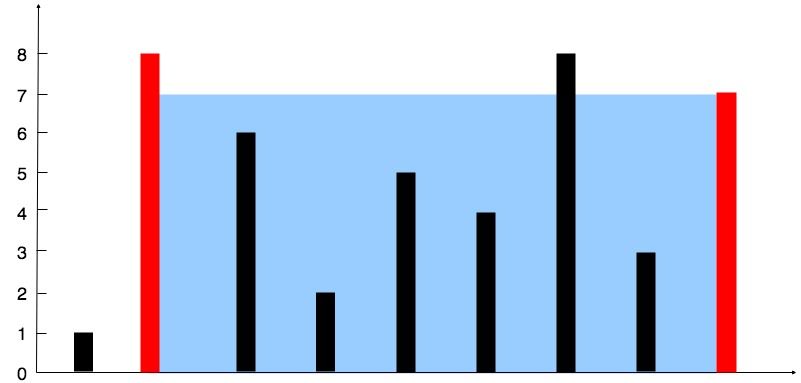
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] Output: 49 Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1] Output: 1
Constraints:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= height[i] <= 104
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
i, j = 0, len(height) - 1
res = 0
while i < j:
t = (j - i) * min(height[i], height[j])
res = max(res, t)
if height[i] < height[j]:
i += 1
else:
j -= 1
return resclass Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int i = 0, j = height.length - 1;
int res = 0;
while (i < j) {
int t = (j - i) * Math.min(height[i], height[j]);
res = Math.max(res, t);
if (height[i] < height[j])
++i;
else
--j;
}
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int i = 0, j = height.size() - 1;
int res = 0;
while (i < j) {
int t = (j - i) * min(height[i], height[j]);
res = max(res, t);
if (height[i] < height[j])
++i;
else
--j;
}
return res;
}
};func maxArea(height []int) int {
i, j := 0, len(height) - 1
res := 0
for i != j {
t := (j - i) * min(height[i], height[j])
res = max(res, t)
if height[i] < height[j] {
i++
} else {
j--
}
}
return res
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return b
}
return a
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}/**
* @param {number[]} height
* @return {number}
*/
var maxArea = function (height) {
let i = 0,
j = height.length - 1;
let res = 0;
while (i < j) {
const t = (j - i) * Math.min(height[i], height[j]);
res = Math.max(res, t);
if (height[i] < height[j]) ++i;
else --j;
}
return res;
};function maxArea(height: number[]): number {
const n = height.length;
let res = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (let j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (height[i] * (j - i) < res) {
break;
}
res = Math.max(res, Math.min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i));
}
}
return res;
}impl Solution {
pub fn max_area(height: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut i = 0;
let mut j = height.len() - 1;
let mut res = 0;
while i < j {
res = res.max(height[i].min(height[j]) * (j - i) as i32);
if height[i] <= height[j] {
i += 1;
} else {
j -= 1;
}
}
res
}
}