You are given an integer matrix isWater of size m x n that represents a map of land and water cells.
- If
isWater[i][j] == 0, cell(i, j)is a land cell. - If
isWater[i][j] == 1, cell(i, j)is a water cell.
You must assign each cell a height in a way that follows these rules:
- The height of each cell must be non-negative.
- If the cell is a water cell, its height must be
0. - Any two adjacent cells must have an absolute height difference of at most
1. A cell is adjacent to another cell if the former is directly north, east, south, or west of the latter (i.e., their sides are touching).
Find an assignment of heights such that the maximum height in the matrix is maximized.
Return an integer matrix height of size m x n where height[i][j] is cell (i, j)'s height. If there are multiple solutions, return any of them.
Example 1:
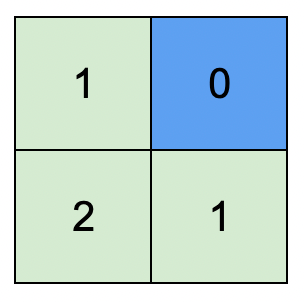
Input: isWater = [[0,1],[0,0]] Output: [[1,0],[2,1]] Explanation: The image shows the assigned heights of each cell. The blue cell is the water cell, and the green cells are the land cells.
Example 2:
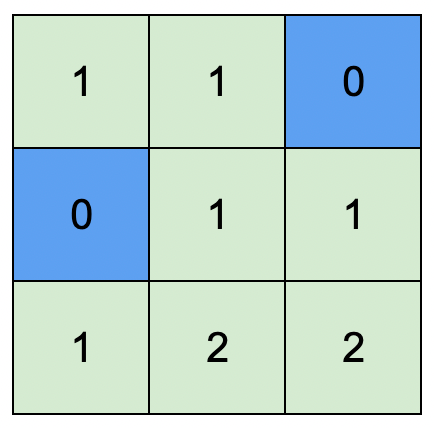
Input: isWater = [[0,0,1],[1,0,0],[0,0,0]] Output: [[1,1,0],[0,1,1],[1,2,2]] Explanation: A height of 2 is the maximum possible height of any assignment. Any height assignment that has a maximum height of 2 while still meeting the rules will also be accepted.
Constraints:
m == isWater.lengthn == isWater[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1000isWater[i][j]is0or1.- There is at least one water cell.
BFS.
class Solution:
def highestPeak(self, isWater: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(isWater), len(isWater[0])
ans = [[-1] * n for _ in range(m)]
q = deque()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if isWater[i][j] == 1:
ans[i][j] = 0
q.append((i, j))
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for a, b in [[0, -1], [0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and ans[x][y] == -1:
ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1
q.append((x, y))
return ansclass Solution {
private int[][] dirs = new int[][] {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
public int[][] highestPeak(int[][] isWater) {
int m = isWater.length, n = isWater[0].length;
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(ans[i], -1);
}
Deque<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (isWater[i][j] == 1) {
ans[i][j] = 0;
q.offerLast(new int[] {i, j});
}
}
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.pollFirst();
int i = p[0], j = p[1];
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int x = i + dir[0], y = j + dir[1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) {
ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1;
q.offerLast(new int[] {x, y});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}function highestPeak(isWater: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = isWater.length,
n = isWater[0].length;
let ans: Array<Array<number>> = Array.from({ length: m }, v =>
new Array(n).fill(-1),
);
// BFS
let queue: Array<Array<number>> = []; // i, j, num
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (isWater[i][j]) {
ans[i][j] = 0;
queue.push([i, j, 0]);
}
}
}
const directions = [
[0, -1],
[-1, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 0],
]; // left, up, right, down
while (queue.length) {
// 消除push/shift出现超时问题
let tmp: Array<Array<number>> = [];
for (const [i, j, num] of queue) {
for (const [dx, dy] of directions) {
const x = i + dx,
y = j + dy;
// 校验合法的相邻格子
if (x > -1 && x < m && y > -1 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) {
ans[x][y] = num + 1;
tmp.push([x, y, num + 1]);
}
}
}
queue = tmp;
}
return ans;
}typedef pair<int, int> PII;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
vector<vector<int>> highestPeak(vector<vector<int>>& isWater) {
int m = isWater.size(), n = isWater[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
queue<PII> q;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (isWater[i][j] == 1) {
ans[i][j] = 0;
q.push({i, j});
}
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
PII p = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = p.first, j = p.second;
for (auto& dir : dirs) {
int x = i + dir[0], y = j + dir[1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1) {
ans[x][y] = ans[i][j] + 1;
q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};func highestPeak(isWater [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(isWater), len(isWater[0])
ans := make([][]int, m)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range ans[i] {
ans[i][j] = -1
}
}
type pair struct{ i, j int }
var q []pair
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if isWater[i][j] == 1 {
ans[i][j] = 0
q = append(q, pair{i, j})
}
}
}
dirs := [4][2]int{{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]
q = q[1:]
for _, dir := range dirs {
x, y := p.i+dir[0], p.j+dir[1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && ans[x][y] == -1 {
ans[x][y] = ans[p.i][p.j] + 1
q = append(q, pair{x, y})
}
}
}
return ans
}