常见的微波炉可以设置加热时间,且加热时间满足以下条件:
- 至少为
1秒钟。 - 至多为
99分99秒。
你可以 最多 输入 4 个数字 来设置加热时间。如果你输入的位数不足 4 位,微波炉会自动加 前缀 0 来补足 4 位。微波炉会将设置好的四位数中,前 两位当作分钟数,后 两位当作秒数。它们所表示的总时间就是加热时间。比方说:
- 你输入
954(三个数字),被自动补足为0954,并表示9分54秒。 - 你输入
0008(四个数字),表示0分8秒。 - 你输入
8090,表示80分90秒。 - 你输入
8130,表示81分30秒。
给你整数 startAt ,moveCost ,pushCost 和 targetSeconds 。一开始,你的手指在数字 startAt 处。将手指移到 任何其他数字 ,需要花费 moveCost 的单位代价。每 输入你手指所在位置的数字一次,需要花费 pushCost 的单位代价。
要设置 targetSeconds 秒的加热时间,可能会有多种设置方法。你想要知道这些方法中,总代价最小为多少。
请你能返回设置 targetSeconds 秒钟加热时间需要花费的最少代价。
请记住,虽然微波炉的秒数最多可以设置到 99 秒,但一分钟等于 60 秒。
示例 1:
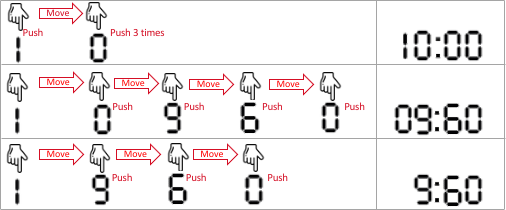
输入:startAt = 1, moveCost = 2, pushCost = 1, targetSeconds = 600 输出:6 解释:以下为设置加热时间的所有方法。 - 1 0 0 0 ,表示 10 分 0 秒。 手指一开始就在数字 1 处,输入 1 (代价为 1),移到 0 处(代价为 2),输入 0(代价为 1),输入 0(代价为 1),输入 0(代价为 1)。 总代价为:1 + 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 6 。这是所有方案中的最小代价。 - 0 9 6 0,表示 9 分 60 秒。它也表示 600 秒。 手指移到 0 处(代价为 2),输入 0 (代价为 1),移到 9 处(代价为 2),输入 9(代价为 1),移到 6 处(代价为 2),输入 6(代价为 1),移到 0 处(代价为 2),输入 0(代价为 1)。 总代价为:2 + 1 + 2 + 1 + 2 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 12 。 - 9 6 0,微波炉自动补全为 0960 ,表示 9 分 60 秒。 手指移到 9 处(代价为 2),输入 9 (代价为 1),移到 6 处(代价为 2),输入 6(代价为 1),移到 0 处(代价为 2),输入 0(代价为 1)。 总代价为:2 + 1 + 2 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 9 。
示例 2:
输入:startAt = 0, moveCost = 1, pushCost = 2, targetSeconds = 76 输出:6 解释:最优方案为输入两个数字 7 6,表示 76 秒。 手指移到 7 处(代价为 1),输入 7 (代价为 2),移到 6 处(代价为 1),输入 6(代价为 2)。总代价为:1 + 2 + 1 + 2 = 6 其他可行方案为 0076 ,076 ,0116 和 116 ,但是它们的代价都比 6 大。
提示:
0 <= startAt <= 91 <= moveCost, pushCost <= 1051 <= targetSeconds <= 6039
class Solution:
def minCostSetTime(
self, startAt: int, moveCost: int, pushCost: int, targetSeconds: int
) -> int:
def f(m, s):
if not 0 <= m < 100 or not 0 <= s < 100:
return inf
arr = [m // 10, m % 10, s // 10, s % 10]
i = 0
while i < 4 and arr[i] == 0:
i += 1
t = 0
prev = startAt
for v in arr[i:]:
if v != prev:
t += moveCost
t += pushCost
prev = v
return t
m, s = divmod(targetSeconds, 60)
ans = min(f(m, s), f(m - 1, s + 60))
return ansclass Solution {
public int minCostSetTime(int startAt, int moveCost, int pushCost, int targetSeconds) {
int m = targetSeconds / 60;
int s = targetSeconds % 60;
return Math.min(
f(m, s, startAt, moveCost, pushCost), f(m - 1, s + 60, startAt, moveCost, pushCost));
}
private int f(int m, int s, int prev, int moveCost, int pushCost) {
if (m < 0 || m > 99 || s < 0 || s > 99) {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
int[] arr = new int[] {m / 10, m % 10, s / 10, s % 10};
int i = 0;
for (; i < 4 && arr[i] == 0; ++i)
;
int t = 0;
for (; i < 4; ++i) {
if (arr[i] != prev) {
t += moveCost;
}
t += pushCost;
prev = arr[i];
}
return t;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int minCostSetTime(int startAt, int moveCost, int pushCost, int targetSeconds) {
int m = targetSeconds / 60, s = targetSeconds % 60;
return min(f(m, s, startAt, moveCost, pushCost), f(m - 1, s + 60, startAt, moveCost, pushCost));
}
int f(int m, int s, int prev, int moveCost, int pushCost) {
if (m < 0 || m > 99 || s < 0 || s > 99) return INT_MAX;
vector<int> arr = {m / 10, m % 10, s / 10, s % 10};
int i = 0;
for (; i < 4 && arr[i] == 0; ++i)
;
int t = 0;
for (; i < 4; ++i) {
if (arr[i] != prev) t += moveCost;
t += pushCost;
prev = arr[i];
}
return t;
}
};func minCostSetTime(startAt int, moveCost int, pushCost int, targetSeconds int) int {
m, s := targetSeconds/60, targetSeconds%60
f := func(m, s int) int {
if m < 0 || m > 99 || s < 0 || s > 99 {
return 0x3f3f3f3f
}
arr := []int{m / 10, m % 10, s / 10, s % 10}
i := 0
for ; i < 4 && arr[i] == 0; i++ {
}
t := 0
prev := startAt
for ; i < 4; i++ {
if arr[i] != prev {
t += moveCost
}
t += pushCost
prev = arr[i]
}
return t
}
return min(f(m, s), f(m-1, s+60))
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}