Kubernetes Cluster up and running with master and node or GKE or EKS or any other type of k8s setup.
Here we are using GCP as a cloud provider for LoadBalancer Service. In case if you do not want to use LoadBalancer you can skip the steps.
1- Download script
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/helm/master/scripts/get > get_helm.sh
2- Helm client install
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh
3- Init Helm
helm init
1- Run the following commands to install the server-side tiller to the Kubernetes cluster with RBAC enabled
kubectl create serviceaccount --namespace kube-system tiller
2- Create a tiller Service Account
kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller
kubectl patch deploy --namespace kube-system tiller-deploy -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"serviceAccount":"tiller"}}}}'
3- Initialize Helm with newly-created service account
helm init --service-account tiller --upgrade
4- Checking tiller running
kubectl get deployments -n kube-system
1- Deploying simple Hello-app
kubectl create deployment hello-app --image=gcr.io/google-samples/hello-app:1.0
2- Expose the hello-app Deployment as a Service
kubectl expose deployment hello-app --port=8080
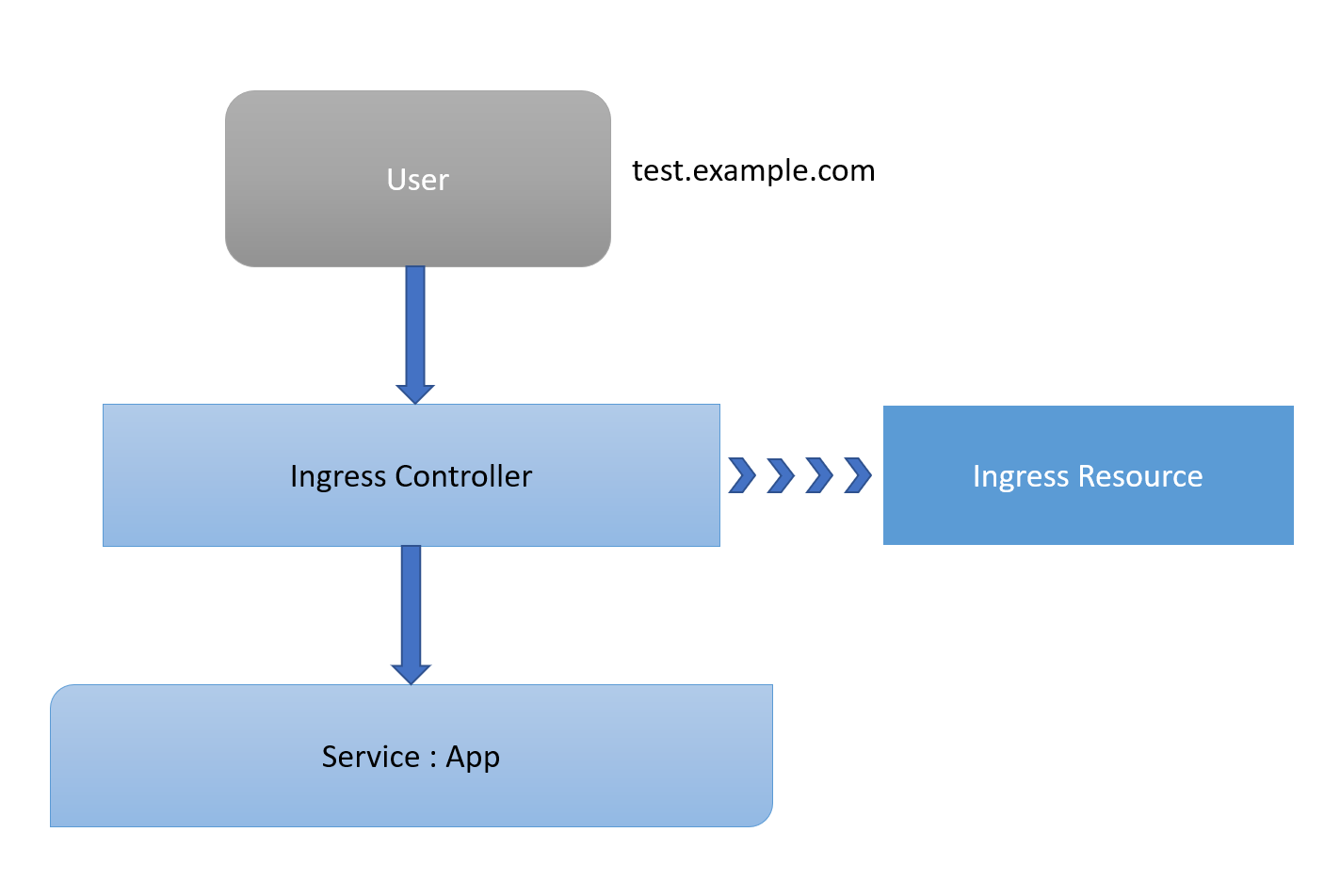
The Kubernetes platform gives administrators flexibility when it comes to Ingress Controllers. You can integrate your own rather than having to work with your provider's built-in offering. The NGINX controller must be exposed for external access. This is done using Service type: LoadBalancer on the NGINX controller service. On Kubernetes Engine, this creates a Google Cloud Network (TCP/IP) Load Balancer with NGINX controller Service as a backend. Google Cloud also creates the appropriate firewall rules within the Service's VPC to allow web HTTP(S) traffic to the load balancer frontend IP address.
1- Deploy NGINX Ingress Controller
helm install --name nginx-ingress stable/nginx-ingress --set rbac.create=true
2- Check Ingress Controller
kubectl get service nginx-ingress-controller
Wait for few moments while GCP LB get deployed and it should show the external IP
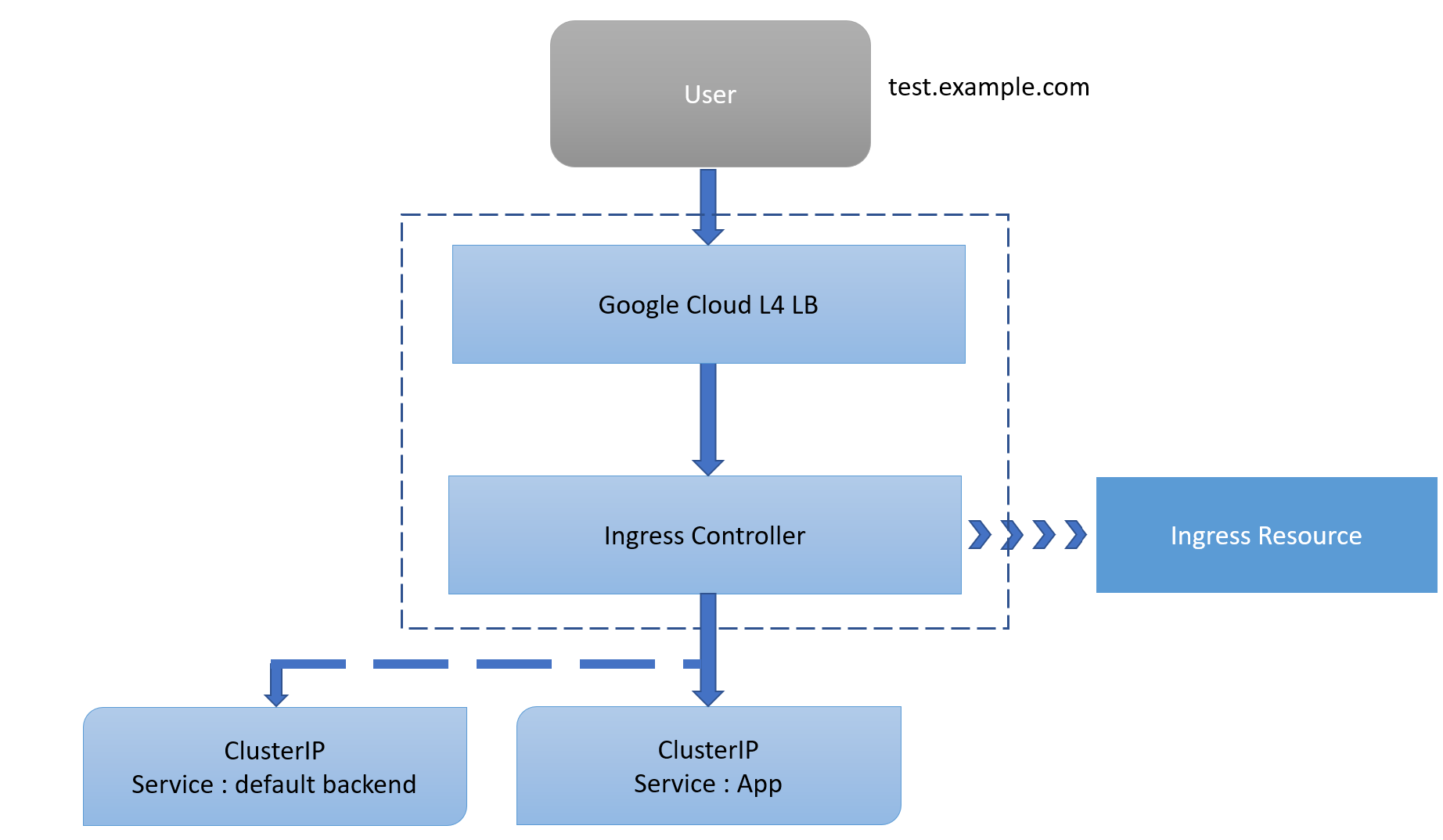
1- Create a simple Ingress Resource file which uses the NGINX Ingress Controller.
This Ingress Resource defines an inbound L7 rule for path /hello to service hello-app on port 8080.
vim ingress-resource.yml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-resource
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /hello
backend:
serviceName: hello-app
servicePort: 8080
2- Apply Rules to Kubernetes
kubectl apply -f ingress-resource.yml
3- Check in backend
kubectl get ingress ingress-resource
4- Check in browser
http://external-ip-of-ingress-controller/hello