I have been testing and reading a lot of way to safely create a bridge between react-native and webview. I'm happy to announced that the wait is over and from React-Native 0.20 and above, the bridge is fully functional.
In order to use this extension, you have to do the following steps:
in your react-native project, run npm install react-native-webview-bridge
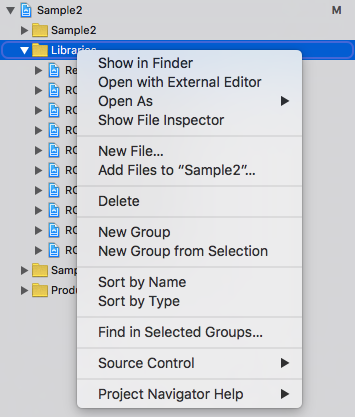
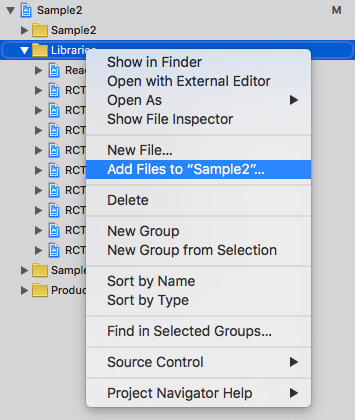
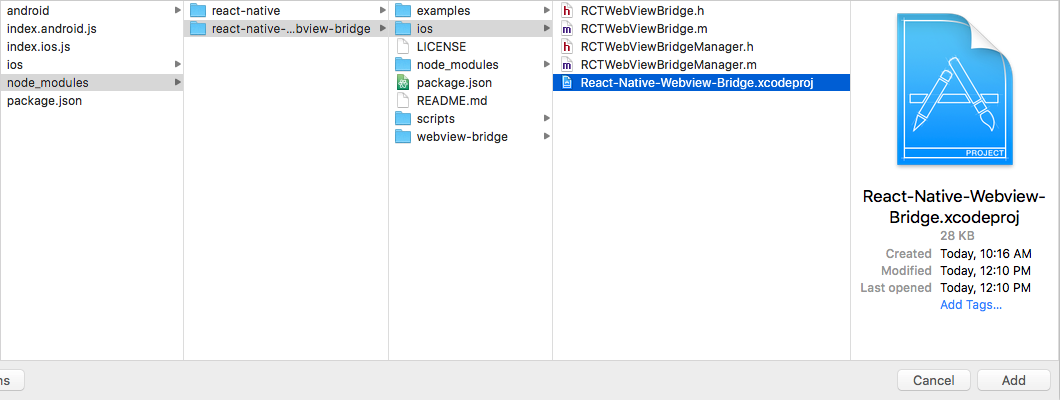
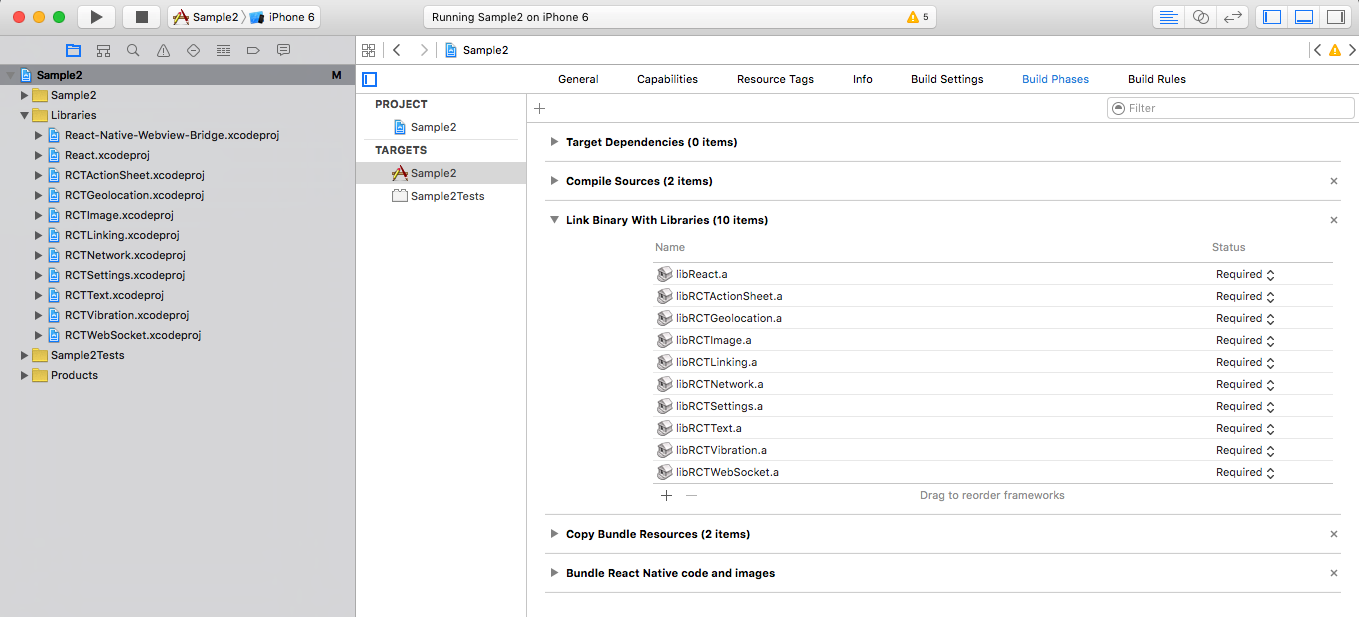
- go to xcode's
Project Navigatortab
- add the following import to
MainActivity.javaof your application
import com.github.alinz.reactnativewebviewbridge.WebViewBridgePackage;- add the following code to add the package to
MainActivity.java
mReactInstanceManager = ReactInstanceManager.builder()
...
.addPackage(new WebViewBridgePackage())
...- add the following codes to your
android/setting.gradle
you might have multiple 3rd party libraries, make sure that you don't create multiple include.
include ':app', ':react-native-webview-bridge'
project(':react-native-webview-bridge').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-webview-bridge/android')
- edit
android/app/build.gradleand add the following line insidedependencies
compile project(':react-native-webview-bridge')
- run
react-native run-androidto see if everything is compilable.
just import the module with one of your choices way:
** CommonJS style **
var WebViewBridge = require('react-native-webview-bridge');** ES6/ES2015 style **
import WebViewBridge from 'react-native-webview-bridge';WebViewBridge is an extension of WebView. It injects special script into any pages once it loads. Also it extends the functionality of WebView by adding 1 new method and 1 new props.
the message must be in string. because this is the only way to send data back and forth between native and webview.
this is a prop that needs to be a function. it will be called once a message is received from webview. The type of received message is also in string.
bridge script is a special script which injects into all the webview. It automatically register a global variable called WebViewBridge. It has 2 optional methods to implement and one method to send message to native side.
this method sends a message to native side. the message must be in string type or onError method will be called.
this method needs to be implemented. it will be called once a message arrives from native side. The type of message is in string.
this is an error reporting method. It will be called if there is an error happens during sending a message. It receives a error message in string type.
a special bridge script will be injected once the page is going to different URL. So you don't have to manage when it needs to be injected.
You can still pass your own javascript to be injected into webview. However, Bridge script will be injected first and then your custom script.
This example can be found in examples folder.
const injectScript = `
function webViewBridgeReady(cb) {
//checks whether WebViewBirdge exists in global scope.
if (window.WebViewBridge) {
cb(window.WebViewBridge);
return;
}
function handler() {
//remove the handler from listener since we don't need it anymore
document.removeEventListener('WebViewBridge', handler, false);
//pass the WebViewBridge object to the callback
cb(window.WebViewBridge);
}
//if WebViewBridge doesn't exist in global scope attach itself to document
//event system. Once the code is being injected by extension, the handler will
//be called.
document.addEventListener('WebViewBridge', handler, false);
}
webViewBridgeReady(function (webViewBridge) {
webViewBridge.onMessage = function (message) {
alert('got a message from Native: ' + message);
webViewBridge.send("message from webview");
};
});
`;
var Sample2 = React.createClass({
componentDidMount() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.refs.webviewbridge.sendToBridge("hahaha");
}, 5000);
},
onBridgeMessage: function (message) {
console.log(message);
},
render: function() {
return (
<WebViewBridge
ref="webviewbridge"
onBridgeMessage={this.onBridgeMessage}
injectedJavaScript={injectScript}
source={{uri: "http://google.com"}}/>
);
}
});