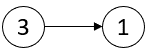
链表中的 临界点 定义为一个 局部极大值点 或 局部极小值点 。
如果当前节点的值 严格大于 前一个节点和后一个节点,那么这个节点就是一个 局部极大值点 。
如果当前节点的值 严格小于 前一个节点和后一个节点,那么这个节点就是一个 局部极小值点 。
注意:节点只有在同时存在前一个节点和后一个节点的情况下,才能成为一个 局部极大值点 / 极小值点 。
给你一个链表 head ,返回一个长度为 2 的数组 [minDistance, maxDistance] ,其中 minDistance 是任意两个不同临界点之间的最小距离,maxDistance 是任意两个不同临界点之间的最大距离。如果临界点少于两个,则返回 [-1,-1] 。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,1] 输出:[-1,-1] 解释:链表 [3,1] 中不存在临界点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [5,3,1,2,5,1,2] 输出:[1,3] 解释:存在三个临界点: - [5,3,1,2,5,1,2]:第三个节点是一个局部极小值点,因为 1 比 3 和 2 小。 - [5,3,1,2,5,1,2]:第五个节点是一个局部极大值点,因为 5 比 2 和 1 大。 - [5,3,1,2,5,1,2]:第六个节点是一个局部极小值点,因为 1 比 5 和 2 小。 第五个节点和第六个节点之间距离最小。minDistance = 6 - 5 = 1 。 第三个节点和第六个节点之间距离最大。maxDistance = 6 - 3 = 3 。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,3,2,2,3,2,2,2,7] 输出:[3,3] 解释:存在两个临界点: - [1,3,2,2,3,2,2,2,7]:第二个节点是一个局部极大值点,因为 3 比 1 和 2 大。 - [1,3,2,2,3,2,2,2,7]:第五个节点是一个局部极大值点,因为 3 比 2 和 2 大。 最小和最大距离都存在于第二个节点和第五个节点之间。 因此,minDistance 和 maxDistance 是 5 - 2 = 3 。 注意,最后一个节点不算一个局部极大值点,因为它之后就没有节点了。
示例 4:
输入:head = [2,3,3,2] 输出:[-1,-1] 解释:链表 [2,3,3,2] 中不存在临界点。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数量在范围
[2, 105]内 1 <= Node.val <= 105
遍历链表,维护第一个临界点 first、最后一个临界点 last,以及相邻临界点的最小距离。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def nodesBetweenCriticalPoints(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> List[int]:
prev, curr = head, head.next
first = last = None
i = 1
ans = [inf, -inf]
while curr.next:
if curr.val < min(prev.val, curr.next.val) or curr.val > max(
prev.val, curr.next.val
):
if last is None:
first = last = i
else:
ans[0] = min(ans[0], i - last)
ans[1] = i - first
last = i
i += 1
prev, curr = curr, curr.next
return ans if first != last else [-1, -1]/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] nodesBetweenCriticalPoints(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = head;
ListNode curr = head.next;
int first = 0, last = 0;
int i = 1;
int[] ans = new int[] {Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE};
while (curr.next != null) {
if (curr.val < Math.min(prev.val, curr.next.val)
|| curr.val > Math.max(prev.val, curr.next.val)) {
if (last == 0) {
first = i;
last = i;
} else {
ans[0] = Math.min(ans[0], i - last);
ans[1] = i - first;
last = i;
}
}
++i;
prev = curr;
curr = curr.next;
}
return first == last ? new int[] {-1, -1} : ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function nodesBetweenCriticalPoints(head: ListNode | null): number[] {
let idx = 1;
let pre = head.val;
head = head.next;
let nums = [];
while (head.next != null) {
let val = head.val,
post = head.next.val;
if (pre < val && val > post) {
nums.push(idx);
}
if (pre > val && val < post) {
nums.push(idx);
}
pre = val;
idx++;
head = head.next;
}
let n = nums.length;
if (n < 2) return [-1, -1];
let min = Infinity;
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
min = Math.min(nums[i] - nums[i - 1], min);
}
return [min, nums[n - 1] - nums[0]];
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nodesBetweenCriticalPoints(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* prev = head;
ListNode* curr = head->next;
int first = 0, last = 0;
int i = 1;
vector<int> ans(2, INT_MAX);
while (curr->next) {
if (curr->val < min(prev->val, curr->next->val) || curr->val > max(prev->val, curr->next->val)) {
if (last == 0)
first = i;
else {
ans[0] = min(ans[0], i - last);
ans[1] = i - first;
}
last = i;
}
++i;
prev = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
if (first == last) return {-1, -1};
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func nodesBetweenCriticalPoints(head *ListNode) []int {
prev, curr := head, head.Next
first, last := 0, 0
i := 1
ans := []int{math.MaxInt32, 0}
for curr.Next != nil {
if curr.Val < min(prev.Val, curr.Next.Val) || curr.Val > max(prev.Val, curr.Next.Val) {
if last == 0 {
first, last = i, i
} else {
ans[0] = min(ans[0], i-last)
ans[1] = i - first
last = i
}
}
i++
prev, curr = curr, curr.Next
}
if first == last {
return []int{-1, -1}
}
return ans
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}