DOM stands for Document Object Model. It's an API (application programming interface) for manipulating HTML and XML documents. The DOM represents a document as a tree of nodes. It allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a document.
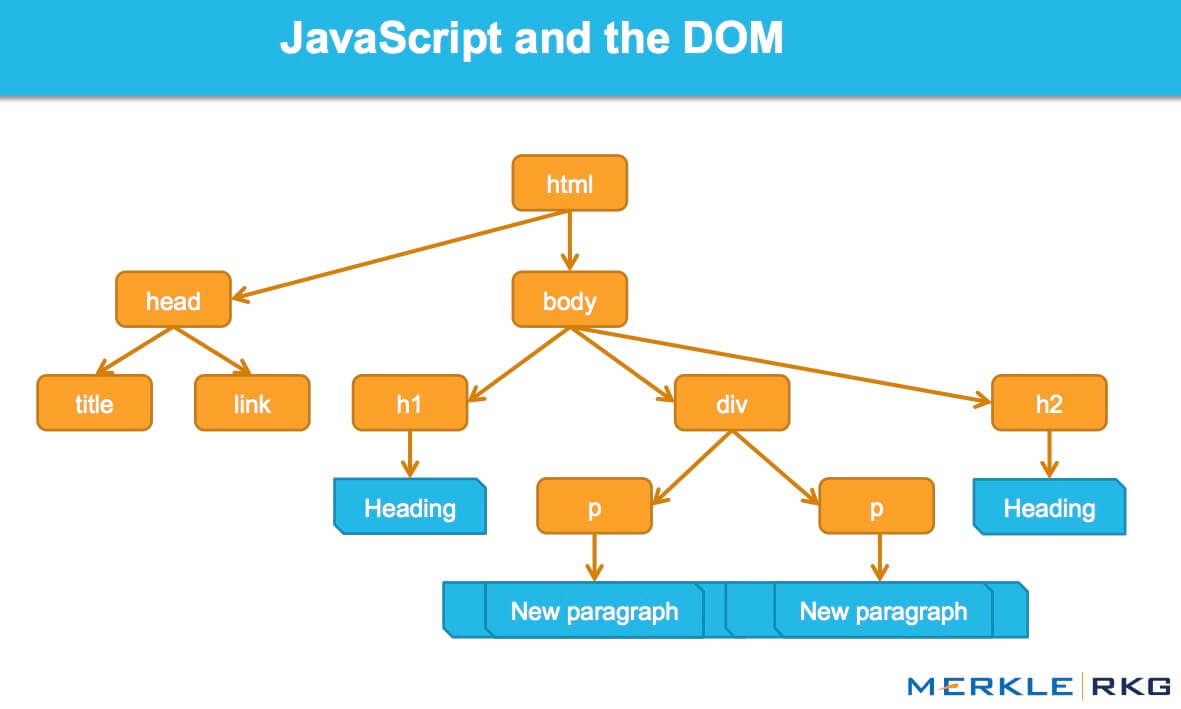
Below image shows a basic heirarchy in DOM :
With the DOM, JavaScript gets all the power it needs to create dynamic web pages. With the DOM :
- JavaScript can change all the HTML elements in the page
- JavaScript can change all the HTML attributes in the page
- JavaScript can change all the CSS styles in the page
- JavaScript can remove existing HTML elements and attributes
- JavaScript can add new HTML elements and attributes
- JavaScript can react to all existing HTML events in the page
- JavaScript can create new HTML events in the page
A web page or say HTML document can be imagined as a nested set of boxes. Tags such as head and body enclose other tags, which in turn contain other tags or text. For example a simple webpage can have following structure :
In the HTML DOM (Document Object Model), everything is a node:
- The document itself is a document node
- All HTML elements are element nodes
- All HTML attributes are attribute nodes
- Text inside HTML elements are text nodes
- Comments are comment nodes.
The HTML DOM document object is the owner of all other nodes in a web page. It provides properties and methods to access all node objects, from within JavaScript.
Now let's talk about few DOM properties .
The head property returns the <head> element of the current document and in case if there are more than one <head> element in the document, this property returns the first one.
E.g.
var x= document.head ; // Assigns head element to x
console.log(x.innerHTML); // Prints text inside head element It returns the content present in the <body> tag. This property is used to view or change the content present inside the <body> element and sets them with the new specified content.
E.g.
var x = document.body; // Assigns body element to x
console.log(x.innerHTML); // Print text inside body element
//New content inside body can also be added
x.innerHTML = "<h1>" + "New Heading added "+ "</h1>" + "<br>"
+ "<h2>"+ "New Content Added"+ "</h2>";The forms collection returns a collection of all <form> elements present in the document. Since there may be multiple forms on a page, the elements are sorted as they are present in the HTML source code.
E.g .
//Assigns forms collection to x
var x= document.forms ;
// Assigns numbers of form elements present in the collection
var len= x.length ;
//To acsess any particular form element we can use indexing like arrays
// Assigns 1st form element
var form1= x[0] ;
//Or we can also use the below method
var form1 = x.item(0);The name attribute which specifies the name of an <input> element is used to reference form elements in JavaScript, or to reference form data after a form is submitted.
E.g.
<form name="myForm" action="/action_page.php" method="get">
...HTML
</form>//For the above HTML form element , We can access the form with name attribute as below
var x= document.forms["myForm"];
x.submit(); //Submits formIt is important to note that only form elements with a name attribute will have their values passed while submitting a form.
To access any particular element, DOM provides various methods. Some of them are as follows :
| Methods | Use |
|---|---|
| document.getElementById(id) | Find an element by element id |
| document.getElementsByName(name) | Finds any element by its name attribute |
| document.getElementsByTagName(name) | Find elements by tag name |
| document.getElementsByClassName(name) | Find elements by class name |
DOM provides various methods to add and delete HTML elements via javascript . Some of them are as follows :
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.createElement(element) | Create an HTML element |
| document.removeChild(element) | Remove an HTML element |
| document.appendChild(element) | Add an HTML element |
| document.replaceChild(new, old) | Replace an HTML element |
| document.write(text) | Write into the HTML output stream |
This was a brief note about DOM .Above methods are frequently used methods , apart from them DOM contains much more methods for manipulating HTML elements . To refer more about DOM , Please visit : DOM
Contributor: Manish Kumar Pandit