Learning algorithm we use is stochastic gradient descent in the weights of a linear function approximator; it is known as the Least-Mean-Square (LMS) algorithm in the literature.
Language: Python 2.7 IDE: Visual Studio 2015
###Description: The sentence above literally describes what is going on. We have three python files here, each with it's own particular purpose.
###Core Files:
SuperLearn.py: Implementing the full learning algorithm, fill with Phiture vectors, weight vectors, etc.
TileCoder.py: Creates a large framework of a staggered, and layered, grid mapping mathematically. Returns the indexes impacted.
plot.py This python file parses the data and hands it over to the imported Axes3D to create the two graphical representations of the algorithm run!
##Additional files: We provided two graphs of the results of the data, which allows a visual representation for anyone interested! :) They are the following:
###Understanding the output At present we just run the tileCoder with it's own examples provided in the code, alongside the superlearn program with it's own training sets.
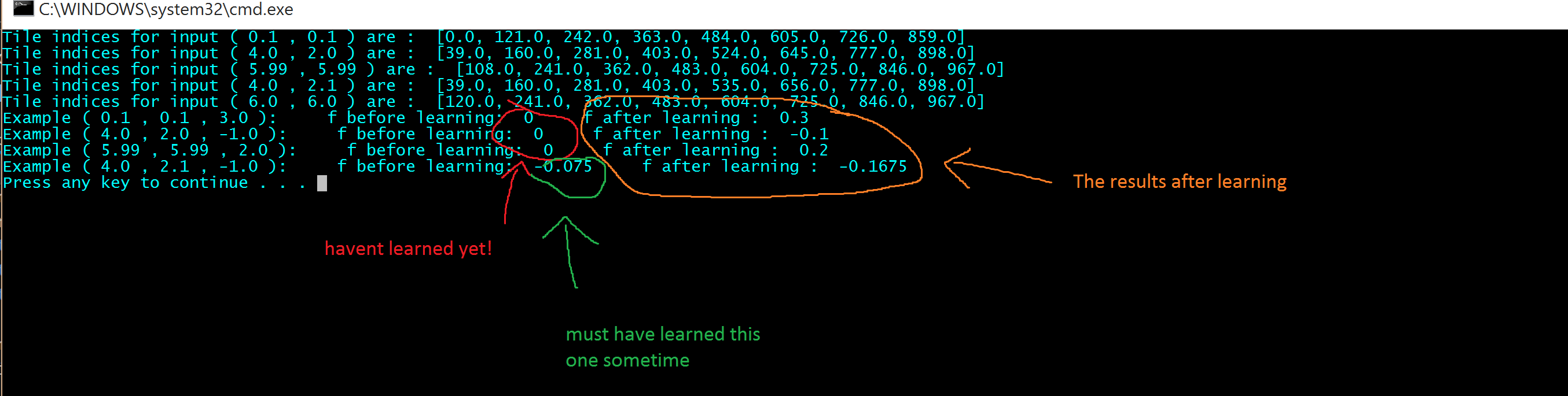
The output of the training sets I will explain below:
Firstly, we initialized the entire map of learning to zero. We have the algorithm in superlearn modify this map so that it can have the power to extrapolate results and predict future behaviors. This being said, the image probably explains it quite well!