You are given a string s and an integer array indices of the same length. The string s will be shuffled such that the character at the ith position moves to indices[i] in the shuffled string.
Return the shuffled string.
Example 1:
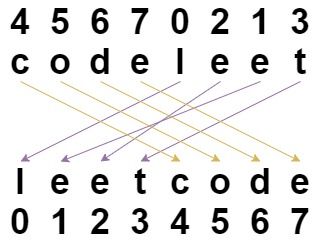
Input: s = "codeleet", indices = [4,5,6,7,0,2,1,3]
Output: "leetcode"
Explanation: As shown, "codeleet" becomes "leetcode" after shuffling.
Example 2:
Input: s = "abc", indices = [0,1,2]
Output: "abc"
Explanation: After shuffling, each character remains in its position.
Constraints:
s.length == indices.length == n1 <= n <= 100sconsists of only lowercase English letters.0 <= indices[i] < n- All values of
indicesare unique.
class Solution:
def restoreString(self, s: str, indices: List[int]) -> str:
ans = [0] * len(s)
for i, c in enumerate(s):
ans[indices[i]] = c
return ''.join(ans)class Solution {
public String restoreString(String s, int[] indices) {
int n = s.length();
char[] ans = new char[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ans[indices[i]] = s.charAt(i);
}
return String.valueOf(ans);
}
}class Solution {
public:
string restoreString(string s, vector<int>& indices) {
int n = s.size();
string ans(n, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ans[indices[i]] = s[i];
return ans;
}
};func restoreString(s string, indices []int) string {
ans := make([]rune, len(s))
for i, c := range s {
ans[indices[i]] = c
}
return string(ans)
}