- This code is released under GPL v.2.0 and implements in Python:
- Symbolic Aggregate approXimation (i.e., SAX) stack [LIN2002]
- a simple function for time series motif discovery [PATEL2001]
- HOT-SAX - a time series anomaly (discord) discovery algorithm [KEOGH2005]
| [LIN2002] | Lin, J., Keogh, E., Patel, P., and Lonardi, S., Finding Motifs in Time Series, The 2nd Workshop on Temporal Data Mining, the 8th ACM Int'l Conference on KDD (2002) |
| [PATEL2001] | Patel, P., Keogh, E., Lin, J., Lonardi, S., Mining Motifs in Massive Time Series Databases, In Proc. ICDM (2002) |
| [KEOGH2005] | Keogh, E., Lin, J., Fu, A., HOT SAX: Efficiently finding the most unusual time series subsequence, In Proc. ICDM (2005) |
Note that the most of the library's functionality is also available in R and Java
If you are using this implementation for you academic work, please cite our Grammarviz 2.0 paper:
| [SENIN2014] | Senin, P., Lin, J., Wang, X., Oates, T., Gandhi, S., Boedihardjo, A.P., Chen, C., Frankenstein, S., Lerner, M., GrammarViz 2.0: a tool for grammar-based pattern discovery in time series, ECML/PKDD, 2014. |
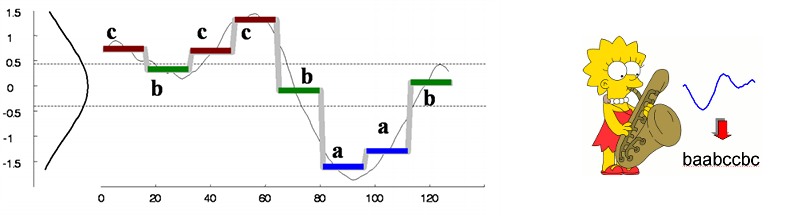
SAX is used to transform a sequence of rational numbers (i.e., a time series) into a sequence of letters (i.e., a string) which is (typically) much shorterthan the input time series. Thus, SAX transform addresses a chief problem in time-series analysis -- the dimensionality curse.
This is an illustration of a time series of 128 points converted into the word of 8 letters:
As discretization is probably the most used transformation in data mining, SAX has been widely used throughout the field. Find more information about SAX at its authors pages: SAX overview by Jessica Lin, Eamonn Keogh's SAX page, or at sax-vsm wiki page.
$ pip install saxpy
GNU General Public License v2.0
saxpy was written by Pavel Senin.