You are given a 2D integer array rectangles where rectangles[i] = [li, hi] indicates that ith rectangle has a length of li and a height of hi. You are also given a 2D integer array points where points[j] = [xj, yj] is a point with coordinates (xj, yj).
The ith rectangle has its bottom-left corner point at the coordinates (0, 0) and its top-right corner point at (li, hi).
Return an integer array count of length points.length where count[j] is the number of rectangles that contain the jth point.
The ith rectangle contains the jth point if 0 <= xj <= li and 0 <= yj <= hi. Note that points that lie on the edges of a rectangle are also considered to be contained by that rectangle.
Example 1:
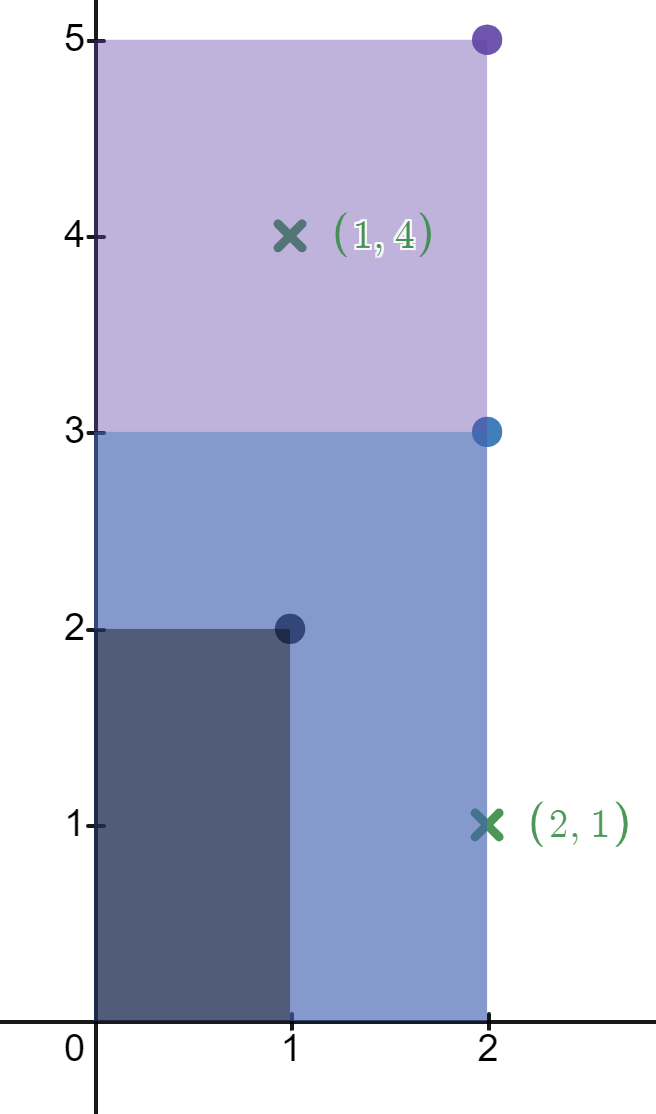
Input: rectangles = [[1,2],[2,3],[2,5]], points = [[2,1],[1,4]] Output: [2,1] Explanation: The first rectangle contains no points. The second rectangle contains only the point (2, 1). The third rectangle contains the points (2, 1) and (1, 4). The number of rectangles that contain the point (2, 1) is 2. The number of rectangles that contain the point (1, 4) is 1. Therefore, we return [2, 1].
Example 2:
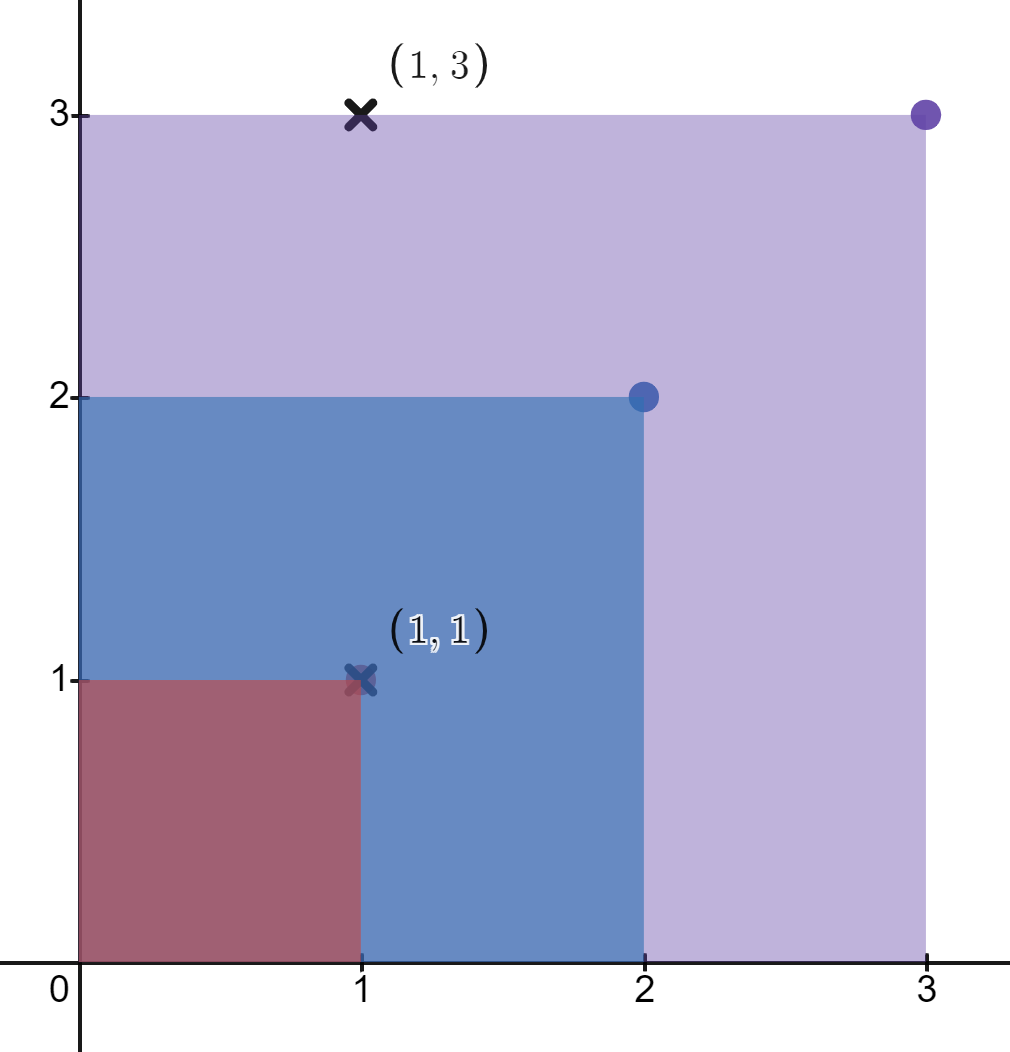
Input: rectangles = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]], points = [[1,3],[1,1]] Output: [1,3] Explanation: The first rectangle contains only the point (1, 1). The second rectangle contains only the point (1, 1). The third rectangle contains the points (1, 3) and (1, 1). The number of rectangles that contain the point (1, 3) is 1. The number of rectangles that contain the point (1, 1) is 3. Therefore, we return [1, 3].
Constraints:
1 <= rectangles.length, points.length <= 5 * 104rectangles[i].length == points[j].length == 21 <= li, xj <= 1091 <= hi, yj <= 100- All the
rectanglesare unique. - All the
pointsare unique.
class Solution:
def countRectangles(
self, rectangles: List[List[int]], points: List[List[int]]
) -> List[int]:
d = defaultdict(list)
for x, y in rectangles:
d[y].append(x)
for y in d.keys():
d[y].sort()
ans = []
for x, y in points:
cnt = 0
for h in range(y, 101):
xs = d[h]
cnt += len(xs) - bisect_left(xs, x)
ans.append(cnt)
return ansclass Solution {
public int[] countRectangles(int[][] rectangles, int[][] points) {
int n = 101;
List<Integer>[] d = new List[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
d[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int[] r : rectangles) {
d[r[1]].add(r[0]);
}
for (List<Integer> v : d) {
Collections.sort(v);
}
int m = points.length;
int[] ans = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int x = points[i][0], y = points[i][1];
int cnt = 0;
for (int h = y; h < n; ++h) {
List<Integer> xs = d[h];
int left = 0, right = xs.size();
while (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (xs.get(mid) >= x) {
right = mid;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
cnt += xs.size() - left;
}
ans[i] = cnt;
}
return ans;
}
}function countRectangles(rectangles: number[][], points: number[][]): number[] {
const n = 101;
let ymap = Array.from({ length: n }, v => []);
for (let [x, y] of rectangles) {
ymap[y].push(x);
}
for (let nums of ymap) {
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
}
let ans = [];
for (let [x, y] of points) {
let count = 0;
for (let h = y; h < n; h++) {
const nums = ymap[h];
let left = 0,
right = nums.length;
while (left < right) {
let mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if (x > nums[mid]) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
count += nums.length - right;
}
ans.push(count);
}
return ans;
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> countRectangles(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles, vector<vector<int>>& points) {
int n = 101;
vector<vector<int>> d(n);
for (auto& r : rectangles) d[r[1]].push_back(r[0]);
for (auto& v : d) sort(v.begin(), v.end());
vector<int> ans;
for (auto& p : points) {
int x = p[0], y = p[1];
int cnt = 0;
for (int h = y; h < n; ++h) {
auto& xs = d[h];
cnt += xs.size() - (lower_bound(xs.begin(), xs.end(), x) - xs.begin());
}
ans.push_back(cnt);
}
return ans;
}
};func countRectangles(rectangles [][]int, points [][]int) []int {
n := 101
d := make([][]int, 101)
for _, r := range rectangles {
d[r[1]] = append(d[r[1]], r[0])
}
for _, v := range d {
sort.Ints(v)
}
var ans []int
for _, p := range points {
x, y := p[0], p[1]
cnt := 0
for h := y; h < n; h++ {
xs := d[h]
left, right := 0, len(xs)
for left < right {
mid := (left + right) >> 1
if xs[mid] >= x {
right = mid
} else {
left = mid + 1
}
}
cnt += len(xs) - left
}
ans = append(ans, cnt)
}
return ans
}