| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Hard |
|
Given the head of a linked list, reverse the nodes of the list k at a time, and return the modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
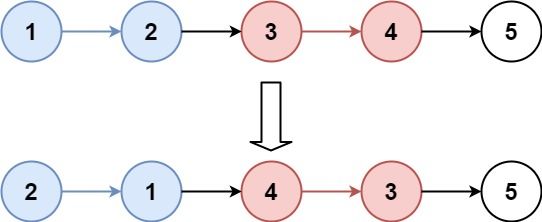
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Example 2:
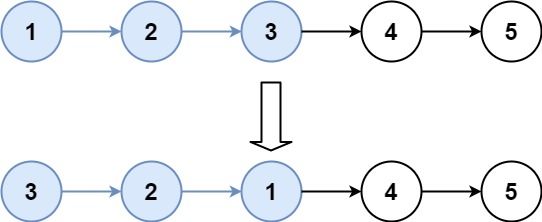
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 Output: [3,2,1,4,5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 50000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Follow-up: Can you solve the problem in O(1) extra memory space?
The time complexity is
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseKGroup(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
def reverseList(head):
pre, p = None, head
while p:
q = p.next
p.next = pre
pre = p
p = q
return pre
dummy = ListNode(next=head)
pre = cur = dummy
while cur.next:
for _ in range(k):
cur = cur.next
if cur is None:
return dummy.next
t = cur.next
cur.next = None
start = pre.next
pre.next = reverseList(start)
start.next = t
pre = start
cur = pre
return dummy.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode pre = dummy, cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < k && cur != null; ++i) {
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur == null) {
return dummy.next;
}
ListNode t = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
ListNode start = pre.next;
pre.next = reverseList(start);
start.next = t;
pre = start;
cur = pre;
}
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null, p = head;
while (p != null) {
ListNode q = p.next;
p.next = pre;
pre = p;
p = q;
}
return pre;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func reverseKGroup(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {
var dummy *ListNode = &ListNode{}
p, cur := dummy, head
for cur != nil {
start := cur
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
if cur == nil {
p.Next = start
return dummy.Next
}
cur = cur.Next
}
p.Next, p = reverse(start, cur), start
}
return dummy.Next
}
func reverse(start, end *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre *ListNode = nil
for start != end {
tmp := start.Next
start.Next, pre = pre, start
start = tmp
}
return pre
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function reverseKGroup(head: ListNode | null, k: number): ListNode | null {
let dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
let pre = dummy;
// pre->head-> ... ->tail-> next
while (head != null) {
let tail = pre;
for (let i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
tail = tail.next;
if (tail == null) {
return dummy.next;
}
}
let t = tail.next;
[head, tail] = reverse(head, tail);
// set next
pre.next = head;
tail.next = t;
// set new pre and new head
pre = tail;
head = t;
}
return dummy.next;
}
function reverse(head: ListNode, tail: ListNode) {
let cur = head;
let pre = tail.next;
// head -> next -> ... -> tail -> pre
while (pre != tail) {
let t = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = t;
}
return [tail, head];
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn reverse_k_group(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>, k: i32) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
fn reverse(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut head = head;
let mut pre = None;
while let Some(mut node) = head {
head = node.next.take();
node.next = pre.take();
pre = Some(node);
}
pre
}
let mut dummy = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(0)));
let mut pre = &mut dummy;
let mut cur = head;
while cur.is_some() {
let mut q = &mut cur;
for _ in 0..k - 1 {
if q.is_none() {
break;
}
q = &mut q.as_mut().unwrap().next;
}
if q.is_none() {
pre.as_mut().unwrap().next = cur;
return dummy.unwrap().next;
}
let b = q.as_mut().unwrap().next.take();
pre.as_mut().unwrap().next = reverse(cur);
while pre.is_some() && pre.as_mut().unwrap().next.is_some() {
pre = &mut pre.as_mut().unwrap().next;
}
cur = b;
}
dummy.unwrap().next
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode pre = dummy, cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < k && cur != null; ++i)
{
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur == null)
{
return dummy.next;
}
ListNode t = cur.next;
cur.next = null;
ListNode start = pre.next;
pre.next = ReverseList(start);
start.next = t;
pre = start;
cur = pre;
}
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null, p = head;
while (p != null)
{
ListNode q = p.next;
p.next = pre;
pre = p;
p = q;
}
return pre;
}
}# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode {
# public $val;
# public $next;
# public function __construct($val = 0, $next = null)
# {
# $this->val = $val;
# $this->next = $next;
# }
# }
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @param int $k
* @return ListNode
*/
function reverseKGroup($head, $k) {
$dummy = new ListNode(0);
$dummy->next = $head;
$prevGroupTail = $dummy;
while ($head !== null) {
$count = 0;
$groupHead = $head;
$groupTail = $head;
while ($count < $k && $head !== null) {
$head = $head->next;
$count++;
}
if ($count < $k) {
$prevGroupTail->next = $groupHead;
break;
}
$prev = null;
for ($i = 0; $i < $k; $i++) {
$next = $groupHead->next;
$groupHead->next = $prev;
$prev = $groupHead;
$groupHead = $next;
}
$prevGroupTail->next = $prev;
$prevGroupTail = $groupTail;
}
return $dummy->next;
}
}The time complexity is
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func reverseKGroup(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {
start, end := head, head
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
if end == nil {
return head
}
end = end.Next
}
res := reverse(start, end)
start.Next = reverseKGroup(end, k)
return res
}
func reverse(start, end *ListNode) *ListNode {
var pre *ListNode = nil
for start != end {
tmp := start.Next
start.Next, pre = pre, start
start = tmp
}
return pre
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function reverseKGroup(head: ListNode | null, k: number): ListNode | null {
if (k === 1) {
return head;
}
const dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
let root = dummy;
while (root != null) {
let pre = root;
let cur = root;
let count = 0;
while (count !== k) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
if (cur == null) {
return dummy.next;
}
}
const nextRoot = pre.next;
pre.next = cur;
let node = nextRoot;
let next = node.next;
node.next = cur.next;
while (node != cur) {
[next.next, node, next] = [node, next, next.next];
}
root = nextRoot;
}
return dummy.next;
}