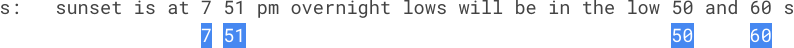A sentence is a list of tokens separated by a single space with no leading or trailing spaces. Every token is either a positive number consisting of digits 0-9 with no leading zeros, or a word consisting of lowercase English letters.
- For example,
"a puppy has 2 eyes 4 legs"is a sentence with seven tokens:"2"and"4"are numbers and the other tokens such as"puppy"are words.
Given a string s representing a sentence, you need to check if all the numbers in s are strictly increasing from left to right (i.e., other than the last number, each number is strictly smaller than the number on its right in s).
Return true if so, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: s = "1 box has 3 blue 4 red 6 green and 12 yellow marbles" Output: true Explanation: The numbers in s are: 1, 3, 4, 6, 12. They are strictly increasing from left to right: 1 < 3 < 4 < 6 < 12.
Example 2:
Input: s = "hello world 5 x 5" Output: false Explanation: The numbers in s are: 5, 5. They are not strictly increasing.
Example 3:
Input: s = "sunset is at 7 51 pm overnight lows will be in the low 50 and 60 s" Output: false Explanation: The numbers in s are: 7, 51, 50, 60. They are not strictly increasing.
Constraints:
3 <= s.length <= 200sconsists of lowercase English letters, spaces, and digits from0to9, inclusive.- The number of tokens in
sis between2and100, inclusive. - The tokens in
sare separated by a single space. - There are at least two numbers in
s. - Each number in
sis a positive number less than100, with no leading zeros. scontains no leading or trailing spaces.
class Solution:
def areNumbersAscending(self, s: str) -> bool:
curr = 0
for t in s.split(' '):
if t[0].isdigit():
if curr >= int(t):
return False
curr = int(t)
return Trueclass Solution {
public boolean areNumbersAscending(String s) {
int curr = 0;
for (String t : s.split(" ")) {
char c = t.charAt(0);
if (Character.isDigit(c)) {
int x = Integer.parseInt(t);
if (curr >= x) {
return false;
}
curr = x;
}
}
return true;
}
}function areNumbersAscending(s: string): boolean {
let strs = s.split(' ');
let prev = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
for (let str of strs) {
let num = Number(str);
if (!isNaN(num)) {
if (num <= prev) return false;
prev = num;
}
}
return true;
}class Solution {
public:
bool areNumbersAscending(string s) {
int curr = 0;
istringstream is(s);
string t;
while (is >> t) {
if (isdigit(t[0])) {
int x = stoi(t);
if (curr >= x) return false;
curr = x;
}
}
return true;
}
};func areNumbersAscending(s string) bool {
curr := 0
for _, t := range strings.Split(s, " ") {
if unicode.IsDigit(rune(t[0])) {
x, _ := strconv.Atoi(t)
if curr >= x {
return false
}
curr = x
}
}
return true
}