给你一棵以 root 为根的二叉树和一个 head 为第一个节点的链表。
如果在二叉树中,存在一条一直向下的路径,且每个点的数值恰好一一对应以 head 为首的链表中每个节点的值,那么请你返回 True ,否则返回 False 。
一直向下的路径的意思是:从树中某个节点开始,一直连续向下的路径。
示例 1:
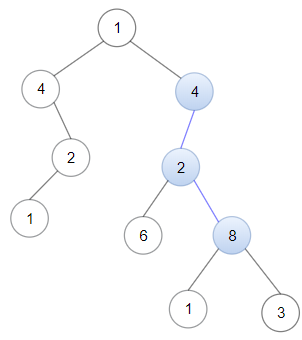
输入:head = [4,2,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] 输出:true 解释:树中蓝色的节点构成了与链表对应的子路径。
示例 2:
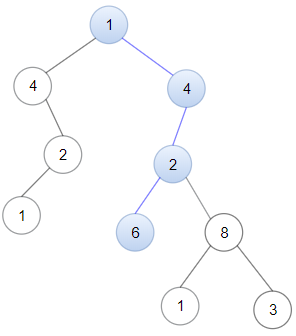
输入:head = [1,4,2,6], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] 输出:true
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,4,2,6,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3] 输出:false 解释:二叉树中不存在一一对应链表的路径。
提示:
- 二叉树和链表中的每个节点的值都满足
1 <= node.val <= 100。 - 链表包含的节点数目在
1到100之间。 - 二叉树包含的节点数目在
1到2500之间。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSubPath(self, head: ListNode, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
def dfs(head, root):
if head is None:
return True
if root is None:
return False
if root.val != head.val:
return False
return dfs(head.next, root.left) or dfs(head.next, root.right)
if root is None:
return False
return (
dfs(head, root)
or self.isSubPath(head, root.left)
or self.isSubPath(head, root.right)
)/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSubPath(ListNode head, TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
return dfs(head, root) || isSubPath(head, root.left) || isSubPath(head, root.right);
}
private boolean dfs(ListNode head, TreeNode root) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.val != head.val) {
return false;
}
return dfs(head.next, root.left) || dfs(head.next, root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
const dfs = (head: ListNode | null, root: TreeNode | null) => {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
if (root == null || head.val !== root.val) {
return false;
}
return dfs(head.next, root.left) || dfs(head.next, root.right);
};
function isSubPath(head: ListNode | null, root: TreeNode | null): boolean {
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
return (
dfs(head, root) ||
isSubPath(head, root.left) ||
isSubPath(head, root.right)
);
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
fn dfs(head: &Option<Box<ListNode>>, root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
if head.is_none() {
return true;
}
if root.is_none() {
return false;
}
let node = head.as_ref().unwrap();
let root = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
if node.val != root.val {
return false;
}
Self::dfs(&node.next, &root.left) || Self::dfs(&node.next, &root.right)
}
fn my_is_sub_path(head: &Option<Box<ListNode>>, root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
if root.is_none() {
return false;
}
let node = root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
Self::dfs(head, root)
|| Self::my_is_sub_path(head, &node.left)
|| Self::my_is_sub_path(head, &node.right)
}
pub fn is_sub_path(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> bool {
Self::my_is_sub_path(&head, &root)
}
}