Added Environment variable to support multiple extracts for people who work across multiple projects environments
Initial release supporting Extract of Customisations.
MSBuild.Xrm.SourceControl provides a simple but powerful method for extracting Dynamics 365 customisations. The extension uses PowerShell scripts that can seamlessly extract customisations from a Dynamics 365 instance and then subsequently rebuild them into a zipped Solution file ready for import when necessary.
The scripts use the SolutionPackager.exe tool provided by the Dynamics 365 SDK. It supports file mappings, managed and unmanaged solutions, and the export of AutoNumber and Calendar settings.
MSBuild.Xrm.SourceControl extends the MSBuild process for the Clean and AfterBuild targets:
- Clean - Executes a custom PowerShell script to export solution files from Dynamics and unpack them with SolutionPackager.exe to the "Src" folder.
- AfterBuild - Executes a custom PowerShell script to pack the "Src" folder into Managed (for Release configuration) and Unmanaged (for Release and Debug configuration) Dynamics solution files using SolutionPackager.exe.
- Minimum .NET Framework: 4.5.1
- PowerShell 4.0+
Create a new class project in Visual Studio and install this extension by either searching for "MSBuild.Xrm.SourceControl" from 'Manage Nuget Packages' or run the command line Install-Package MSBuild.Xrm.SourceControl in the 'Package Manager Console'.
More detailed installation instructions can be found on the wiki.
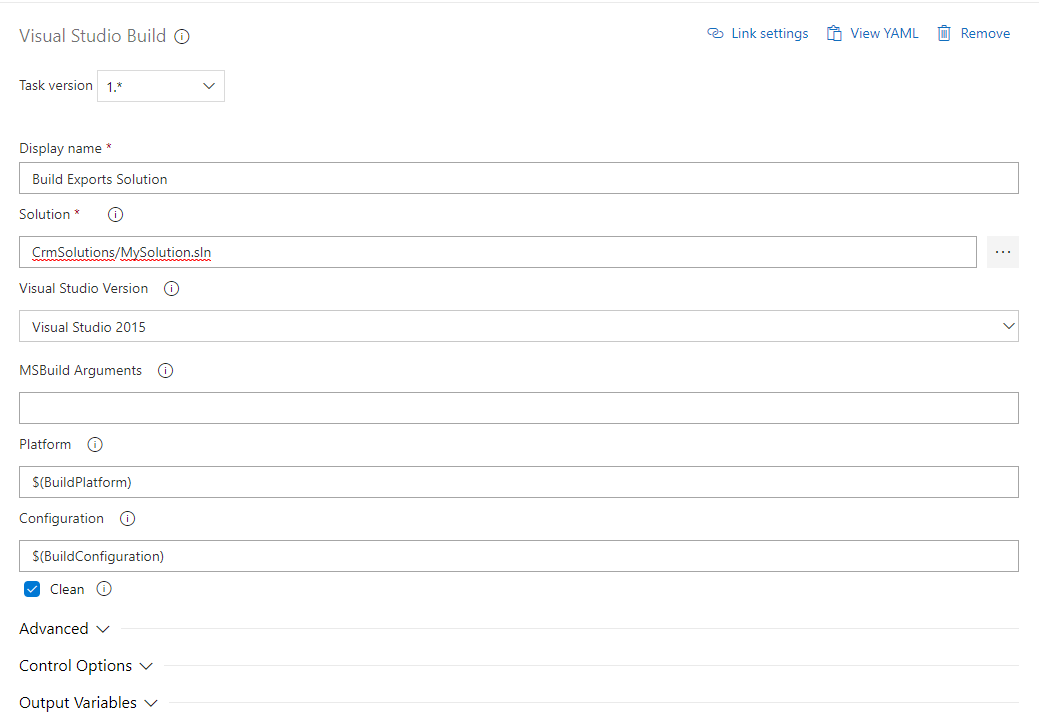
The configuration shown below demonstrates a basic setup to extract the customisations into source control.
When the Nuget package is first installed, two configuration files will be added into the project.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Project ToolsVersion="4.0" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/developer/msbuild/2003">
<PropertyGroup>
<CrmSolutionName>NOT_DEFINED</CrmSolutionName>
<CrmConnectionString>AuthType=OAuth;Url=url; Username=user; Password=password;ClientId=clientid;RedirectUri=redirectUri;</CrmConnectionString>
<ExportAutoNumberSettings>0</ExportAutoNumberSettings>
<ExportCallendarSettings>0</ExportCallendarSettings>
</PropertyGroup>
</Project>The first step is to populate the values for each of the elements:
- CrmSolutionName: The Name of the Dynamics Solution
- CrmConnectionString: The connection string that will be used to connect to the Dynamics instance, for more information, see here
- ExportAutoNumberSettings: Option for whether to Export the AutoNumber Settings for the Solution, 0 for No, 1 for Yes
- ExportCallendarSettings: Option for whether to Export the Calendar Settings for the Solution, 0 for No, 1 for Yes
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Mapping>
</Mapping>The Mapping configuration is used when the Solution is being rebuilt from the extracted files. The mapping file can define mappings between a file that is contained in the extracted solution files, to a file that is in another location on the file system. An example usage of this is for Web Resources, but it can also be used for compiled solution components such as Plugin .dll files. When the solution is being built, the mapped files will be used instead of the ones already in the solution. This is to try to make sure that the latest version of the files are used.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Mapping>
<FileToPath map="WebResources\*.*" to="..\..\XXX.Base.CrmPackage\WebResources\**" />
<FileToPath map="WebResources\**\*.*" to="..\..\XXX.Base.CrmPackage\WebResources\**" />
<FileToFile map="Capgemini.Base.Workflows.dll" to="..\..\XXX.Base.Workflows\bin\**\Capgemini.Base.Workflows.dll" />
<FileToFile map="Capgemini.Base.Plugins.dll" to="..\..\XXX.Base.Plugins\bin\**\Capgemini.Base.Plugins.dll" />
</Mapping>You can either use the FileToPath or FileToFile elements to map a collection of files or just a single file.
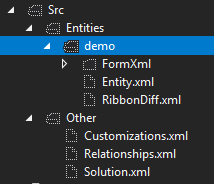
The installation of the Nuget package will modify the .csproj file to add tasks into the project build process. When the "Clean" command is run on the project, the ExtractCrmCustomizations.ps1 PowerShell script will be executed using the configuration files that are mentioned on the Setup page to connect to Dynamics and extract the solution files into the "Src" folder of the project.
NOTE: It is not recommended to select the 'Include in Project' option for the Src folder or any of its contents, as this will lead to unnecessary modifications to the project file every time a "Clean" is performed. Instead it is recommended to simply use the "Show All Files" button, to show the files. 
The "Src" folder and its contents should be included in Source Control. Every time the "Clean" command is executed, and the changes are synced, a history will be built in Source Control giving more visibility of changes.
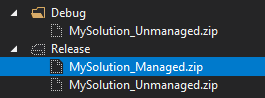
When the "Build" command is run on the project, the BuildCrmCustomizations.ps1 PowerShell script will be executed using the configuration files that are previously mentioned and pack the solution files in the "Src" folder into a Dynamics Solution file. There are two different types of Dynamics solution, Managed or Unmanaged. If the Build Configuration in Visual Studio is set to Debug, only the Unmanaged version of the Dynamics solution will be built, if the Build Configuration is set to Release, both Managed and Unmanaged versions will be built.
The built solution files will be output to the project's "bin" folder. Ready to be manually deployed to another environment or used in an automated CI process:
As the extensions are for MSBuild, they can be used not only through Visual Studio, but anywhere that MSBuild can be executed, this means that the rebuilding of the solution files can be done and is recommended to be done through a CI pipeline, such as those available in Azure DevOps:
NOTE: You may need to include the /bin/coretools/ folder and its contents into Source Control for this to work. For git repositories, this would involve editing your git.ignore file.
The source code for the extension will be made available soon. All contributions will be appreciated.
To contact us, please email [email protected].
Capgemini UK Microsoft Team
This extension uses the excellent Microsoft.Xrm.Data.Powershell, by seanmcne.