Credit to mdang for creating much of this document.
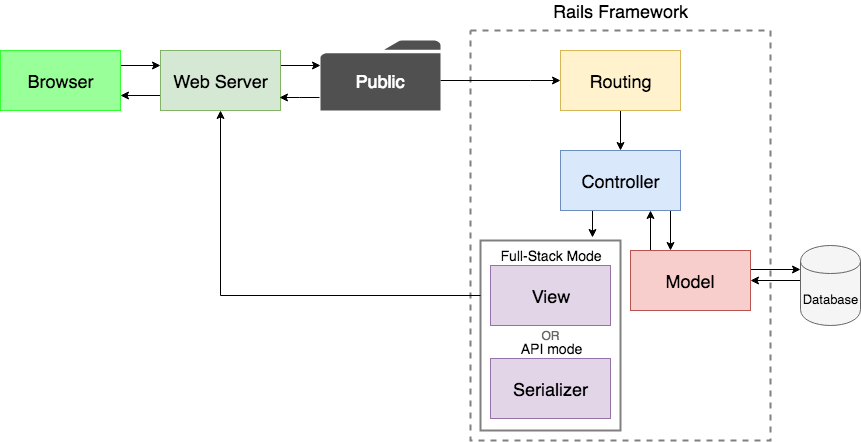
- Architecture
- Creating an Application
- Routes
- Controllers
- Models
- Migrations
- Scaffolding
- Rake
- Path Helpers
- Asset Pipeline
- Form Helpers
Install the Rails gem if you haven't done so before
$ gem install rails
Generate a new Rails app w/ Postgres support
$ rails new my_app --database=postgresql
Initialize the database
$ rake db:create
Start the Rails server
$ rails s
Create a route that maps a URL to the controller action
# config/routes.rb
get 'welcome' => 'pages#home'
# The above is the same as:
get :welcome, to: 'pages#home'Shorthand for connecting a route to a controller/action
# config/routes.rb
get 'photos/show'
# The above is the same as:
get 'photos/show', to: 'photos#show'
# and
get 'photos/show' => 'photos#show'Automagically create all the routes for a RESTful resource
# config/routes.rb
resources :photos | HTTP Verb | Path | Controller#Action | Used for |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /photos | photos#index | display a list of all photos |
| GET | /photos_new | photos#new | return an HTML form for creating a new photo |
| POST | /photos | photos#create | create a new photo |
| GET | /photos/:id | photos#show | display a specific photo |
| GET | /photos/:id/edit | photos#edit | return an HTML form for editing a photo |
| PATCH/PUT | /photos/:id | photos#update | update a specific photo |
| DELETE | /photos/:id | photos#destroy | delete a specific photo |
Create resources for only certain actions
# config/routes.rb
resources :photos, :only => [:index]
# On the flip side, you can create a resource with exceptions
resources :photos, :except => [:new, :create, :edit, :update, :show, :destroy]
# Remember `resources :photos` from before? That's the same as:
resources :photos, only: [:index, :show, :new, :create, :edit, :update, :destroy]Create a route to a static view, without an action in the controller
# config/routes.rb
# If there's a file called 'about.html.erb' in 'app/views/photos', this file will be
# automatically rendered when you call localhost:3000/photos/about
get 'photos/about', to: 'photos#about'Reference: http://guides.rubyonrails.org/routing.html
Generate a new controller
Note: Name controllers in Pascal case and pluralize
$ rails g controller Photos
Generate a new controller with default actions, routes and views
$ rails g controller Photos index show
Reference: http://guides.rubyonrails.org/action_controller_overview.html
A killer Rails model cheatsheet: https://devhints.io/rails-models
Generate a model and create a migration for the table
Note: Name models in Pascal case and singular
$ rails g model Photo
Generate a model and create a migration with table columns
$ rails g model Photo path:string caption:text
The migration automatically created for the above command:
class CreatePhotos < ActiveRecord::Migration
def change
create_table :photos do |t|
t.string :path
t.text :caption
t.timestamps null: false
end
end
endReference: http://guides.rubyonrails.org/active_model_basics.html
Migration Data Types
:boolean:date:datetime:decimal:float:integer:primary_key:references:string:text:time:timestamp
Special block methods
:timestamps- Createscreated_atandupdated_atdatetime columns (i.e.t.timestamps, null: false):index- Creates an index for the specified column (i.e.t.index :created_at)
When the name of the migration follows the format AddXXXToYYY followed by a list of columns, it will add those columns to the existing table
$ rails g migration AddDateTakenToPhotos date_taken:datetime
The above creates the following migration:
class AddDateTakenToPhotos < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
add_column :photos, :date_taken, :datetime
end
endYou can also add a new column to a table with an index
$ rails g migration AddDateTakenToPhotos date_taken:datetime:index
The above command generates the following migration:
class AddDateTakenToPhotos < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
add_column :photos, :date_taken, :datetime
add_index :photos, :date_taken
end
endThe opposite goes for migration names following the format: RemoveXXXFromYYY
$ rails g migration RemoveDateTakenFromPhotos date_taken:datetime
The above generates the following migration:
class RemoveDateTakenFromPhotos < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
remove_column :photos, :date_taken, :datetime
end
endMigration Creation Methods
- Standard
create_tableadd_columnadd_indexchange_tablechange_columnrename_tablerename_columnadd_timestamps
- Advanced
create_join_tableadd_foreign_keyadd_reference
Migration Modification Methods
- Standard
change_tablechange_columnrename_tablerename_columnrename_index
- Advanced
change_column_defaultchange_column_null
Migration Deletion Methods
- Standard
drop_tableremove_columnremove_columnsremove_index- By column name, i.e.remove_index :posts, :photo_idremove_timestamps
- Advanced
drop_join_tableremove_foreign_keyremove_referenceremove_index- By index name, i.e.remove_index :posts, name: :index_posts_on_photo_id
Scaffolding is great for prototypes but don't rely too heavily on it: http://stackoverflow.com/a/25140503. After an initial product launch, it's usually a good idea to manually create the files you need, avoiding scaffolding altogether.
$ rails g scaffold Photo path:string caption:text
$ rake db:migrate
View all the routes in an application
$ rake routes
Seed the database with sample data from db/seeds.rb
$ rake db:seed
Run any pending migrations
$ rake db:migrate
Rollback the last migration performed
NOTE: Be VERY careful with the following commands in production, it's destructive and you could potentially lose data. Make sure you absolutely understand what will happen when you run it
$ rake db:rollback
Rollback a specific number of migrations. i.e. Rollback 5 times:
$ rake db:rollback STEP=5
Rollback any particular migration without affecting preceeding/proceeding migrations, where the version is the migration filename's timestamp prefix. i.e. Rollback 20170103201478_create_photos.rb:
$ rake db:migrate:down VERSION=20170103201478
Creating a path helper for a route
# Creating a path helper for a route
get '/photos/:id', to: 'photos#show', as: 'photo'# app/controllers/photos_controller.rb
@photo = Photo.find(17)# View for the action
<%= link_to 'Photo Record', photo_path(@photo) %>Path helpers are automatically created when specifying a resource in config/routes.rb
# config/routes.rb
resources :photos| HTTP Verb | Path | Controller#Action | Named Helper |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /photos | photos#index | photos_path |
| GET | /photos/new | photos#new | new_photo_path |
| POST | /photos | photos#create | photos_path |
| GET | /photos/:id | photos#show | photo_path(:id) |
| GET | /photos/:id/edit | photos#edit | edit_photo_path(:id) |
| PATCH/PUT | /photos/:id | photos#update | photo_path(:id) |
| DELETE | /photos/:id | photos#destroy | photo_path(:id) |
Access images in the app/assets/images directory like this:
<%= image_tag "rails.png" %>Within views, link to JavaScript and CSS assets
<%= stylesheet_link_tag "application" %>
<%= javascript_include_tag "application" %><!-- Filenames are fingerprinted for cache busting -->
<link href="/assets/application-4dd5b109ee3439da54f5bdfd78a80473.css" media="screen"
rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="/assets/application-908e25f4bf641868d8683022a5b62f54.js"></script>Reference: http://guides.rubyonrails.org/asset_pipeline.html
Bind a form to a model for creating/updating a resource
Use this method if you're using strong params to protect against mass assignment
# app/controllers/photos_controller.rb
def new
@photo = Photo.new
end# ERB view
<%= form_for @photo, url: {action: "create"}, html: {class: "nifty_form"} do |f| %>
<%= f.text_field :path %>
<%= f.text_area :caption, size: "60x12" %>
<%= f.submit "Create" %>
<% end %><!-- HTML output -->
<form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/photos/create" method="post" class="nifty_form">
<input id="photos_path" name="photo[path]" type="text" />
<textarea id="photos_caption" name="photo[caption]" cols="60" rows="12"></textarea>
<input name="commit" type="submit" value="Create" />
</form>Create a form with a custom action and method
<%= form_tag("/search", method: "get") do %>
<%= label_tag(:q, "Search for:") %>
<%= text_field_tag(:q) %>
<%= submit_tag("Search") %>
<% end %><form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/search" method="get">
<input name="utf8" type="hidden" value="✓" />
<label for="q">Search for:</label>
<input id="q" name="q" type="text" />
<input name="commit" type="submit" value="Search" />
</form>