Kind: global class
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [network] | Network |
|
| [options] | Object |
|
| [options._dataset] | Dataset |
Testing dataset |
| [options.dataset] | Dataset |
Training dataset |
Test the bots performance on the test dataset
Kind: instance method of Bot
Returns: number - Returns the average error on the test dataset
| Param | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| options | Object |
||
| [options.accuracy] | boolean |
false |
Iff true, returns model accuracy instead of error |
| [options.round] | boolean |
false |
Iff true, rounds the output when testing |
Bot.fromDataset(dataset, [options]) ⇒ Bot
Kind: static method of Bot
| Param | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| dataset | Dataset |
||
| [options] | Object |
||
| [options.train] | boolean | number |
1 |
Will train bot for options.train iterations before creating it |
| [options.test] | number |
0 |
Will use options.test ratio (e.g. 0.2 === 20%) of the dataset for testing the bot's accuracy |
| [options.shuffle] | boolean |
false |
Iff true, the dataset will be shuffled before splitting the dataset or training the bot. |
Kind: static method of Bot
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| url | string |
| [options] | Object |
Example
const bot = Bot.fromURL(https://liquidcarrot.io/dataset/monkeys.csv)Kind: static method of Bot
Example
JSON
const bot = Bot.fromPath("./data.train.json");
bot.test(dataset); // { error: 0.01457, accuracy: 96.453%, fitness: 34.3412 }Example
CSV
const bot = Bot.fromPath("./data.train.csv", { outputs: ["age", "height"] });
bot.test(dataset); // { error: 0.01457, accuracy: 96.453%, fitness: 34.3412 }Example
XML
const bot = Bot.fromPath("./data.train.xml");
bot.test(dataset); // { error: 0.01457, accuracy: 96.453%, fitness: 34.3412 }Kind: static method of Bot
Example
Advanced CSV - White Wine Quality
const dataset = require("data.cjyvyspsy0000l2m932iv07k1");
const bot = Bot.fromString(dataset, {
type: "csv",
headers: true,
outputs: ["quality"],
delimeter: ";",
test: 0.2 // 20% of data will used for testing, not training
});
bot.test(); // { error: 0.01457, accuracy: 96.453%, fitness: 34.3412 }Kind: static method of Bot
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| json | Array.<Object> |
|
| options | Object |
|
| options.test | number |
Ratio of dataset to test (e.g. 0.2 is 20%) |
| options.outputs | Array.<string> |
JSON Keys which hold "outputs" desired outputs - bots will try to mimic or recreate these keys given all the other keys in the objects given |
Example
const dataset = require("@liquid-carrot/data.cjyvyspsy0000l2m932iv07k1");
const bot = Bot.fromJSON(dataset, {
outputs: ["quality"],
test: 0.2 // 20% of data will used for testing, not training
})Kind: global class
Properties
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | string |
Unique connection ID |
| a | Neuron | Group |
Side "A" of connection(s) |
| b | Neuron | Group |
Side "B" of connection(s) |
| [weight] | number | Array.<number> |
Weight of connection(s) |
Connections help: * a) control the flow information inside of a neural network * b) describe the shape of a neural network * c) ease the use of Evolutionary Algoriths
To facilitate the use of Evolutionary Algoriths, Connections are given Unique Temporal-Structural IDs using the Cantor Pairing Algorithm.
Temporal-Structural IDs: are not only a method of uniquely identifying a connection, they also allow us to identify a) where in the network the connection exists (i.e. between what neurons), and b) when it was "created-ish".
Connection IDs created using the Cantor Pairing Algorithm enable stronger algorithms, i.e. NEAT/HyperNEAT, to create networks of arbitrary sizes/shapes.
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| a | Neuron | Group |
Neuron(s) on one edge of the connection |
| b | Neuron | Group |
Neruon(s) on another edge of the connection |
| [weight] | number | Array.<number> |
Weight of connection(s) |
| [options] | Object |
Example
const connection = new Connection(neuron, other) // Connection { a: neuron, b: other }
const connection = new Connection(neuron, other, 0.3) // Connection { a: neuron, b: other, weight: 0.3 }Creates a unique structural ID for connection between two neurons using the Cantor Pairing Algorithm.
The Cantor Pairing Algorithm us to a) mathematically, map any two
non-negative integers to a unique positive integer - it even is sensetive to
order (i.e. Connection.uid([2,3]) !== Connection.uid([3,2])), and b) "AI-ly"
it allows to keep track of unique structural connections across time as a
neural network mutates (i.e. changes "shape").
Kind: static method of Connection
Returns: number - A unique integer ID created using the Cantor Pairing Algorithm
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| fromID | number |
ID of source neuron |
| toID | number |
ID of destination neuron |
Kind: global class
Properties
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| id | string |
| neurons | Array.<Neuron> |
- Group
- new Group([size], [bias])
- .connect(target, [weights])
- .activate([inputs]) ⇒
Array.<number> - .propagate([targets], [rate]) ⇒
Array.<number>
A Group is an abstraction of Neuron and a tool for creating and manipulating a group of neurons - with Group we can create neural network layers and and build networks faster than neuron-by-neuron construction.
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| [size] | number |
| [bias] | number |
Kind: instance method of Group
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| target | Group |
| [weights] | Array.<number> |
Example
//===============================================
// 2x2 (No Weights) =============================
//===============================================
const { Group } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const group = new Group(2);
const other = new Group(2);
group.connect(other);
//===============================================
// 2x2 (Weights) =============================
//===============================================
const { Group } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const group = new Group(2);
const other = new Group(2);
// group[0] -- weights[0] --> other[0]
// group[0] -- weights[1] --> other[1]
// group[1] -- weights[2] --> other[0]
// group[1] -- weights[3] --> other[1]
group.connect(other, [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4]);Kind: instance method of Group
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| [inputs] | Array.<number> |
Example
//===============================================
// One Group (No Hidden Layers) =================
//===============================================
const { Group } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const group = new Group(2);
neuron.activate([0, 0]); // [0, 0]
//===============================================
// Three Groups (Hidden Layers) =================
//===============================================
const { Group } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const input = new Group(2); // Input Neuron (Layer)
const hidden = new Group(2,0.1); // Hidden Neuron (Layer)
const output = new Group(2,0.15); // Output Neuron (Layer)
input.connect(hidden, [0.2,0.25,0.3,0.35]); // Connects input layer to hidden layer
hidden.connect(output, [0.4,0.45,0.5,0.55]); // Connects hidden layer to output layer
input.activate([0,0]); // [0,0]
hidden.activate(); // [0.###, 0.###]
output.activate(); // [0.###, 0.###]Kind: instance method of Group
| Param | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| [targets] | Array.<number> |
|
| [rate] | number |
0.3 |
Example
//===============================================
// One Group (No Hidden Layers) =================
//===============================================
const { Group } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const group = new Group(2);
neuron.activate([0, 0]); // [0, 0]
neuron.propagate([0, 1]); // [0, -1]
//===============================================
// Three Groups (Hidden Layers) =================
//===============================================
const { Group } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const input = new Group(2); // Input Neuron (Layer)
const hidden = new Group(2,0.1); // Hidden Neuron (Layer)
const output = new Group(2,0.15); // Output Neuron (Layer)
input.connect(hidden, [0.2,0.25,0.3,0.35]); // Connects input layer to hidden layer
hidden.connect(output, [0.4,0.45,0.5,0.55]); // Connects hidden layer to output layer
input.activate([0,0]); // [0,0]
hidden.activate(); // [0.###, 0.###]
output.activate(); // [0.###, 0.###]
output.propagate([0, 1]); // [0, -1]
hidden.propagate(); // [0.###, 0.###]
input.propagate(); // [0.###, 0.###]Kind: global class
Properties
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| id | string |
| groups | Array.<Group> |
- Network
- new Network(sizes, [biases], [weights])
- instance
- .activate(inputs) ⇒
Array.<number> - .propagate(targets) ⇒
number - .toJSON() ⇒
Object - .toGraph(element, [options])
- .activate(inputs) ⇒
- static
Each Network is a collective of neurons functioning as an individual and indepent agent (brain).
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| sizes | Array.<number> |
| [biases] | Array.<number> |
| [weights] | Array.<Array.<number>> |
Example
const { Network } = require("@liquid-carrot/nn");
const network = new Network([2,2,1]);
network.activate([0,1]);
network.propagate([1]);Activates network
Kind: instance method of Network
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| inputs | Array.<number> |
Calculates error & updates network weights
Kind: instance method of Network
Returns: number - Returns Mean-Squared Error (MSE)
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| targets | Array.<number> |
Returns a JSON representation of the network
Kind: instance method of Network
BROWSER ONLY
Creates a graph of the network using vis-network on the given DOMElement
or DOMElement ID.
Kind: instance method of Network
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| element | string | DOMElement |
DOMElement, or ID, where graph will ported into |
| [options] | Object |
vis-network options - learn more |
Network.fromSizes(sizes) ⇒ Network
Kind: static method of Network
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sizes | Array.<number> |
Array of layer fromSizes |
Example
const network = Network.fromSizes([20, 10, 3]);Network.fromShape(inputs, outputs) ⇒ Network
Creates a network with the given shape (i.e. INPUTSxOUTPUTS). The created network will not have any hidden neurons.
Kind: static method of Network
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| inputs | number |
Size of the network's input layer |
| outputs | number |
Size of the network's output layer |
Network.fromGenome(genome) ⇒ Network
Creates a deep copy of the given genome
Kind: static method of Network
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| genome | Genome |
Kind: global class
Properties
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| id | string |
| bias | number |
| optimizer | Object |
| optimizer.rate | number |
| optimizer.momentum | number |
| optimizer.decay | number |
| optimizer.alpha | number |
| optimizer.beta | number |
| optimizer.gamma | number |
| incoming | Object |
| incoming.targets | Object |
| incoming.weights | Object |
| outgoing | Object |
| outgoing.targets | Object |
| outgoing.weights | Object |
| _output | number |
| output | number |
| error | number |
- Neuron
- new Neuron(options)
- instance
- .connect(neuron, [weight])
- .activate([input]) ⇒
number - .propagate(target, [rate]) ⇒
number - .weights([array]) ⇒
Object|Array.<Array.<Number>>
- static
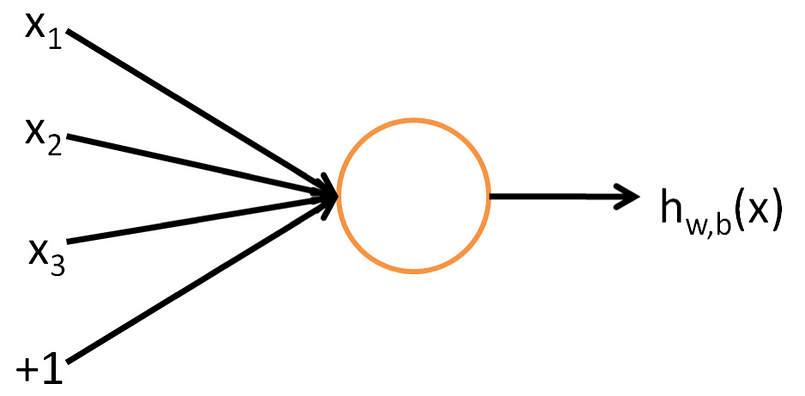
Neurons are the engines that process and guide information though a neural network. A neural networks "intelligence" is usually measured by the ability for neurons to effectively process information as a group.
A Neuron is a simplified mathematical model of a biological neuron.
In people, a neuron is a cell that collects inputs from synapses (i.e. eyes,
ears, etc. or other neurons) and triggers an output signal when the
incoming signals pass a certain threshold.
In biological neurons (in animals) or in artificial neurons (i.e. AI, NN, Deep Learning, etc.), one neuron doesn’t do much, but when combined, neural networks allow us to recognize the world around us, solve problems, and interact with our environment.
Neural networks were inspired by the human brain, and like in a human brain
the basic building block is called a Neuron. Its functionality is similar
to a human neuron, i.e. it takes in some inputs and fires an output. In
purely mathematical terms, a neuron in the machine learning world is a
placeholder for a mathematical function, and its only job is to provide an
output by applying the function on the inputs provided.
The function used in a neuron is generally called an "activation function". There have been 5 major activation functions tried to date, step, sigmoid, tanh, and ReLU. For this neuron we are using a "sigmoid" activation function.
A sigmoid function - or logistic function - is defined mathematically as:
The value of the function tends to zero when z tends to negative infinity and tends to 1 when z tends to infinity. A sigmoid activation function is an approximation of how a "real neuron" would behave; it's an assumption in the field of deep learning.
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| options | Object |
| [options.id] | number |
| [options.bias] | number |
| options.optimizer | Object |
| options.optimizer.rate | number |
| options.optimizer.momentum | number |
| options.optimizer.decay | number |
| options.optimizer.alpha | number |
| options.optimizer.beta | number |
| options.optimizer.gamma | number |
Example
//===============================================
// One Neuron (No Hidden Layers) ================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
neuron.activate(0); // 0
neuron.propagate(1); // -1
//===============================================
// Three Neurons (Hidden Layers) ================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const input = new Neuron(); // Input Neuron (Layer)
const hidden = new Neuron(0.1); // Hidden Neuron (Layer)
const output = new Neuron(0.2); // Output Neuron (Layer)
input.connect(hidden, 0.3); // Connects input layer to hidden layer
hidden.connect(output, 0.4); // Connects hidden layer to output layer
input.activate(0); // 0
hidden.activate(); // 0.52497918747894
output.activate(); // 0.6010858826658407
output.propagate(1); // -0.09565228299910712
hidden.propagate(); // -0.009900697661026392
input.propagate(); // -0.0029702092983079176Kind: instance method of Neuron
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| neuron | Neuron |
| [weight] | number |
Example
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
const other = new Neuron();
neuron.connect(other);Kind: instance method of Neuron
Returns: number - Returns the neuron's output
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| [input] | number |
Example
//===============================================
// One Neuron ===================================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
neuron.activate(3);
//===============================================
// Two Neurons ==================================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
const other = new Neuron(0.1);
neuron.connect(other, 0.2);
neuron.activate(3); // 3
other.activate(); // 0.6681877721681662Kind: instance method of Neuron
Returns: number - Returns neuron's marginal error
| Param | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| target | number |
|
| [rate] | number |
0.3 |
Example
//===============================================
// One Neuron ===================================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
neuron.activate(3); // 3
neuron.propagate(0); // 3
//===============================================
// Two Neurons ==================================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
const other = new Neuron(0.1);
neuron.connect(other, 0.2);
neuron.activate(3); // 3
other.activate(); // 0.6681877721681662
other.propagate(0); // 0.14814583086672545
neuron.propagate(); // 0.009876697690471913Kind: instance method of Neuron
Returns: Object | Array.<Array.<Number>> - Returns an Array or Object of incoming and outgoing weights
| Param | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| [array] | boolean |
false |
Iff true, will return an Array ([[INCOMING_WEIGHTS], [OUTGOING_WEIGHTS]]) - instead of a JSON Object ({ incoming: [INCOMING_WEIGHTS], outgoing: [OUTGOING_WEIGHTS]) |
Optimizers are initiated with { rate, momentum, decay, alpha, beta, epsilon, gamma }
Kind: static property of Neuron
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| inputs | Array.<number> |
| outputs | Array.<number> |
Example
{
"inputs": [0,1],
"outputs": [1]
}Dataset : Array.<Datum>
Kind: global typedef
Example
[{
"inputs": [0,0],
"outputs": [0]
}, {
"inputs": [0,1],
"outputs": [1]
}, {
"inputs": [1,0],
"outputs": [1]
}, {
"inputs": [1,1],
"outputs": [0]
}]Kind: global typedef
Example
[{
"a": 0,
"b": 0,
"c": 0
}, {
"a": 0,
"b": 1,
"c": 1
}, {
"a": 1,
"b": 0,
"c": 1
}, {
"a": 1,
"b": 1,
"c": 0
}]Kind: global typedef
Example
a,b,c
0,0,0
0,1,1
1,0,1
1,1,0Example
0,0,0
0,1,1
1,0,1
1,1,0Example
0;0;0
0;1;1
1;0;1
1;1;0Kind: global typedef
Example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<dataset>
<datum>
<a>0</a>
<b>0</b>
<c>0</c>
</datum>
<datum>
<a>0</a>
<b>1</b>
<c>1</c>
</datum>
<datum>
<a>1</a>
<b>0</b>
<c>1</c>
</datum>
<datum>
<a>1</a>
<b>1</b>
<c>0</c>
</datum>
</dataset>