In a binary tree, a lonely node is a node that is the only child of its parent node. The root of the tree is not lonely because it does not have a parent node.
Given the root of a binary tree, return an array containing the values of all lonely nodes in the tree. Return the list in any order.
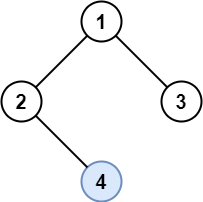
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4] Output: [4] Explanation: Light blue node is the only lonely node. Node 1 is the root and is not lonely. Nodes 2 and 3 have the same parent and are not lonely.
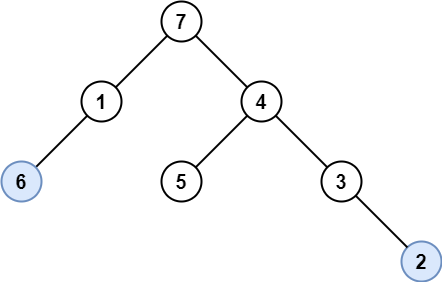
Example 2:
Input: root = [7,1,4,6,null,5,3,null,null,null,null,null,2] Output: [6,2] Explanation: Light blue nodes are lonely nodes. Please remember that order doesn't matter, [2,6] is also an acceptable answer.
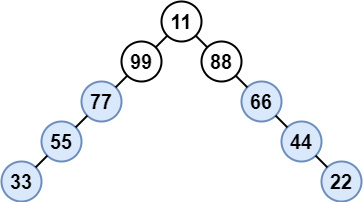
Example 3:
Input: root = [11,99,88,77,null,null,66,55,null,null,44,33,null,null,22] Output: [77,55,33,66,44,22] Explanation: Nodes 99 and 88 share the same parent. Node 11 is the root. All other nodes are lonely.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the
treeis in the range[1, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 106
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def getLonelyNodes(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
def dfs(root):
if root is None or (root.left is None and root.right is None):
return
if root.left is None:
ans.append(root.right.val)
if root.right is None:
ans.append(root.left.val)
dfs(root.left)
dfs(root.right)
ans = []
dfs(root)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> getLonelyNodes(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null || (root.left == null && root.right == null)) {
return;
}
if (root.left == null) {
ans.add(root.right.val);
}
if (root.right == null) {
ans.add(root.left.val);
}
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getLonelyNodes(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans;
function<void(TreeNode* root)> dfs;
dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) {
if (!root || (!root->left && !root->right)) return;
if (!root->left) ans.push_back(root->right->val);
if (!root->right) ans.push_back(root->left->val);
dfs(root->left);
dfs(root->right);
};
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func getLonelyNodes(root *TreeNode) []int {
ans := []int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) {
if root == nil || (root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil) {
return
}
if root.Left == nil {
ans = append(ans, root.Right.Val)
}
if root.Right == nil {
ans = append(ans, root.Left.Val)
}
dfs(root.Left)
dfs(root.Right)
}
dfs(root)
return ans
}