| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
困难 |
2415 |
第 322 场周赛 Q4 |
|
给你一个正整数 n ,表示一个 无向 图中的节点数目,节点编号从 1 到 n 。
同时给你一个二维整数数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示节点 ai 和 bi 之间有一条 双向 边。注意给定的图可能是不连通的。
请你将图划分为 m 个组(编号从 1 开始),满足以下要求:
- 图中每个节点都只属于一个组。
- 图中每条边连接的两个点
[ai, bi],如果ai属于编号为x的组,bi属于编号为y的组,那么|y - x| = 1。
请你返回最多可以将节点分为多少个组(也就是最大的 m )。如果没办法在给定条件下分组,请你返回 -1 。
示例 1:
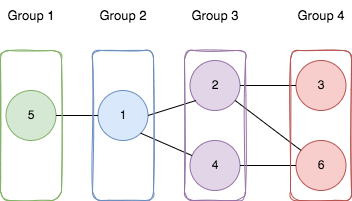
输入:n = 6, edges = [[1,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,3],[4,6]] 输出:4 解释:如上图所示, - 节点 5 在第一个组。 - 节点 1 在第二个组。 - 节点 2 和节点 4 在第三个组。 - 节点 3 和节点 6 在第四个组。 所有边都满足题目要求。 如果我们创建第五个组,将第三个组或者第四个组中任何一个节点放到第五个组,至少有一条边连接的两个节点所属的组编号不符合题目要求。
示例 2:
输入:n = 3, edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,1]] 输出:-1 解释:如果我们将节点 1 放入第一个组,节点 2 放入第二个组,节点 3 放入第三个组,前两条边满足题目要求,但第三条边不满足题目要求。 没有任何符合题目要求的分组方式。
提示:
1 <= n <= 5001 <= edges.length <= 104edges[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= nai != bi- 两个点之间至多只有一条边。
由于题目给定的图可能是不连通的,所以我们需要对每个连通分量进行处理,找出每个连通分量的最大分组数,累加得到最终结果。
我们可以枚举每一个点作为第一组的节点,然后使用 BFS 遍历整个连通分量,用一个数组
在 BFS 的过程中,我们使用一个队列
在遍历过程中,如果发现某个节点
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def magnificentSets(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for a, b in edges:
g[a - 1].append(b - 1)
g[b - 1].append(a - 1)
d = defaultdict(int)
for i in range(n):
q = deque([i])
dist = [0] * n
dist[i] = mx = 1
root = i
while q:
a = q.popleft()
root = min(root, a)
for b in g[a]:
if dist[b] == 0:
dist[b] = dist[a] + 1
mx = max(mx, dist[b])
q.append(b)
elif abs(dist[b] - dist[a]) != 1:
return -1
d[root] = max(d[root], mx)
return sum(d.values())class Solution {
public int magnificentSets(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<Integer>[] g = new List[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e[0] - 1, b = e[1] - 1;
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
int[] d = new int[n];
int[] dist = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(i);
Arrays.fill(dist, 0);
dist[i] = 1;
int mx = 1;
int root = i;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int a = q.poll();
root = Math.min(root, a);
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (dist[b] == 0) {
dist[b] = dist[a] + 1;
mx = Math.max(mx, dist[b]);
q.offer(b);
} else if (Math.abs(dist[b] - dist[a]) != 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
d[root] = Math.max(d[root], mx);
}
return Arrays.stream(d).sum();
}
}class Solution {
public:
int magnificentSets(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<int> g[n];
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0] - 1, b = e[1] - 1;
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
vector<int> d(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
queue<int> q{{i}};
vector<int> dist(n);
dist[i] = 1;
int mx = 1;
int root = i;
while (q.size()) {
int a = q.front();
q.pop();
root = min(root, a);
for (int b : g[a]) {
if (dist[b] == 0) {
dist[b] = dist[a] + 1;
mx = max(mx, dist[b]);
q.push(b);
} else if (abs(dist[b] - dist[a]) != 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
d[root] = max(d[root], mx);
}
return accumulate(d.begin(), d.end(), 0);
}
};func magnificentSets(n int, edges [][]int) (ans int) {
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0]-1, e[1]-1
g[a] = append(g[a], b)
g[b] = append(g[b], a)
}
d := make([]int, n)
for i := range d {
q := []int{i}
dist := make([]int, n)
dist[i] = 1
mx := 1
root := i
for len(q) > 0 {
a := q[0]
q = q[1:]
root = min(root, a)
for _, b := range g[a] {
if dist[b] == 0 {
dist[b] = dist[a] + 1
mx = max(mx, dist[b])
q = append(q, b)
} else if abs(dist[b]-dist[a]) != 1 {
return -1
}
}
}
d[root] = max(d[root], mx)
}
for _, x := range d {
ans += x
}
return
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number}
*/
var magnificentSets = function (n, edges) {
const g = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a - 1].push(b - 1);
g[b - 1].push(a - 1);
}
const d = Array(n).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
const q = [i];
const dist = Array(n).fill(0);
dist[i] = 1;
let mx = 1;
let root = i;
while (q.length) {
const a = q.shift();
root = Math.min(root, a);
for (const b of g[a]) {
if (dist[b] === 0) {
dist[b] = dist[a] + 1;
mx = Math.max(mx, dist[b]);
q.push(b);
} else if (Math.abs(dist[b] - dist[a]) !== 1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
d[root] = Math.max(d[root], mx);
}
return d.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
};