| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
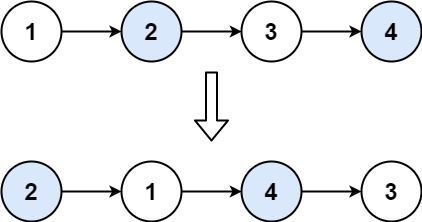
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You must solve the problem without modifying the values in the list's nodes (i.e., only nodes themselves may be changed.)
Example 1:
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1]
Output: [1]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,2,3]
Output: [2,1,3]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 100
We can implement swapping two nodes in the linked list through recursion.
The termination condition of recursion is that there are no nodes in the linked list, or there is only one node in the linked list. At this time, swapping cannot be performed, so we directly return this node.
Otherwise, we recursively swap the linked list
The time complexity is
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
t = self.swapPairs(head.next.next)
p = head.next
p.next = head
head.next = t
return p/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode t = swapPairs(head.next.next);
ListNode p = head.next;
p.next = head;
head.next = t;
return p;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) {
return head;
}
ListNode* t = swapPairs(head->next->next);
ListNode* p = head->next;
p->next = head;
head->next = t;
return p;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil || head.Next == nil {
return head
}
t := swapPairs(head.Next.Next)
p := head.Next
p.Next = head
head.Next = t
return p
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
if (!head || !head.next) {
return head;
}
const t = swapPairs(head.next.next);
const p = head.next;
p.next = head;
head.next = t;
return p;
}// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
impl Solution {
pub fn swap_pairs(head: Option<Box<ListNode>>) -> Option<Box<ListNode>> {
let mut dummy = Some(Box::new(ListNode { val: 0, next: head }));
let mut cur = dummy.as_mut().unwrap();
while cur.next.is_some() && cur.next.as_ref().unwrap().next.is_some() {
cur.next = {
let mut b = cur.next.as_mut().unwrap().next.take();
cur.next.as_mut().unwrap().next = b.as_mut().unwrap().next.take();
let a = cur.next.take();
b.as_mut().unwrap().next = a;
b
};
cur = cur.next.as_mut().unwrap().next.as_mut().unwrap();
}
dummy.unwrap().next
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var swapPairs = function (head) {
if (!head || !head.next) {
return head;
}
const t = swapPairs(head.next.next);
const p = head.next;
p.next = head;
head.next = t;
return p;
};# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode
# attr_accessor :val, :next
# def initialize(val = 0, _next = nil)
# @val = val
# @next = _next
# end
# end
# @param {ListNode} head
# @return {ListNode}
def swap_pairs(head)
dummy = ListNode.new(0, head)
pre = dummy
cur = head
while !cur.nil? && !cur.next.nil?
t = cur.next
cur.next = t.next
t.next = cur
pre.next = t
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
end
dummy.next
endWe set a dummy head node
Next, we traverse the linked list. Each time we need to swap the two nodes after
The time complexity is
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(next=head)
pre, cur = dummy, head
while cur and cur.next:
t = cur.next
cur.next = t.next
t.next = cur
pre.next = t
pre, cur = cur, cur.next
return dummy.next/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
ListNode t = cur.next;
cur.next = t.next;
t.next = cur;
pre.next = t;
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode* pre = dummy;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur && cur->next) {
ListNode* t = cur->next;
cur->next = t->next;
t->next = cur;
pre->next = t;
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func swapPairs(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
dummy := &ListNode{Next: head}
pre, cur := dummy, head
for cur != nil && cur.Next != nil {
t := cur.Next
cur.Next = t.Next
t.Next = cur
pre.Next = t
pre, cur = cur, cur.Next
}
return dummy.Next
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function swapPairs(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
const dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
let [pre, cur] = [dummy, head];
while (cur && cur.next) {
const t = cur.next;
cur.next = t.next;
t.next = cur;
pre.next = t;
[pre, cur] = [cur, cur.next];
}
return dummy.next;
}/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var swapPairs = function (head) {
const dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
let [pre, cur] = [dummy, head];
while (cur && cur.next) {
const t = cur.next;
cur.next = t.next;
t.next = cur;
pre.next = t;
[pre, cur] = [cur, cur.next];
}
return dummy.next;
};# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode {
# public $val;
# public $next;
# public function __construct($val = 0, $next = null)
# {
# $this->val = $val;
# $this->next = $next;
# }
# }
class Solution {
/**
* @param ListNode $head
* @return ListNode
*/
function swapPairs($head) {
$dummy = new ListNode(0);
$dummy->next = $head;
$prev = $dummy;
while ($head !== null && $head->next !== null) {
$first = $head;
$second = $head->next;
$first->next = $second->next;
$second->next = $first;
$prev->next = $second;
$prev = $first;
$head = $first->next;
}
return $dummy->next;
}
}