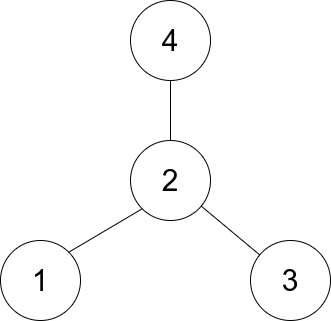
There is an undirected star graph consisting of n nodes labeled from 1 to n. A star graph is a graph where there is one center node and exactly n - 1 edges that connect the center node with every other node.
You are given a 2D integer array edges where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between the nodes ui and vi. Return the center of the given star graph.
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[4,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: As shown in the figure above, node 2 is connected to every other node, so 2 is the center.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[1,2],[5,1],[1,3],[1,4]] Output: 1
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 105edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 21 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi- The given
edgesrepresent a valid star graph.
class Solution:
def findCenter(self, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
return edges[0][0] if edges[0][0] in edges[1] else edges[0][1]class Solution {
public int findCenter(int[][] edges) {
int a = edges[0][0], b = edges[0][1];
int c = edges[1][0], d = edges[1][1];
return a == c || a == d ? a : b;
}
}function findCenter(edges: number[][]): number {
for (let num of edges[0]) {
if (edges[1].includes(num)) {
return num;
}
}
}class Solution {
public:
int findCenter(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int a = edges[0][0], b = edges[0][1];
int c = edges[1][0], d = edges[1][1];
return a == c || a == d ? a : b;
}
};func findCenter(edges [][]int) int {
a, b := edges[0][0], edges[0][1]
c, d := edges[1][0], edges[1][1]
if a == c || a == d {
return a
}
return b
}impl Solution {
pub fn find_center(edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
if edges[0][0] == edges[1][0] || edges[0][0] == edges[1][1] {
return edges[0][0];
}
edges[0][1]
}
}/**
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number}
*/
var findCenter = function (edges) {
const [a, b] = edges[0];
const [c, d] = edges[1];
return a == c || a == d ? a : b;
};