You are given the root of a binary tree. We install cameras on the tree nodes where each camera at a node can monitor its parent, itself, and its immediate children.
Return the minimum number of cameras needed to monitor all nodes of the tree.
Example 1:
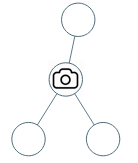
Input: root = [0,0,null,0,0] Output: 1 Explanation: One camera is enough to monitor all nodes if placed as shown.
Example 2:
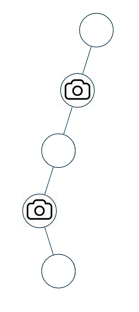
Input: root = [0,0,null,0,null,0,null,null,0] Output: 2 Explanation: At least two cameras are needed to monitor all nodes of the tree. The above image shows one of the valid configurations of camera placement.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. Node.val == 0
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minCameraCover(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def dfs(root):
nonlocal ans
if root is None:
return 2
left, right = dfs(root.left), dfs(root.right)
if left == 0 or right == 0:
ans += 1
return 1
return 2 if left == 1 or right == 1 else 0
ans = 0
return (dfs(root) == 0) + ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ans;
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
ans = 0;
return (dfs(root) == 0) ? ans + 1 : ans;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 2;
}
int left = dfs(root.left);
int right = dfs(root.right);
if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
++ans;
return 1;
}
if (left == 1 || right == 1) {
return 2;
}
return 0;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans;
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
ans = 0;
if (dfs(root) == 0) return ans + 1;
return ans;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 2;
int left = dfs(root->left), right = dfs(root->right);
if (left == 0 || right == 0) {
++ans;
return 1;
}
if (left == 1 || right == 1) return 2;
return 0;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func minCameraCover(root *TreeNode) int {
ans := 0
var dfs func(root *TreeNode) int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 2
}
left, right := dfs(root.Left), dfs(root.Right)
if left == 0 || right == 0 {
ans++
return 1
}
if left == 1 || right == 1 {
return 2
}
return 0
}
if dfs(root) == 0 {
return ans + 1
}
return ans
}