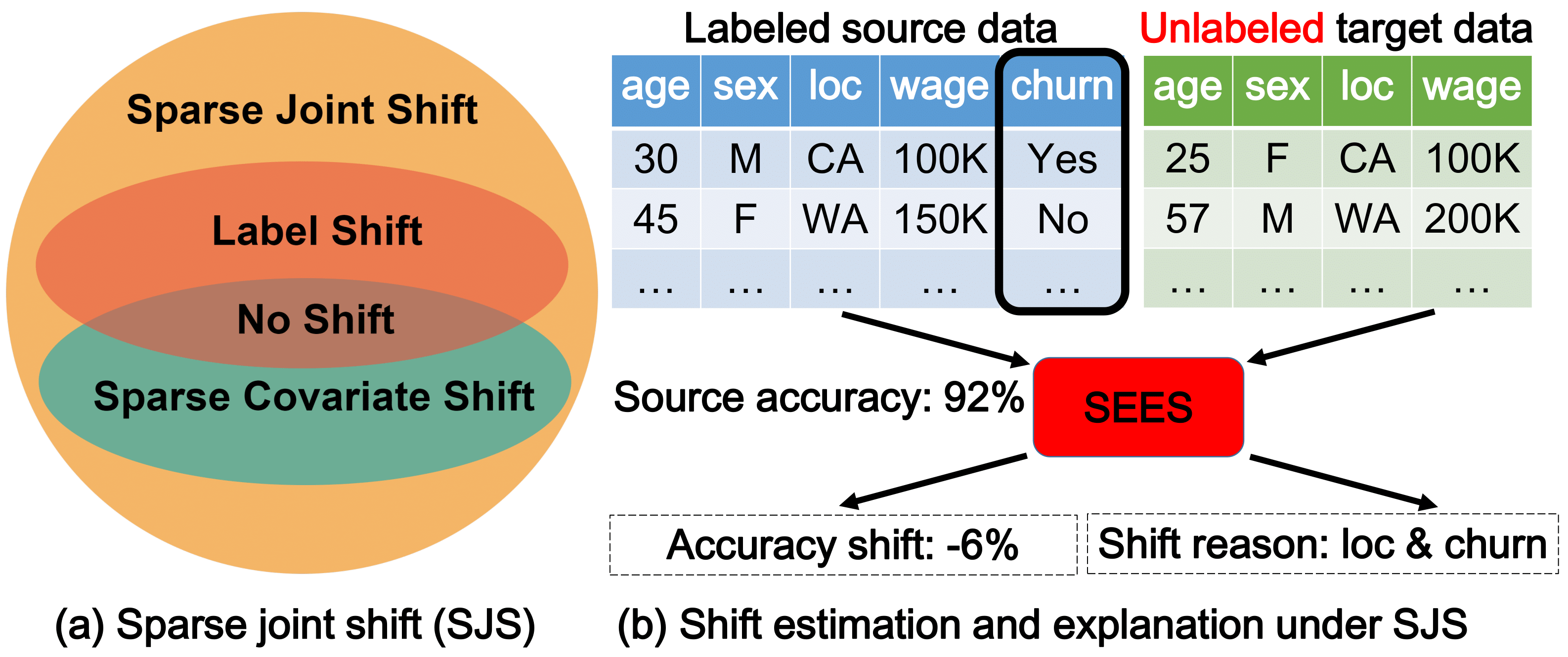
Deployed machine learning (ML) models often encounter new user data that differs from their training data. Therefore, estimating how well a given model might perform on the new data is an important step toward reliable ML applications. This is very challenging, however, as the data distribution can change in flexible ways, and we may not have any labels on the new data, which is often the case in monitoring settings. In this paper, we propose a new distribution shift model, Sparse Joint Shift (SJS), which considers the joint shift of both labels and a few features. This unifies and generalizes several existing shift models including label shift and sparse covariate shift, where only marginal feature or label distribution shifts are considered. We describe mathematical conditions under which SJS is identifiable. We further propose SEES, an algorithmic framework to characterize the distribution shift under SJS and to estimate a model's performance on new data without any labels. We conduct extensive experiments on several real-world datasets with various ML models. Across different datasets and distribution shifts, SEES achieves significant (up to an order of magnitude) shift estimation error improvements over existing approaches.
This code was tested with python3.8. To install it, simply clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/stanford-futuredata/SparseJointShift
and then execute
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
The core performance estimation method is implemented in sees.py. To use it for performance estimation on unlabeled target datasets, one can create a sees object, and then invoke the estimate_shift() method.
For example, the following code snippet shows how to estimate performance on a given target dataset
from sees import Seesd
SSEst = Seesd() # SEES-d
result_est = SSEst.estimate_shift(source=source,
target=target,
source_y=source_y,
source_yhat=source_yhat,
target_yhat=target_yhat,
source_proba = source_proba,
target_proba = target_proba,
)
Here, source and target are the feature vectors from the source and target data, source_y is the label on the source data. source_yhat, source_proba, target_yhat and target_proba are the predicted labels and label confidences produced by the model on the source and target data, respectively. It returns (i) the estimated shifted features, and (ii) estimated performance gap (accuracy on target-accuracy on source).
More examples can be found in the examples.py.
If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to reach out to lingjiao [at] stanford [dot] edu.
If you find our work useful in your research, please cite:
@inproceedings{Chen2022SparseJointShift,
author = {Lingjiao Chen
and Matei Zaharia
and James Zou},
title = {Estimating and Explaining Model Performance When Both Covariates and Labels Shift},
booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)},
year={2022}
}
Apache 2.0 © Lingjiao Chen.