Given an m x n integer matrix grid, return the maximum score of a path starting at (0, 0) and ending at (m - 1, n - 1) moving in the 4 cardinal directions.
The score of a path is the minimum value in that path.
- For example, the score of the path
8 → 4 → 5 → 9is4.
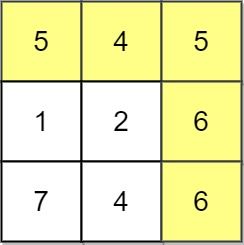
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[5,4,5],[1,2,6],[7,4,6]] Output: 4 Explanation: The path with the maximum score is highlighted in yellow.
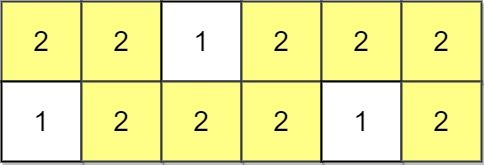
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[2,2,1,2,2,2],[1,2,2,2,1,2]] Output: 2
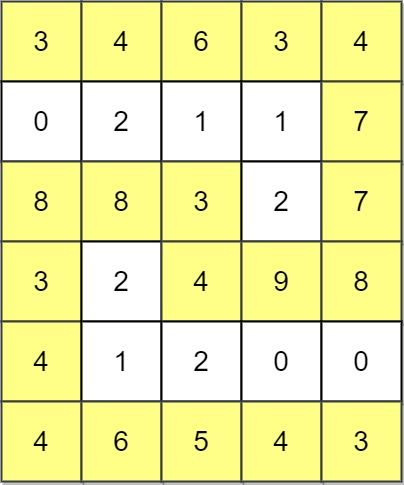
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[3,4,6,3,4],[0,2,1,1,7],[8,8,3,2,7],[3,2,4,9,8],[4,1,2,0,0],[4,6,5,4,3]] Output: 3
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 109
class Solution:
def maximumMinimumPath(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def find(x):
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
p = list(range(m * n))
ans = min(grid[0][0], grid[-1][-1])
vis = {(0, 0), (m - 1, n - 1)}
scores = [[grid[i][j], i, j] for i in range(m) for j in range(n)]
scores.sort()
while find(0) != find(m * n - 1):
score, i, j = scores.pop()
ans = min(ans, score)
vis.add((i, j))
for a, b in [[0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]:
x, y = i + a, j + b
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and (x, y) in vis:
p[find(x * n + y)] = find(i * n + j)
return ansclass Solution {
private int[] p;
public int maximumMinimumPath(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
p = new int[m * n];
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
}
int ans = Math.min(grid[0][0], grid[m - 1][n - 1]);
Set<Integer> vis = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(0, m * n - 1));
List<int[]> scores = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
scores.add(new int[] {grid[i][j], i, j});
}
}
scores.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (find(0) != find(m * n - 1)) {
int[] t = scores.remove(scores.size() - 1);
int score = t[0], i = t[1], j = t[2];
ans = Math.min(ans, score);
vis.add(i * n + j);
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && vis.contains(x * n + y)) {
p[find(x * n + y)] = find(i * n + j);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<int> p;
int maximumMinimumPath(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
p.resize(m * n);
for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); ++i) p[i] = i;
int ans = min(grid[0][0], grid[m - 1][n - 1]);
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m, vector<bool>(n));
vis[0][0] = true;
vis[m - 1][n - 1] = true;
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> scores;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
scores.emplace_back(grid[i][j], i, j);
sort(scores.begin(), scores.end());
vector<int> dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
while (find(0) != find(m * n - 1)) {
auto [score, i, j] = scores.back();
scores.pop_back();
ans = min(ans, score);
vis[i][j] = true;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k], y = j + dirs[k + 1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && vis[x][y])
p[find(x * n + y)] = find(i * n + j);
}
}
return ans;
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
};func maximumMinimumPath(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
p := make([]int, m*n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
}
var find func(x int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
vis := make([][]bool, m)
var scores [][]int
for i := range vis {
vis[i] = make([]bool, n)
for j := range grid[i] {
scores = append(scores, []int{grid[i][j], i, j})
}
}
sort.Slice(scores, func(i, j int) bool {
return scores[i][0] > scores[j][0]
})
vis[0][0] = true
vis[m-1][n-1] = true
dirs := []int{-1, 0, 1, 0, -1}
ans := min(grid[0][0], grid[m-1][n-1])
for find(0) != find(m*n-1) {
t := scores[0]
scores = scores[1:]
score, i, j := t[0], t[1], t[2]
vis[i][j] = true
ans = min(ans, score)
for k := 0; k < 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k], j+dirs[k+1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && vis[x][y] {
p[find(x*n+y)] = find(i*n + j)
}
}
}
return ans
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}